Integrating wired connectivity into the era of automation and digital networking involves more than just traditional hardware. A H...
READ MOREThree Phases Four Wires Rail Type Combined Terminal Manufacturer
Three Phases Four Wires Rail Type Combined Terminal Blocks are professionally used for managing electrical connections in three-phase, four-wire power distribution systems, specifically designed for easy installation and integration into rail-mounted electrical panels and distribution boards. These terminal blocks are ideal for applications requiring a compact, organized, and reliable solution for combining and distributing power across multiple circuits.
These rail type combined terminal blocks feature a modular design that allows for secure and stable connections of both phase and neutral wires, without the need for excessive wiring or additional conductors. The rail mounting design ensures easy installation and scalability, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial and commercial applications.
Three Phases Four Wires Rail Type Combined Terminal Blocks are currently a novel product offering a convenient and highly reliable solution for managing three-phase power distribution. They simplify the wiring process, enhance system reliability, and provide a safe and efficient way to manage multiple circuits in a single terminal block, all while being easily integrated into rail-mounted systems.
The FJ6DI-150-04 is built to handle high currents, making it ideal for large-scale industrial applications where power demands are substantial. Its robust design ensures that it can withstand the rigors of continuous heavy use without compromising on performance.
In environments where space is at a outstanding, the compact design of the FJ6DI-150-04 is a significant advantage. It saves space on the DIN rail, allowing for more components to be installed in a smaller area without sacrificing functionality.
The terminal's compatibility with standard DIN rail systems means it can be easily integrated into existing electrical setups. This compatibility reduces the need for extensive modifications, saving time and resources during installation.
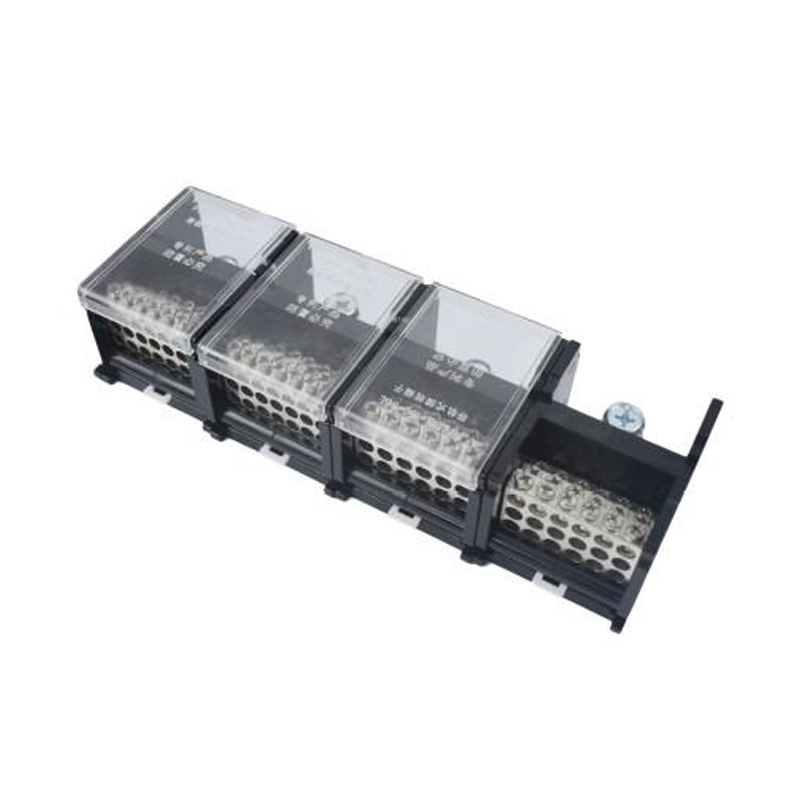
FJ6DI-150-04/16x 16 55L Three Phases and Four Wires Rail Combined Terminal
FJ6DI-150-04/16x16(55L)
One-inlet, sixteen-outlue
Inlet wire:10-50mm², outlet wire:1.5-16mm²
Ordernumber:152371
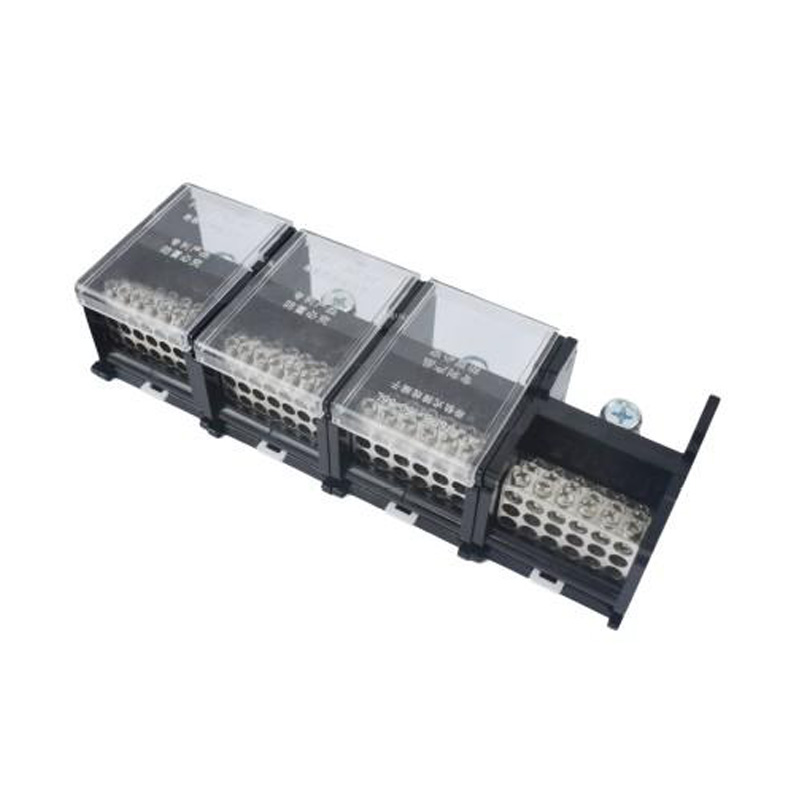
FJ6DI-150-04/18x 16 55L Three Phases and Four Wires Rail Combined Terminal
FJ6DI-150-04/18x16(55L)
One-inlet, eighteen-outlue
Inlet wire:10-50mm²,outlet wire:1.5-16mm²
Ordernumber:152372
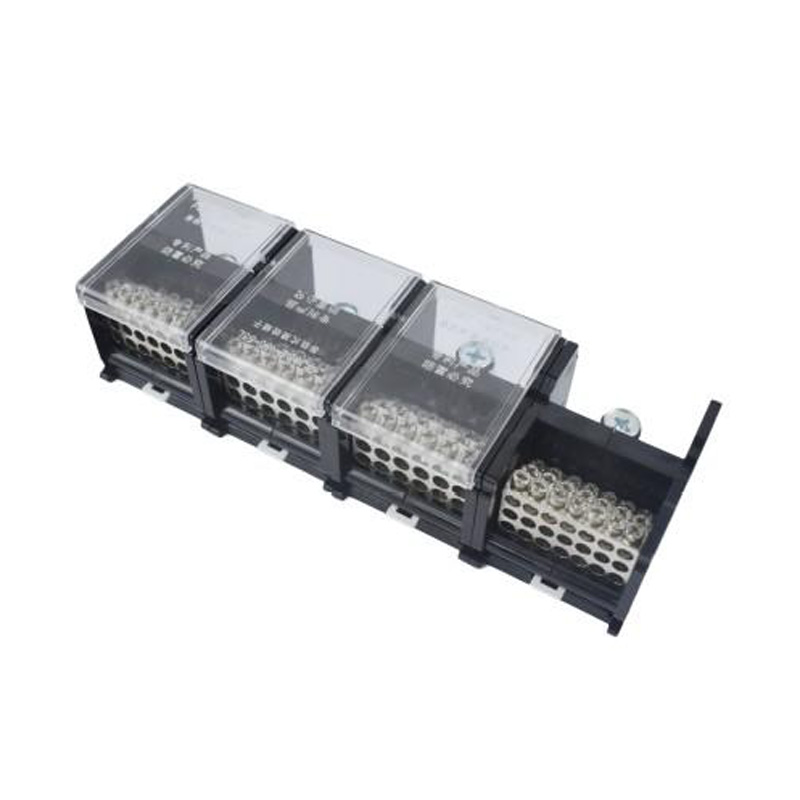
FJ6DI-150-04/21x10 55L Three Phases and Four Wires Rail Combined Terminal
FJ6DI-150-04/21x10(55L)
One-inlet, twenty-outlue
Inlet wire:10-50mm²,outlet wire:1.5-10mm²
Order number:152373
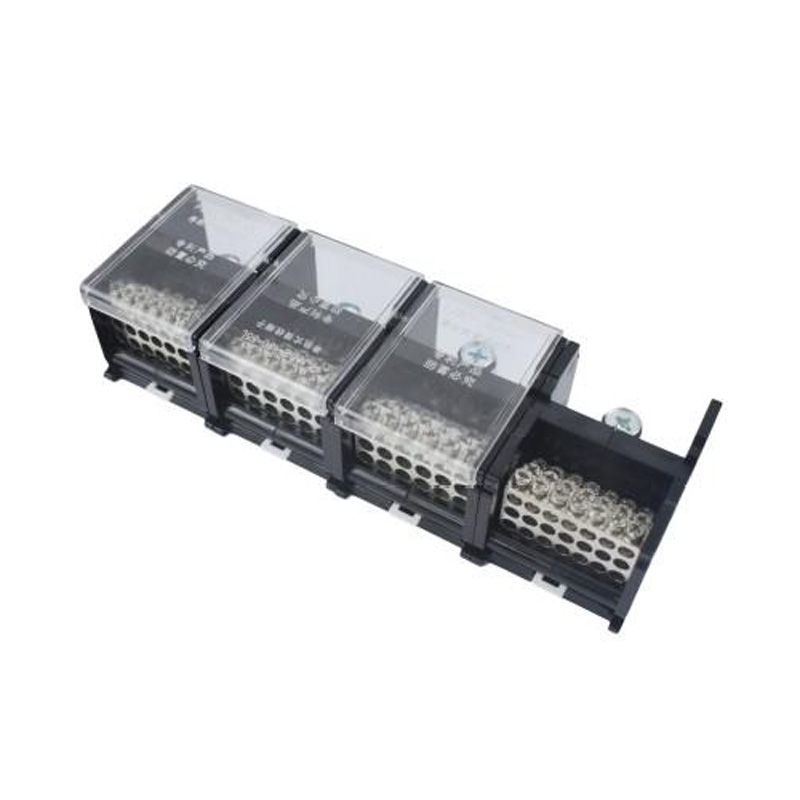
FJ6DI-150-04/24x6 55L Three Phases and Four Wires Rail Combined Terminal
FJ6DI-150-04/24 x6(55L)
One-inlet, twenty-four-outlue
Inlet wire:10-50mm²,outlet wire:1.5-6mm²
Order number:152374
Search
Categories
-
Energy Measuring Terminal Block(314)
- Energy Measuring Joint Terminal Block(16)
- Polycarbonate Energy Measuring Terminal Block(24)
- Standard Wiring Energy Measuring Terminal Block(4)
- Transparent Shell Energy Measuring Terminal Block(6)
- Multifunctional Test Energy Measuring Terminal Block(10)
- Intelligent Safety Energy Measuring Terminal Block(6)
- Single-Phase Multi-Circuit Output Terminal Block(12)
- Self-Elevating Metering Box Terminal Block(7)
- One Household One-Meter Meter Box Dedicated Terminal Block(56)
- Three-Phase Metering Box Dedicated Terminal Block(24)
- Repeatable Grounding Line Terminal Block(20)
- Terminal Block for One-Inlet Multi-Outlet Metering Box(15)
- Closed Terminal Block(11)
- Heavy Current Terminal Block(48)
- Self-Boosting Terminal Block(5)
- Intelligent Self-Locking Terminal Block(3)
- Tool-Free Crimping Type Terminal Block(5)
- Wide Range of Wire Diameters Terminal Block(5)
- Combined Type Energy Measuring Terminal Block(37)
-
Switch Terminal Block(55)
- Pin-Type Incoming Line Switch Terminal Block(4)
- Multi-Way Connection Switch Terminal Block(4)
- Plug-pin Switch Terminal Block(7)
- Combined Type Switch Terminal Block(7)
- High Contact Cross Section Switch Terminal Block(7)
- Wide Range Switch Terminal Block(11)
- One Way in Switch Terminal Block(12)
- Equipped with Circuit Breaker Switch Terminal(3)
-
Heavy-current Terminal Block(631)
- Modular Building Block Terminal Block(156)
- Spherical Non-Destructive Crimp Terminal(120)
- Dual-Mode Connection Electrical Terminal(90)
- Anti-Electricity-Theft Terminal Block(74)
- Convenient Connection Terminal Block(12)
- High-Contact Section Terminal Block(12)
- Wide Range of Wire Diameters Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Heavy-Current Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Upper and Lower Rows of Neutral Terminal(2)
- Independent Neutral Line Terminal(7)
- Nose-Type Neutral Line Terminal(7)
- Rail Type Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Fixed Neutral Line Terminal(12)
- Double Rail Assembly Electrical Terminal(19)
- Blue Jack-Up Terminal(6)
- Black Base Copper Bar Terminal(5)
- Compact Terminal Block(16)
- Precision Terminal Block(23)
- U-Shaped Harpoon Terminal(2)
- Grounding Metering Box Terminal Block(12)
- High-Performance Terminal Block(19)
- Multifunctional Terminal Block(10)
- Din Rail Terminal Block(76)
- Watt-hour Meter Connector(49)
-
Energy Meter Accessories(116)
-
-
Secure connections are essential for reliable electrical distribution, especially when installing a High-performance Terminal Bloc...
READ MORE -
For engineers and panel builders striving for both efficiency and reliability, wiring errors remain a persistent headache — even w...
READ MORE -
In modern electrical systems, a High-performance Terminal Block plays a critical role in ensuring secure and reliable connections ...
READ MORE -
When building or maintaining electrical systems, one frequently overlooked but critical factor is matching the conductor size to t...
READ MORE -
Effective electrical connections depend on more than simply matching cable sizes. Whether you’re securing a power conductor with a...
READ MORE
What Are The Characteristics Of a Three-Phase, Four-Wire, Rail-Type Combined Terminal?
A three-phase four-wire rail type combined terminal block is a specialized component designed for three-phase electrical systems that also require a neutral connection. Its design incorporates specific features to manage this type of power distribution efficiently and safely.
1. Integrated Design for System Completeness: This terminal block is characterized by its unified structure that houses four separate connection points within a single, modular unit. These points correspond to the three phase conductors (often labeled L1, L2, L3) and the neutral conductor (N). By combining these into one block that mounts directly onto a standard DIN rail, it offers a compact and organized solution for terminating the main incoming and outgoing lines in a three-phase system. This integrated design simplifies panel layout, reduces wiring time, and ensures all critical power connections are located in one centralized, easy-to-access location.
2. Construction for Safety and Identification: A key characteristic is its focus on safe and clear operation. The block is manufactured from high-quality insulating materials, such as heat-resistant polyamide or other engineered plastics, which provide dielectric strength to prevent short circuits between the closely spaced phases and neutral. Furthermore, these blocks almost always include permanent, embossed, or color-coded markings for L1, L2, L3, and N. This clear identification is a critical safety feature that helps prevent miswiring, which could equipment damage or hazardous situations. The construction often includes internal barriers and segregation to maintain proper creepage and clearance distances between poles, enhancing overall system safety.
3. Current and Application Considerations: These combined terminals are available in a range of current ratings to suit different loads, from lighter industrial equipment to heavier power distribution applications. The choice of materials for the current-carrying components, typically tin-plated or silver-plated copper, ensures low resistance and reliable conductivity. It is important to select a block whose current rating matches or exceeds the system's expected load. This type of terminal is commonly found in the main power entry section of control panels, distribution boards, and machinery that operates on a standard three-phase four-wire supply.
Can a Power Distribution Block Be Used In High-Temperature Environments?
The suitability of a power distribution block for use in a high-temperature environment is not a simple yes or no question. It depends on the specific product's design, materials, and manufacturer's specifications. Standard blocks have defined operating temperature ranges, and using them outside these limits can affect performance.
1. Material Selection and Temperature Ratings: The foremost consideration is the manufacturer's stated temperature rating. Every power distribution block is designed and tested to operate reliably within a specific ambient temperature range, which is always provided in its technical datasheet. This rating is determined by the materials used in its construction. The insulating housing is typically made from plastics like polyamide (nylon) or polycarbonate, which have defined service temperatures, often around 105°C to 120°C for standard grades. The metal conductors also have a role; while metals can withstand higher heat, the interaction between the metal and plastic at elevated temperatures is crucial. Special high-temperature blocks utilize advanced engineering plastics or thermosetting materials that can withstand ambient temperatures of 140°C or higher without deforming or losing their insulating properties.
2. Understanding Derating and Heat Management: In electrical terms, "derating" is a critical concept for high-temperature applications. As the ambient temperature increases, a component's ability to dissipate heat decreases. Consequently, the current a block can safely carry is reduced. A datasheet will include a derating curve or chart that shows exactly how much the current capacity must be reduced as the temperature rises. For instance, a block rated for 100A at 40°C might only be rated for 80A in a 60°C environment. Therefore, even if a block is placed in a high-temperature area, it may still be used if the actual current flowing through it is sufficiently lower than its derated capacity. Additional heat management strategies, such as ensuring adequate ventilation around the block or using heat sinks, can also help maintain a safe operating temperature.


 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى