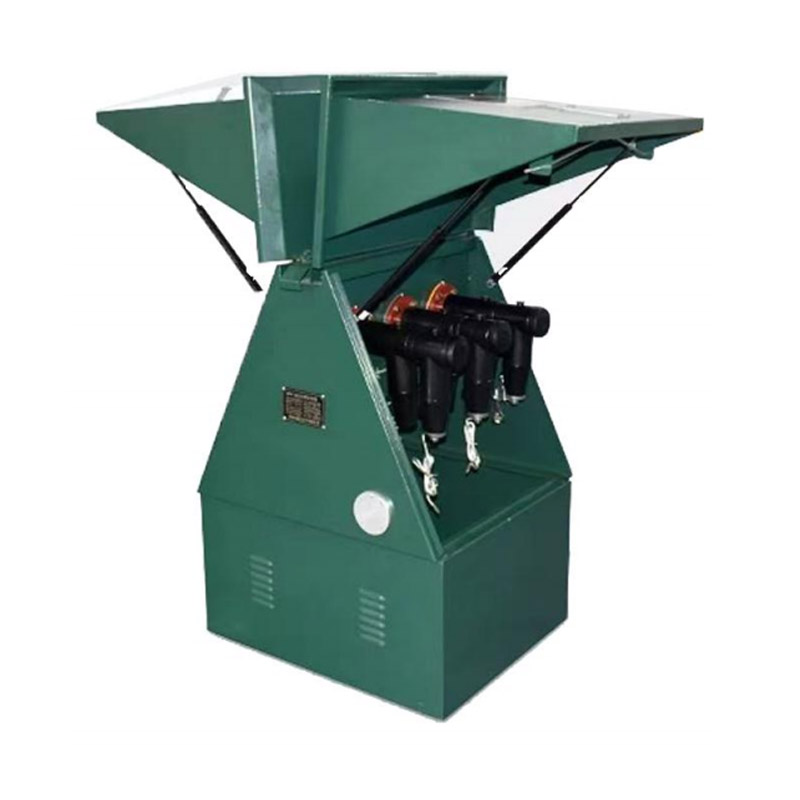
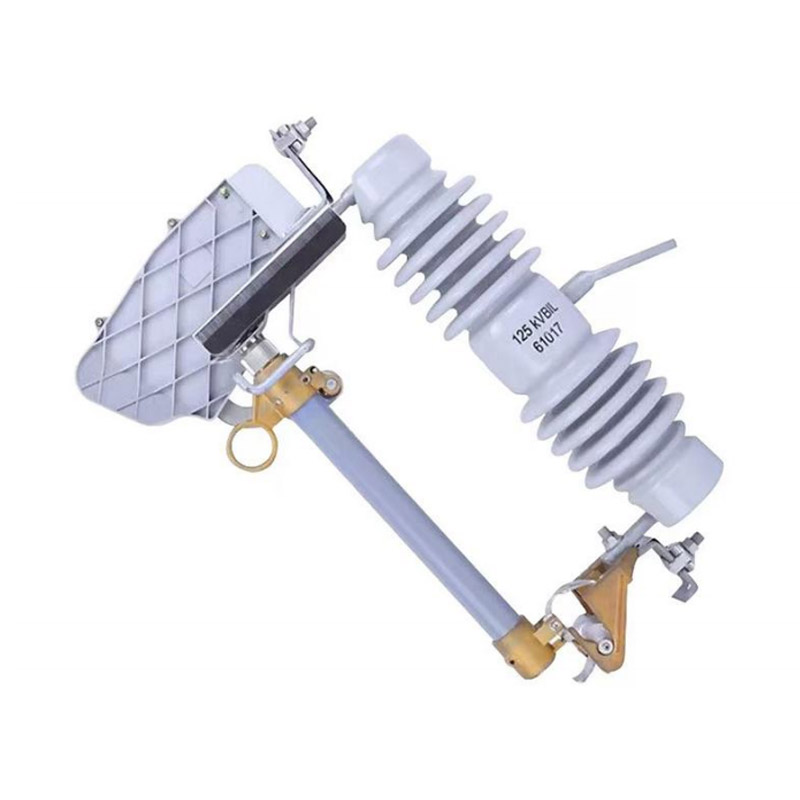
In any electrical installation, both junction boxes and circuit breaker block junction boxes are essential for safe and reliable system operation. Without well-designed enclosures, the risk of faults, shock, and failure dramatically increases. In this article, we explore why circuit breaker block junction boxes matter for electrical safety, how they mitigate hazards, and what ideal practices installers and system designers should follow.
Principal Safety Risks in Electrical Systems
To understand why these boxes matter, we must understand the common hazards:
Loose or degraded connections — over time, thermal expansion/contraction or vibration can loosen screw terminals, causing to arcing or overheating.
External damage or intrusion — wires or splices left unprotected may be damaged by tools, rodents, or debris.
Moisture, dust, or corrosion — environmental intrusion can degrade insulation or cause short circuits.
Overcrowded wiring or poor layout — if wires are crammed in, heat dissipation suffers, and insulation may be compromised.
Unshielded or exposed live parts — creating shock risks or violation of electrical safety codes and standards.
A well-designed junction box (especially a circuit breaker block junction box) helps mitigate all of these risks by enforcing physical protection, spatial organization, and compliance discipline.
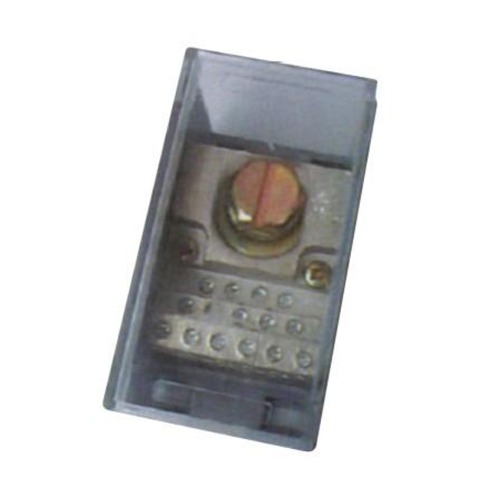

How Circuit Breaker Block Junction Boxes Enhance Safety
Here are the key benefits of using circuit breaker block junction boxes (versus leaving wiring loose or poorly enclosed):
1. Localized Overcurrent Protection in Place
By embedding circuit breakers or breaker blocks in the junction box, any fault in the wiring segment hosted in that box is detected and disconnected right there. That containment reduces stress on upstream wiring and limits propagation of damage.
2. Containment of Arc & Heat Events
If a fault or short occurs within wiring or a terminal inside the junction box, the enclosure can contain the arc, sparks, or heating to prevent damage to adjacent wiring or surroundings. This is far safer than letting such events go uncontained.
3. Separation & Organization of Conductors
Inside a circuit breaker block junction box, you can ensure that phases, neutrals, grounds, and control circuits are neatly segregated. This organization reduces inadvertent cross-connections or mis-wiring errors — a frequent concern raised in electrical forums. For example, debates appear about putting junction boxes adjacent to breaker panels — “Is there any reason I can’t mount a junction box a foot away from my breaker box?” — users worry about maintaining safe spacing and wiring routes.
4. Easier Maintenance & Inspection
Since junction boxes must remain accessible, having breakers inside them allows maintenance personnel or inspectors to isolate circuits, inspect wiring joints, and perform servicing without tearing into concealed splices. Code often requires junction boxes to remain accessible.
5. Compliance with Code & Regulations
Electrical codes (such as NEC in the U.S.) require that all splices, joints, or terminations be enclosed within boxes. Further, boxes must permit adequate volume (box fill), must seal unused openings, and conductors entering boxes must be protected from abrasion. A circuit breaker block junction box naturally helps satisfy these requirements by providing space and appropriate structure for wiring plus breaker modules.
A circuit breaker block junction box is much more than a container — it is a vital safety element in electrical systems. By combining wiring protection, overcurrent devices, and a thoughtfully designed enclosure, these boxes help contain faults, organize wiring, and satisfy regulatory requirements. Meanwhile, proper junction box design ensures all splices and terminations remain protected, accessible, and safe.


 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى