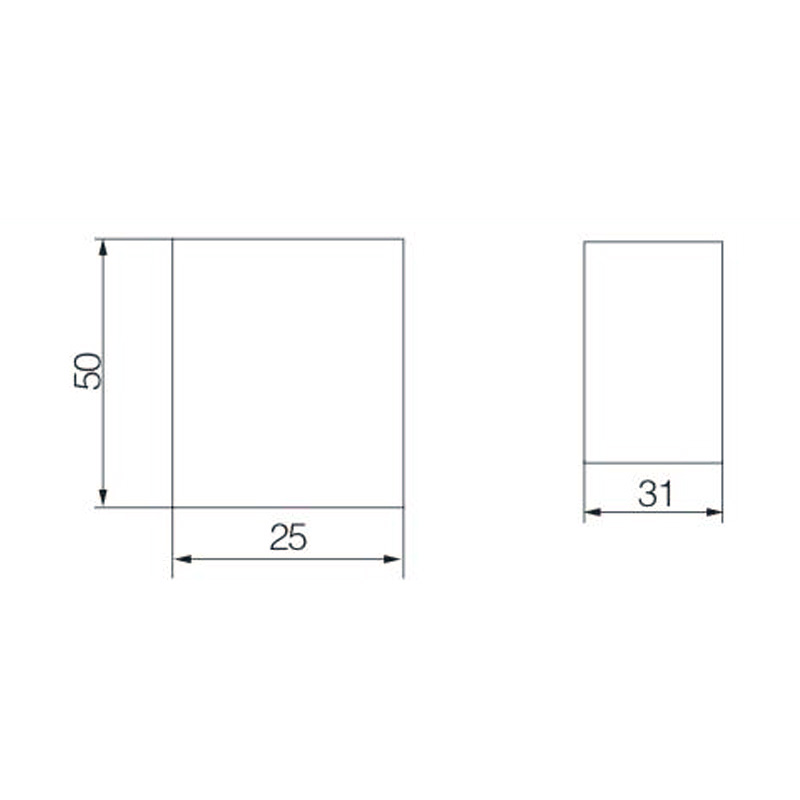
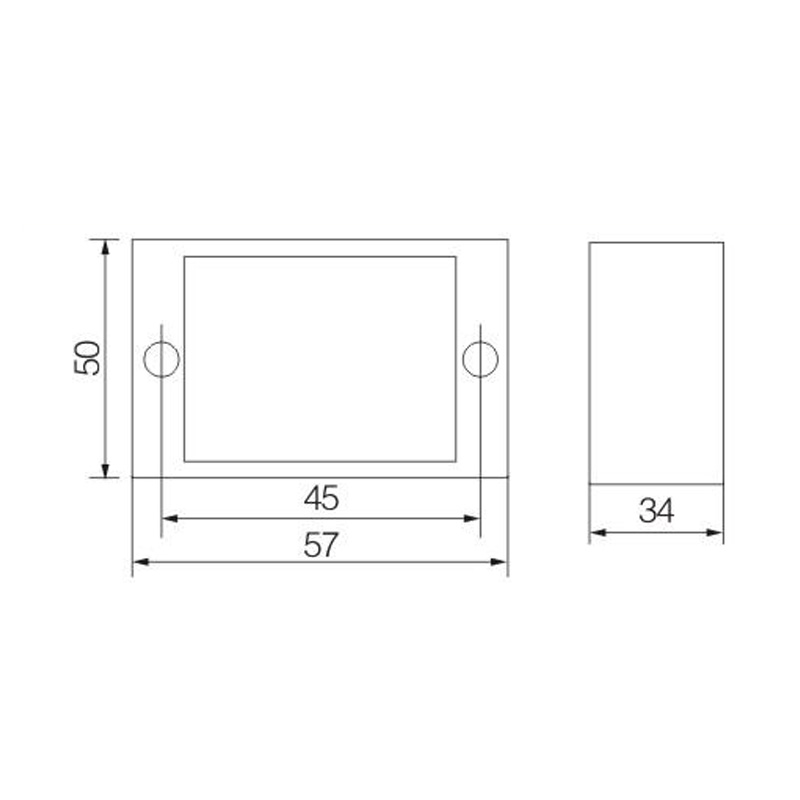
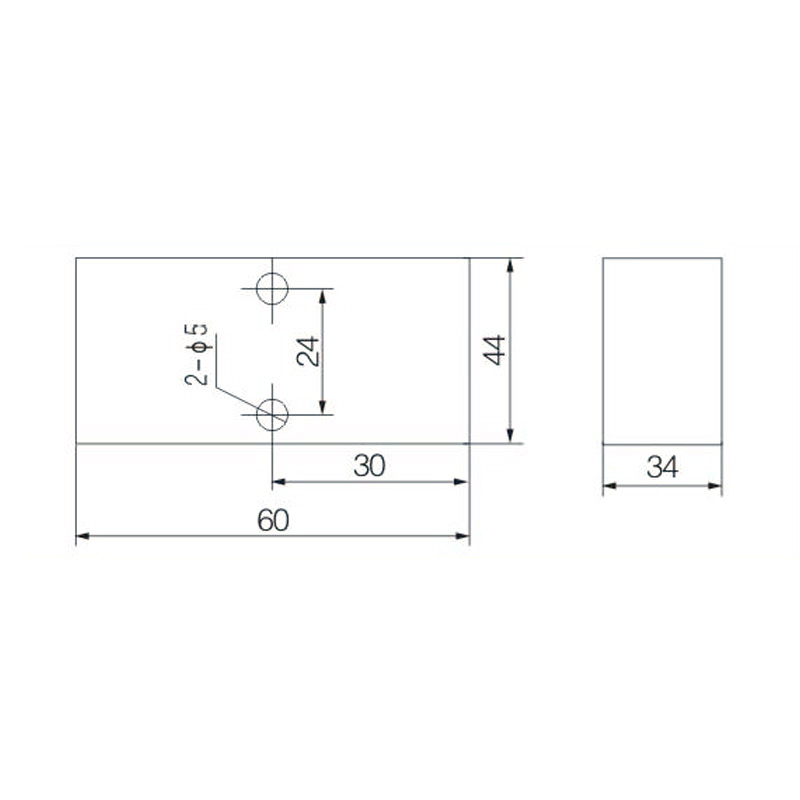
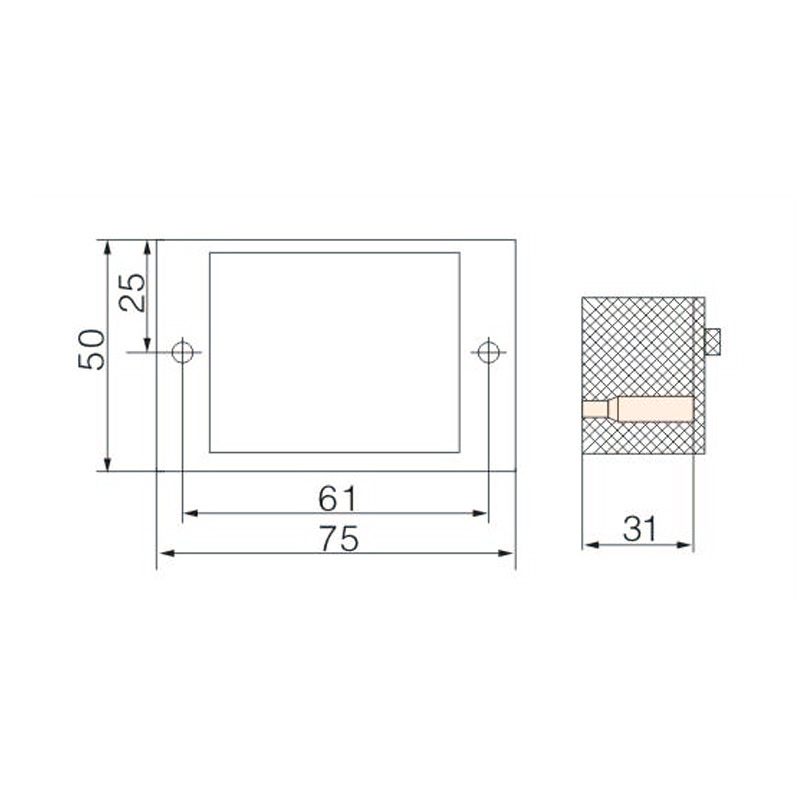
Integrating wired connectivity into the era of automation and digital networking involves more than just traditional hardware. A H...
READ MOREClosed Terminal Block Manufacturer
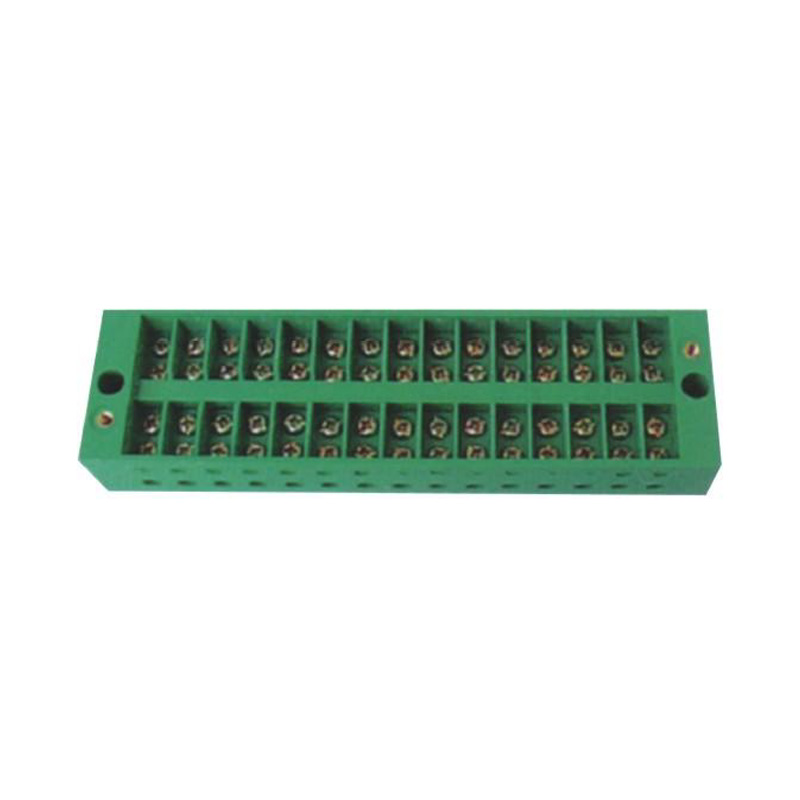
With the strong cooperation of relevant departments, our company has successfully developed a Closed Terminal Block. It provides guarantees for solving the problem of irregular metering wiring and implementing standardized and standardized management of metering and distribution devices. The product design complies with the principle of "special and closed" in the electricity metering specifications, and all technical indicators meet the requirements of IEC standards, and are very popular with electricity and pipe units.
All of the products are made of polymer polycarbonate (PC) materials. Therefore, it has many high-quality characteristics such as flame retardant, high temperature resistant, water-absorbent, moisture-resistant, good insulation performance, impact-resistant, non-fragmentable, and anti-aging. Small size, large current carrying capacity, high pressure resistance, reasonable structure, bright color and beautiful appearance. Since the cover plate is made of transparent material, the working state inside the junction box can be observed, which is convenient to install, and ensures reliability of wiring, achieving the purpose of convenient maintenance and safe use of electricity.
One of the primary selling points of this terminal block is its construction from materials that have high thermal resistance. The use of high-quality thermoplastics or heat-resistant alloys ensures that the terminal block can maintain its structural integrity and electrical conductivity even under prolonged exposure to high temperatures. This characteristic is crucial for applications in industrial settings, power plants, or any environment where heat is a constant factor.
Safety is a important concern in any electrical installation, and the Closed Terminal Block is designed with safety in mind. The terminal block includes features such as insulated housings, secure connection points, and heat-shielding components that protect against electrical arcing and potential short circuits. These features not only protect the electrical system but also safeguard the individuals working in close proximity to the installation.
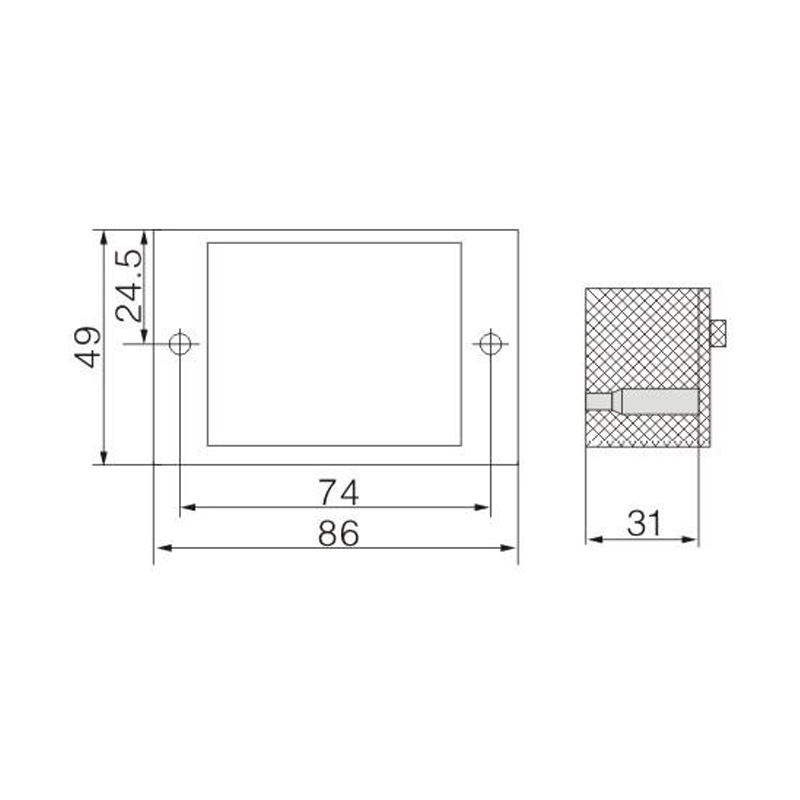
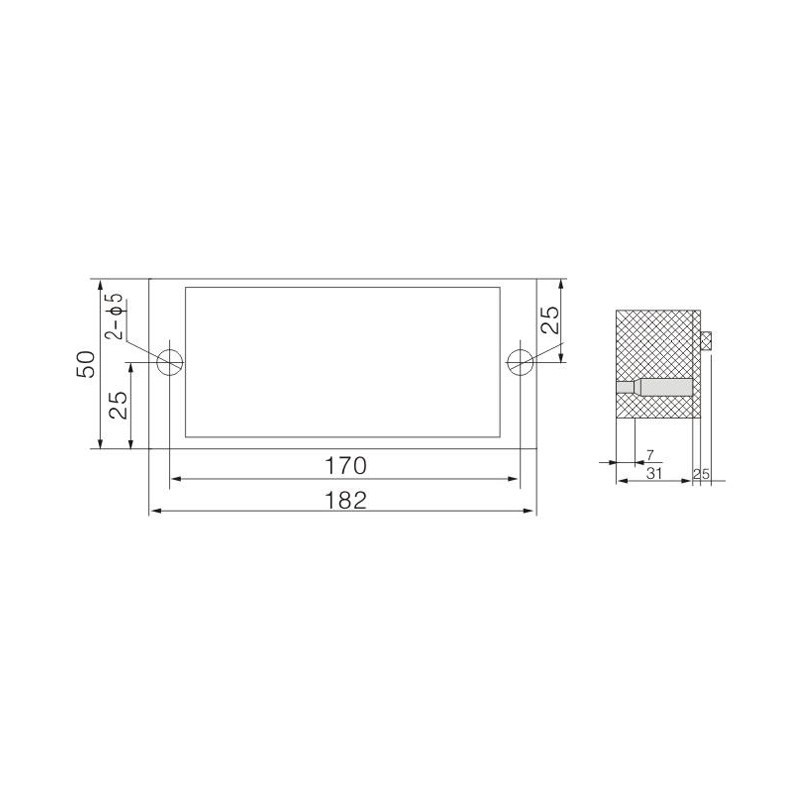
FJ6/JHD-5/D 2-Gear Terminal Block for Electric Energy Metering Box
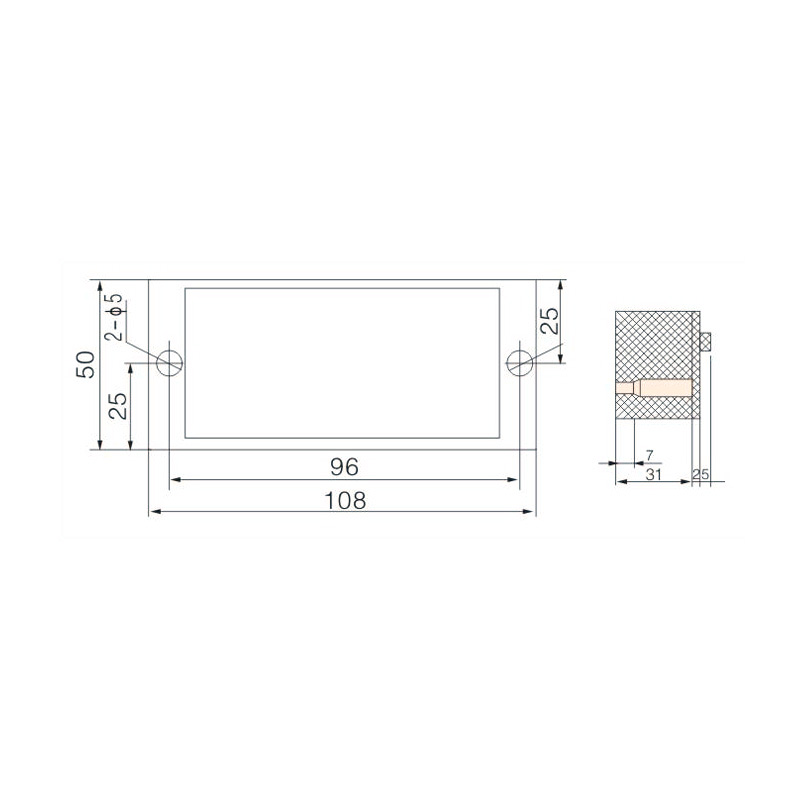
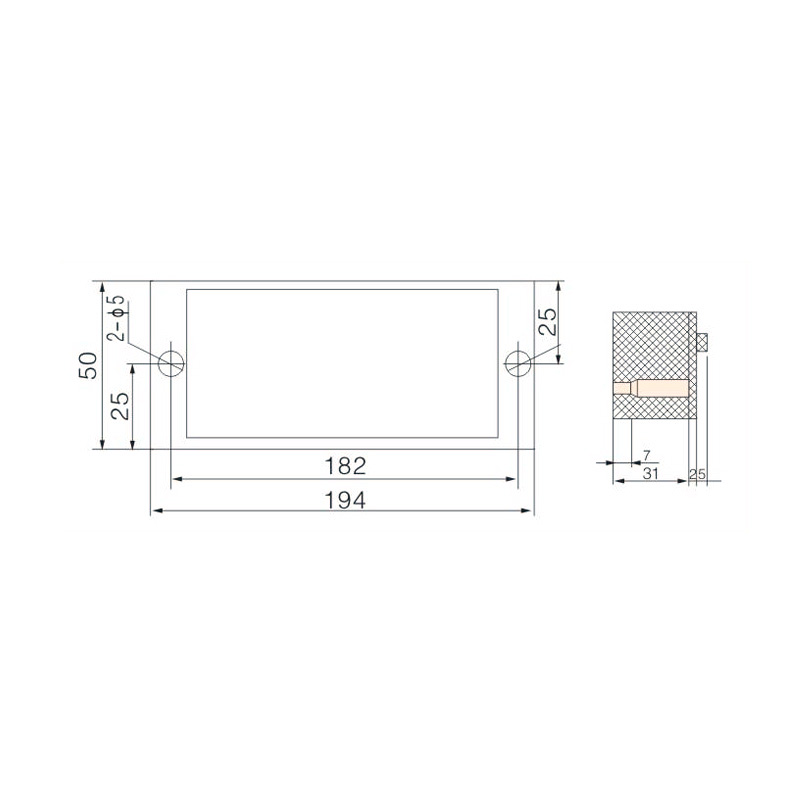
FJ6/JHD-5/G 3-Gear Terminal Block for Electric Energy Metering Box
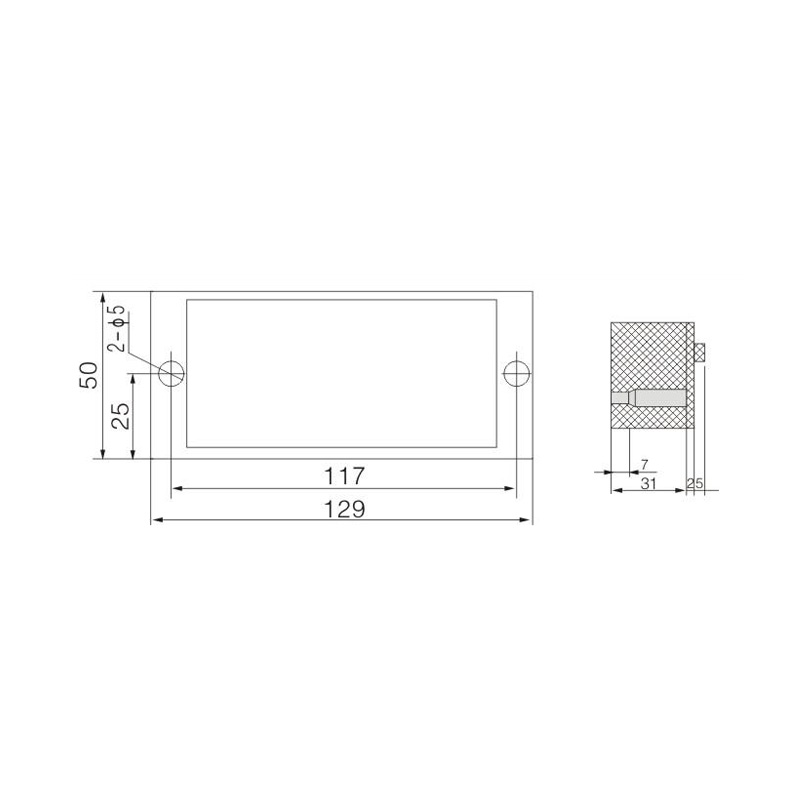
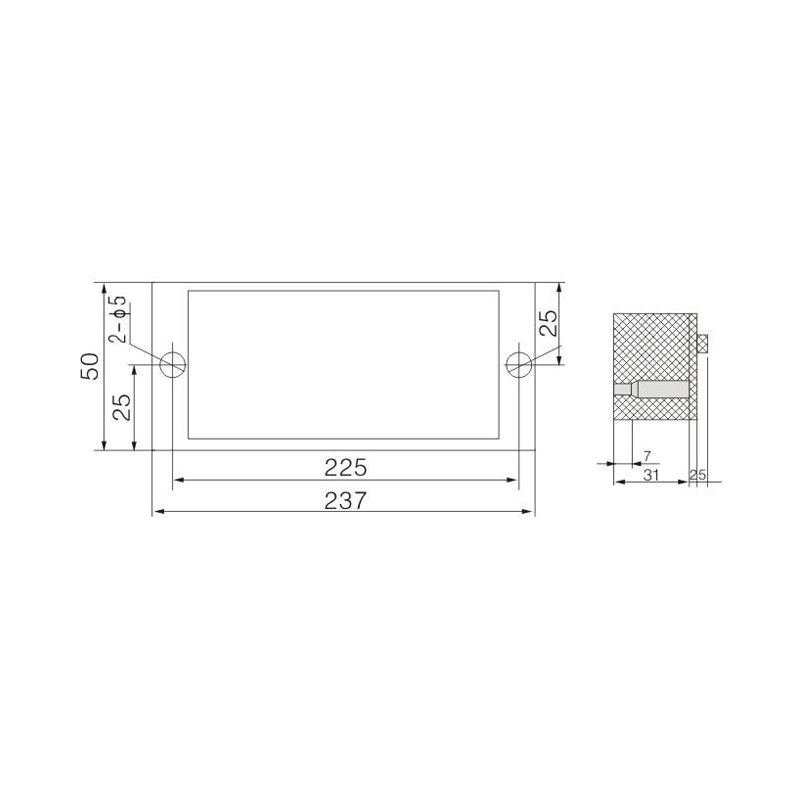
FJ6/JHD-5/B 4-Gear Terminal Block for Electric Energy Metering Box
FJ6/JHD-5/K 4-Gear Terminal Block for Electric Energy Metering Box
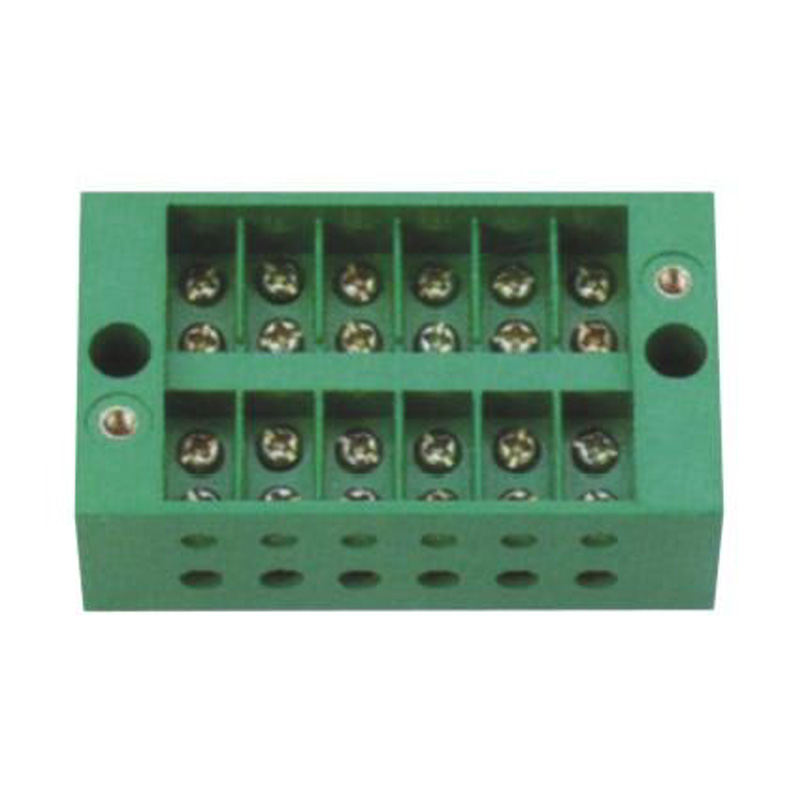
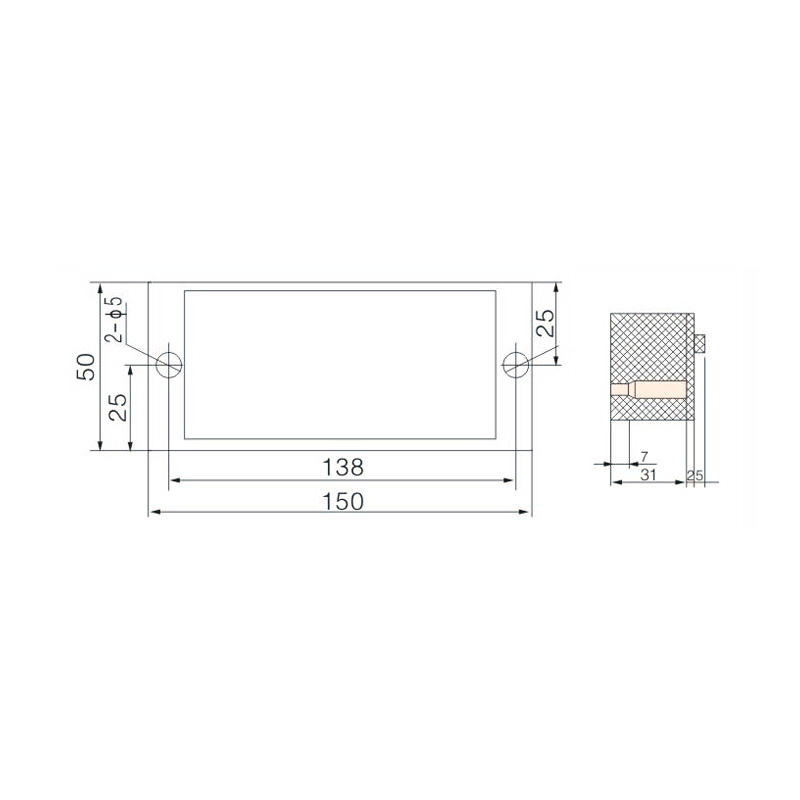
FJ6/JHD-5/F 6-Gear Terminal Block for Electric Energy Metering Box
FJ6/JHD-5/a 8-Gear Terminal Block for Electric Energy Metering Box
FJ6/JHD-5/L 10-Gear Terminal Block for Electric Energy Metering Box
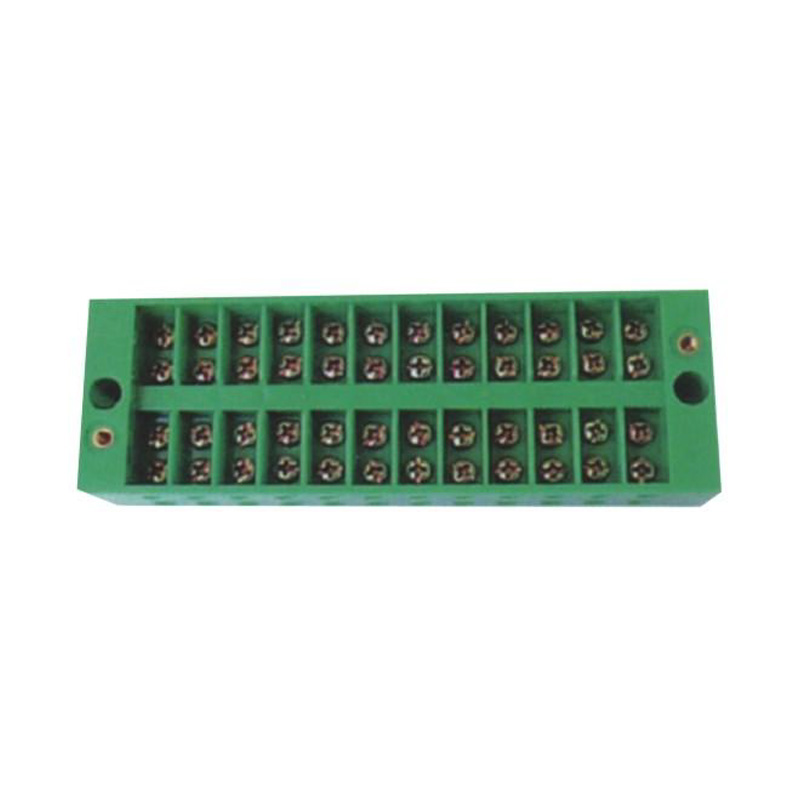
FJ6/JHD-5 12-Gear Terminal Block for Electric Energy Metering Box
FJ6/JHD-5/c 15-Gear Terminal Block for Electric Energy Metering Box
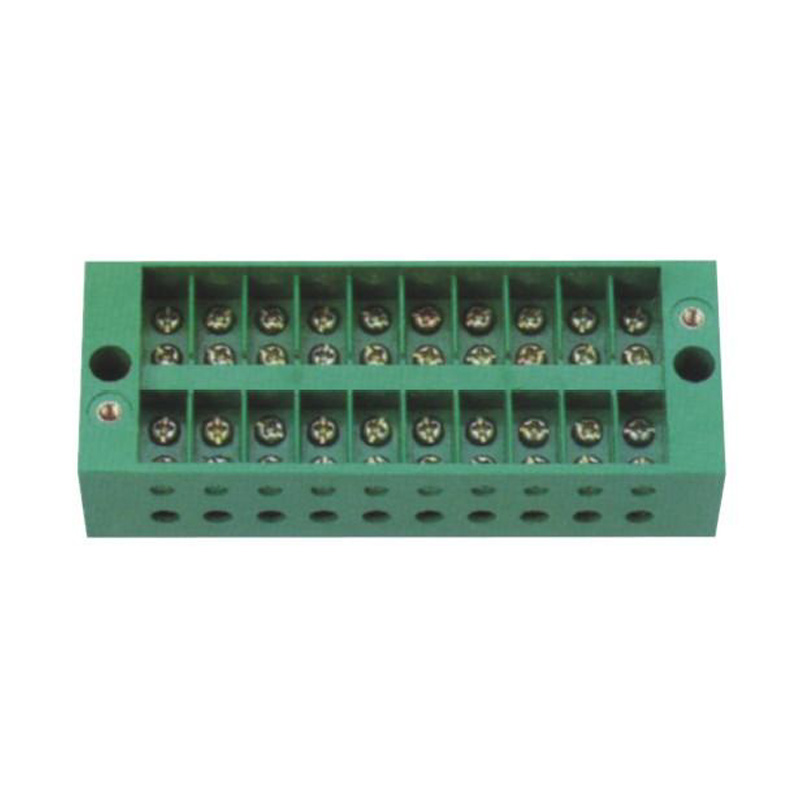
FJ6/JHD-5/D 16-Gear Terminal Block for Electric Energy Metering Box
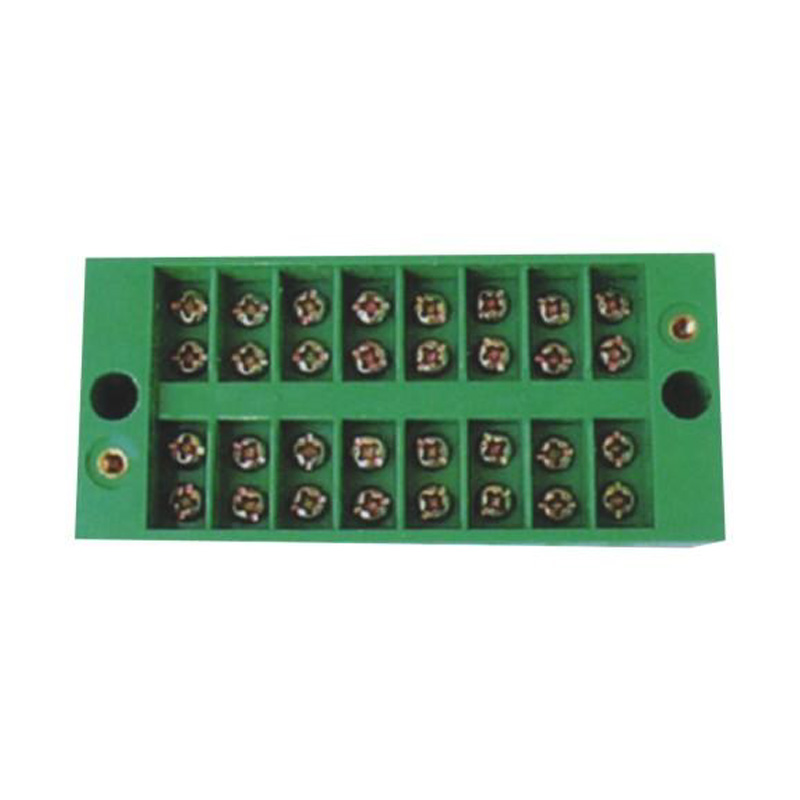
FJ6/JHD-5/E 20-Gear Terminal Block for Electric Energy Metering Box
Search
Categories
-
Energy Measuring Terminal Block(314)
- Energy Measuring Joint Terminal Block(16)
- Polycarbonate Energy Measuring Terminal Block(24)
- Standard Wiring Energy Measuring Terminal Block(4)
- Transparent Shell Energy Measuring Terminal Block(6)
- Multifunctional Test Energy Measuring Terminal Block(10)
- Intelligent Safety Energy Measuring Terminal Block(6)
- Single-Phase Multi-Circuit Output Terminal Block(12)
- Self-Elevating Metering Box Terminal Block(7)
- One Household One-Meter Meter Box Dedicated Terminal Block(56)
- Three-Phase Metering Box Dedicated Terminal Block(24)
- Repeatable Grounding Line Terminal Block(20)
- Terminal Block for One-Inlet Multi-Outlet Metering Box(15)
- Closed Terminal Block(11)
- Heavy Current Terminal Block(48)
- Self-Boosting Terminal Block(5)
- Intelligent Self-Locking Terminal Block(3)
- Tool-Free Crimping Type Terminal Block(5)
- Wide Range of Wire Diameters Terminal Block(5)
- Combined Type Energy Measuring Terminal Block(37)
-
Switch Terminal Block(55)
- Pin-Type Incoming Line Switch Terminal Block(4)
- Multi-Way Connection Switch Terminal Block(4)
- Plug-pin Switch Terminal Block(7)
- Combined Type Switch Terminal Block(7)
- High Contact Cross Section Switch Terminal Block(7)
- Wide Range Switch Terminal Block(11)
- One Way in Switch Terminal Block(12)
- Equipped with Circuit Breaker Switch Terminal(3)
-
Heavy-current Terminal Block(631)
- Modular Building Block Terminal Block(156)
- Spherical Non-Destructive Crimp Terminal(120)
- Dual-Mode Connection Electrical Terminal(90)
- Anti-Electricity-Theft Terminal Block(74)
- Convenient Connection Terminal Block(12)
- High-Contact Section Terminal Block(12)
- Wide Range of Wire Diameters Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Heavy-Current Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Upper and Lower Rows of Neutral Terminal(2)
- Independent Neutral Line Terminal(7)
- Nose-Type Neutral Line Terminal(7)
- Rail Type Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Fixed Neutral Line Terminal(12)
- Double Rail Assembly Electrical Terminal(19)
- Blue Jack-Up Terminal(6)
- Black Base Copper Bar Terminal(5)
- Compact Terminal Block(16)
- Precision Terminal Block(23)
- U-Shaped Harpoon Terminal(2)
- Grounding Metering Box Terminal Block(12)
- High-Performance Terminal Block(19)
- Multifunctional Terminal Block(10)
- Din Rail Terminal Block(76)
- Watt-hour Meter Connector(49)
-
Energy Meter Accessories(116)
-
-
Secure connections are essential for reliable electrical distribution, especially when installing a High-performance Terminal Bloc...
READ MORE -
For engineers and panel builders striving for both efficiency and reliability, wiring errors remain a persistent headache — even w...
READ MORE -
In modern electrical systems, a High-performance Terminal Block plays a critical role in ensuring secure and reliable connections ...
READ MORE -
When building or maintaining electrical systems, one frequently overlooked but critical factor is matching the conductor size to t...
READ MORE -
Effective electrical connections depend on more than simply matching cable sizes. Whether you’re securing a power conductor with a...
READ MORE
Are You Familiar with the Safety Features of Closed Terminal Blocks?
Closed terminal blocks are built with safety as a central feature. Unlike open designs, they enclose and protect the connection area, reducing risks associated with accidental contact or environmental factors. Two commonly recognized safety features include terminal covers and locking mechanisms, each serving distinct purposes.
1. Terminal Covers: Terminal covers are protective shields that prevent users from directly touching live conductors. By enclosing the connection points, they reduce the chance of accidental electric contact. In addition, covers protect the terminals from dust and debris, which can otherwise interfere with performance. For applications in harsh or crowded environments, this protection supports both user safety and long-term reliability.
2. Locking Mechanisms: Locking mechanisms secure conductors firmly within the block. This feature ensures that wires do not loosen under vibration, handling, or changes in load. By maintaining constant pressure, the locking system supports a reliable electrical path and minimizes interruptions. This is particularly useful in industrial environments where equipment is subject to continuous movement.
Together, terminal covers and locking mechanisms highlight how closed terminal blocks combine physical safety with dependable electrical performance.
When Did 12 Volt Power Terminal Blocks Appear?
The history of 12-volt power terminal blocks is closely tied to the broader adoption of 12-volt systems in the mid-20th century. While terminal blocks as a general concept date back more than a century, their application in 12-volt systems began once industries started standardizing low-voltage power.
In the automotive industry, the shift to 12-volt batteries became widespread around the 1950s and 1960s. This transition required suitable components to organize wiring for ignition systems, lighting, and accessories. Terminal blocks specifically designed for 12-volt circuits began appearing to meet this need, offering organized distribution points in vehicles.
Beyond transportation, 12-volt systems grew in popularity in telecommunications, small machinery, and renewable energy setups. In these applications, terminal blocks allowed installers to distribute power clearly and safely across multiple devices, supporting both functionality and organization.
As renewable energy expanded in the late 20th century, off-grid solar systems also adopted 12-volt designs for storage and distribution. Terminal blocks became essential here, as they ensured connections remained neat and manageable while handling multiple circuits.
Today, 12-volt terminal blocks are standard in automotive, marine, and energy applications, demonstrating how a simple connection component adapted alongside low-voltage technology to meet changing demands.
Structural Design of Barrier Terminal Blocks
Barrier terminal blocks are designed with partitions that separate connections, improving both safety and clarity. Their structure is versatile and can be categorized into common forms as outlined below:
1. Single Row: Terminals arranged in one straight line
This form is straightforward and often used for compact installations. The linear arrangement makes it simple to trace circuits, ensuring each connection is easily identifiable. Single-row designs are common in smaller control panels where space is available and clarity is important.
2. Double Row: Terminals arranged in two parallel lines
This form increases connection density without enlarging the footprint. By placing terminals in two rows, panels can accommodate more circuits within limited space. Double-row barrier blocks are often used in industrial applications where wiring density is high, but separation between circuits is still necessary for safety.
3. Feed-Through: Connections designed for input and output continuity
Feed-through forms allow conductors to pass from one side to another while remaining isolated. This arrangement is useful for applications that require straightforward energy transfer without complex branching.
4. Dual-Level: Terminals stacked vertically in two levels
This design maximizes panel space efficiency by stacking terminals. It provides more connections in a smaller area, making it suitable for complex installations where compact layouts are a priority.


 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى