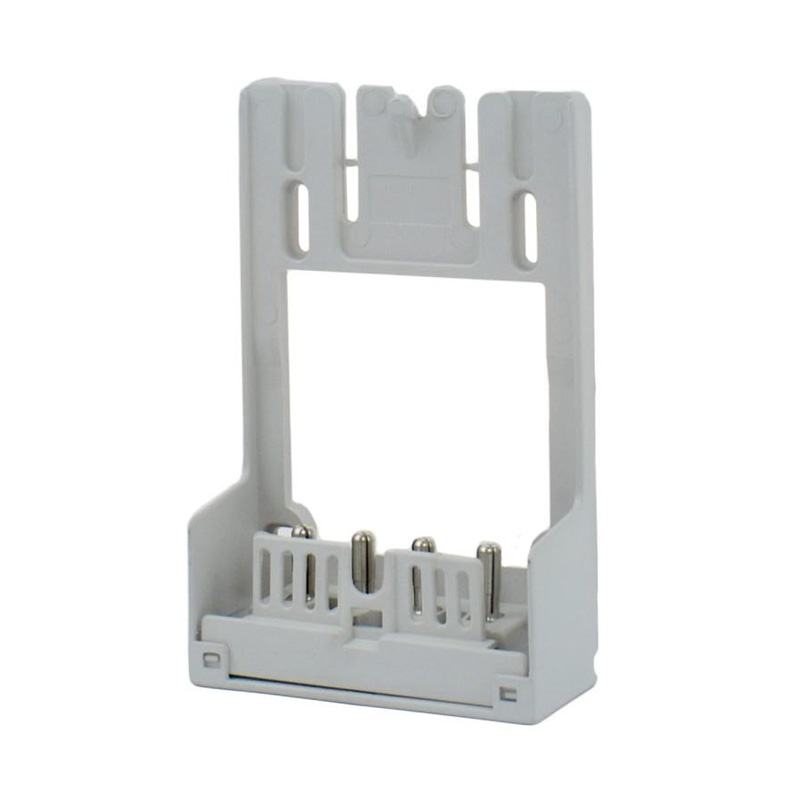
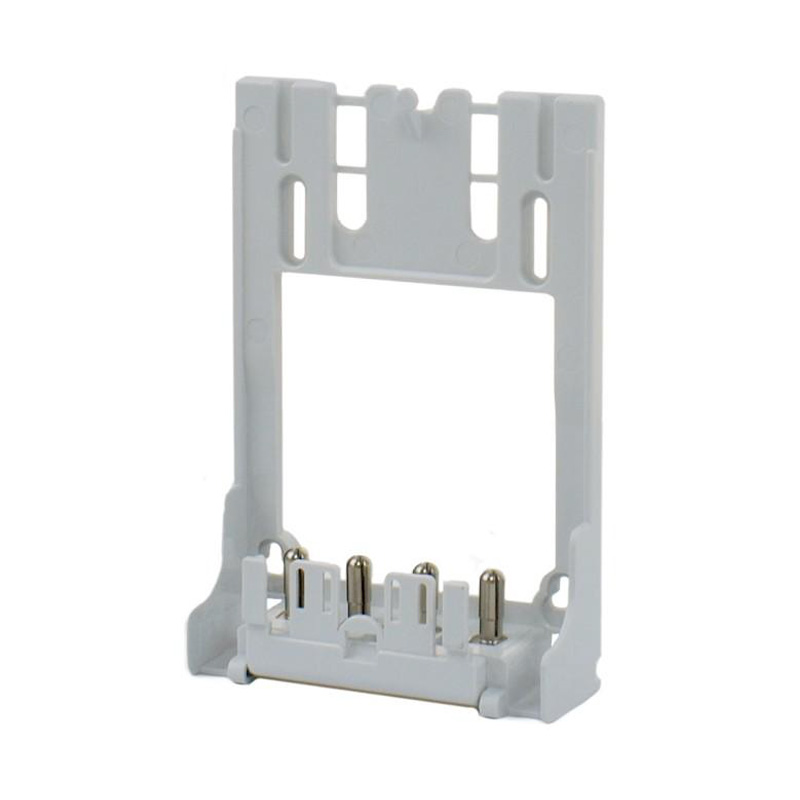
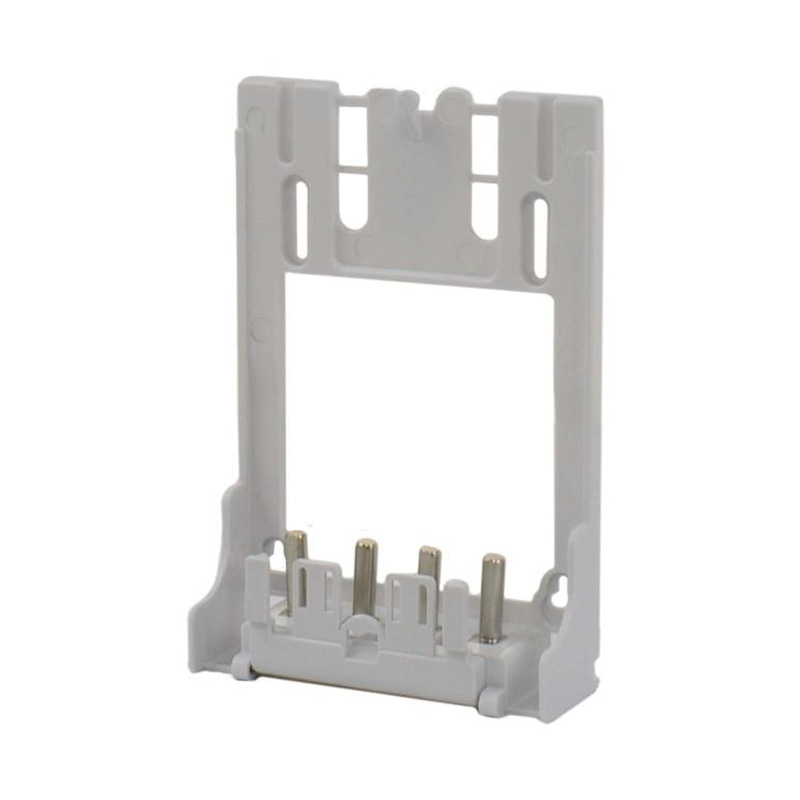
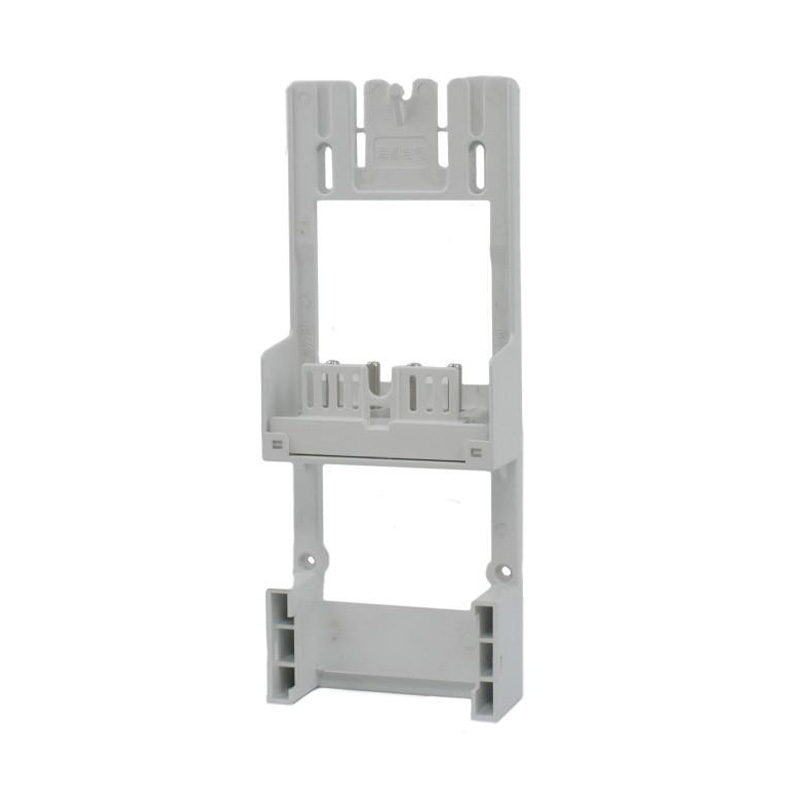
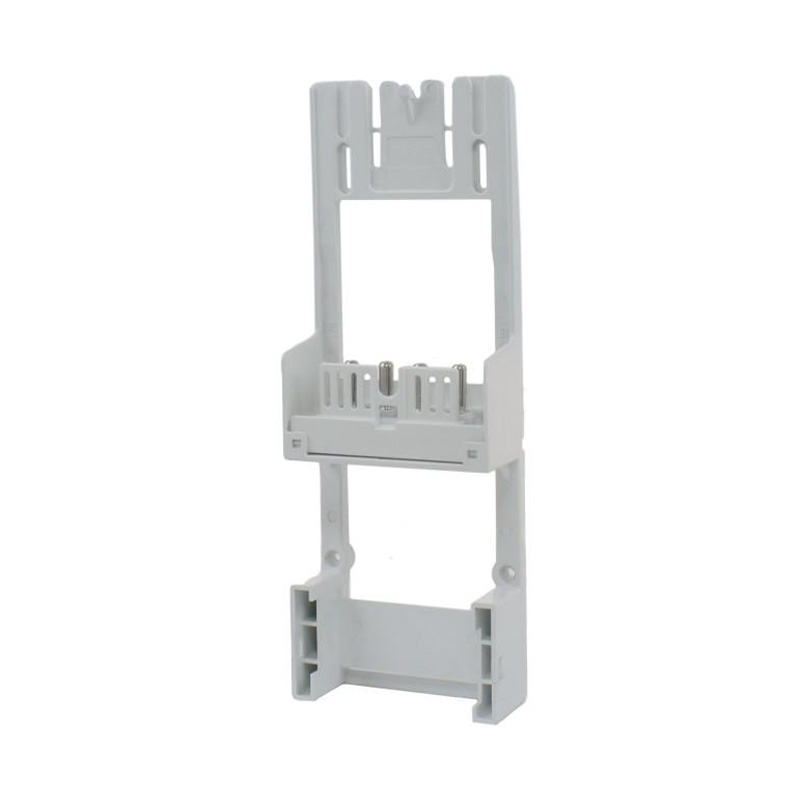
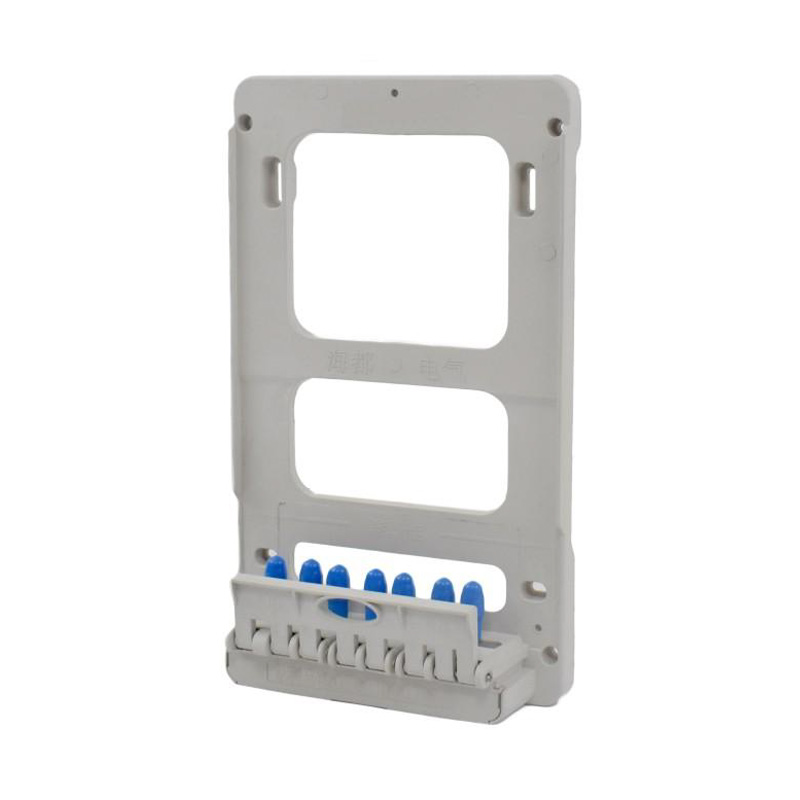
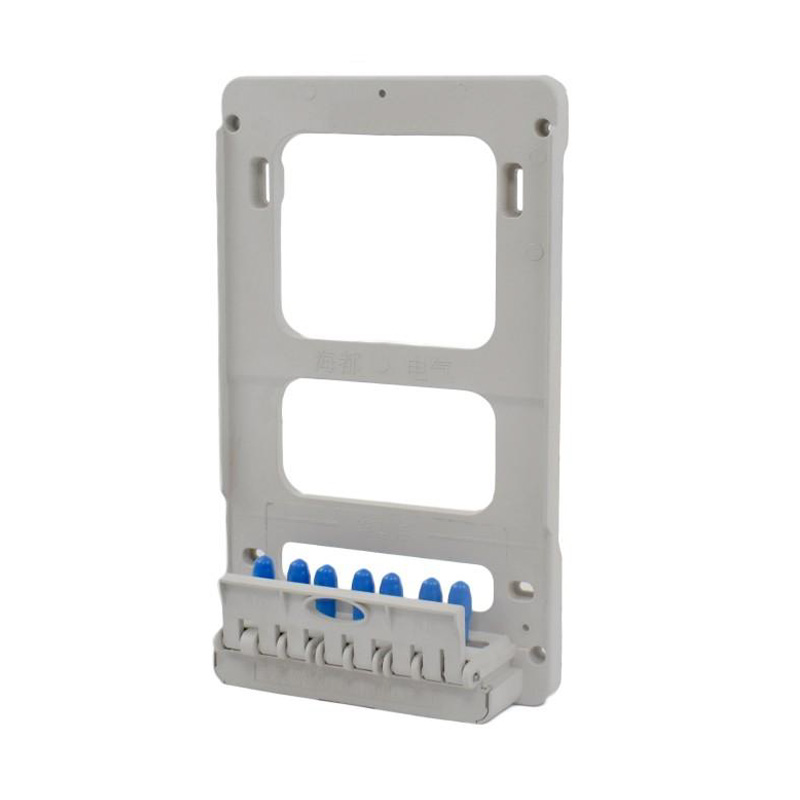
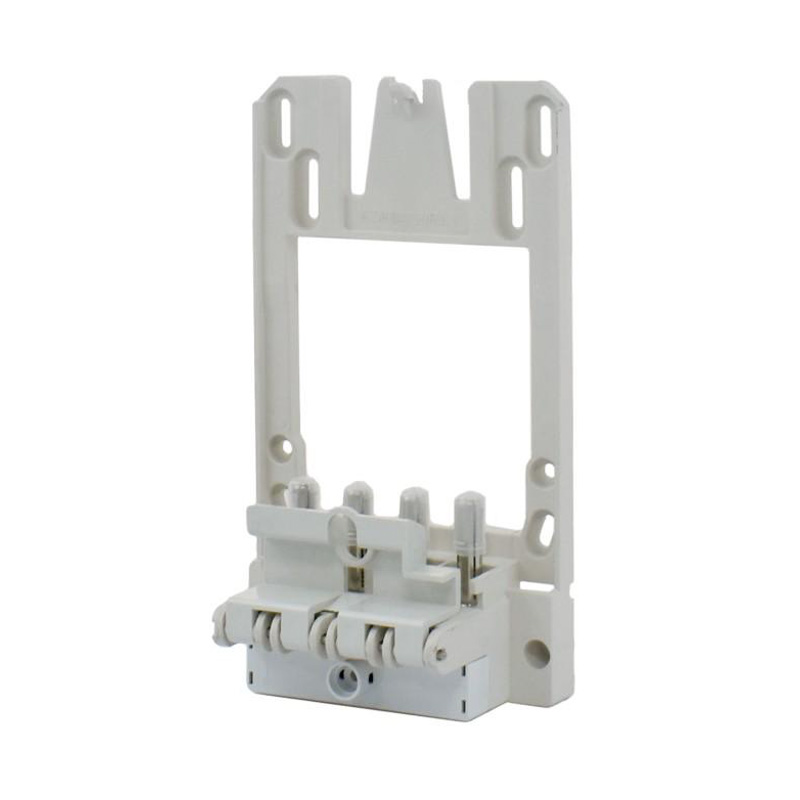
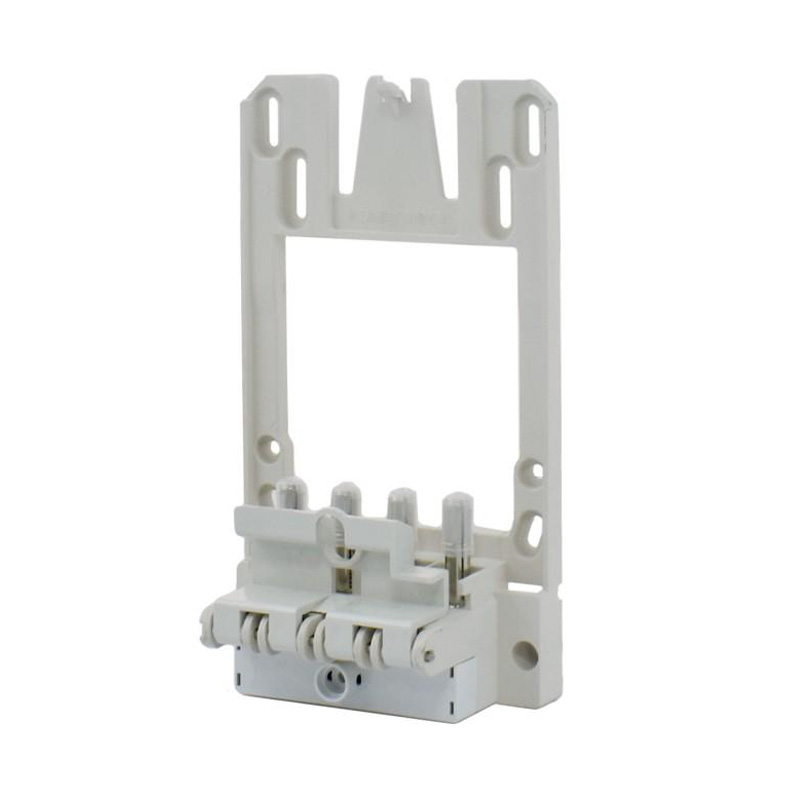
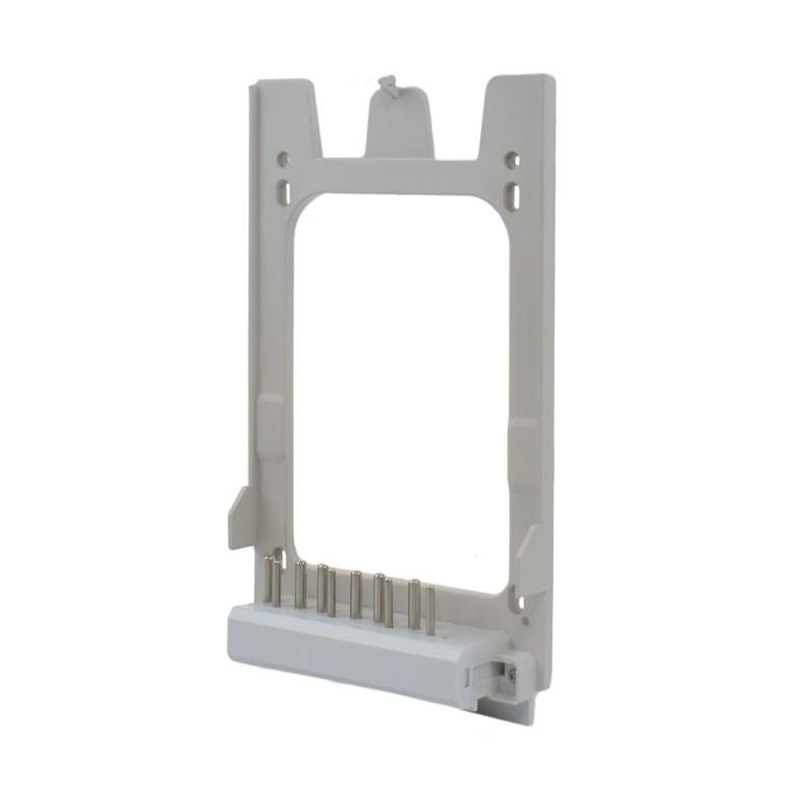
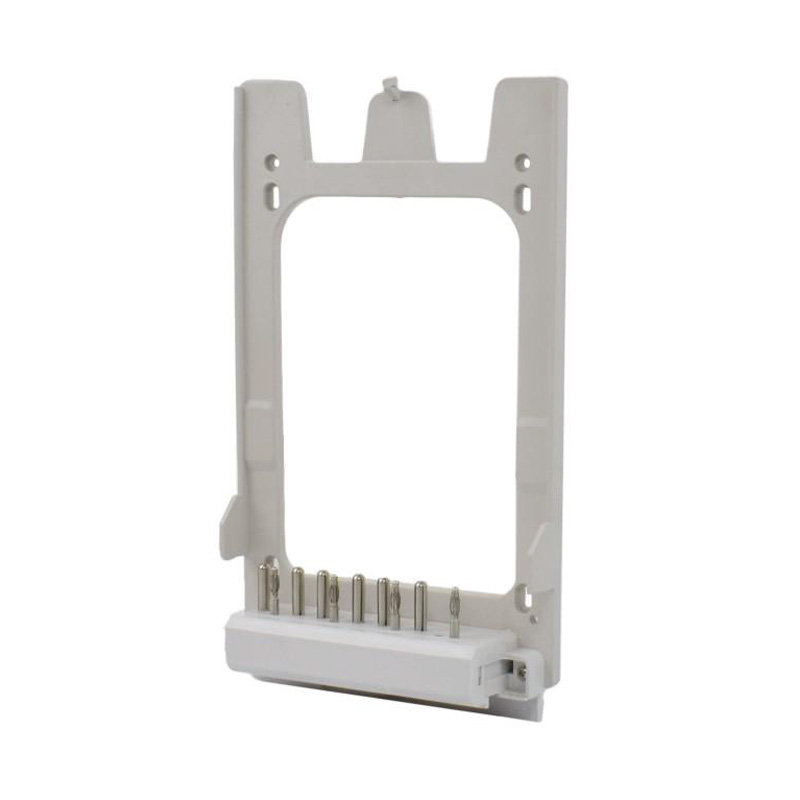
Integrating wired connectivity into the era of automation and digital networking involves more than just traditional hardware. A H...
READ MOREWatt-hour Meter Connector And Accessories Manufacturer
Watt-hour Meter Connectors are specialized electrical connectors designed to interface with watt-hour meters, which are devices used to measure electrical energy consumption. These connectors play a crucial role in the accurate measurement and billing of electricity usage in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. They are engineered to ensure reliable data transmission and less energy loss, making them an essential component in the energy management infrastructure.
1. High Accuracy and Reliability:
Watt-hour Meter Connectors are precision-engineered to maintain high levels of accuracy in energy measurement. They are designed to withstand the rigors of continuous electrical current and to provide a secure connection that less the risk of data corruption or loss.
2. Durable Construction:
These connectors are built with robust materials that can withstand harsh environmental conditions, including temperature fluctuations, humidity, and exposure to various pollutants. Their durable construction ensures longevity and reduces the need for frequent replacements.
3. Compatibility and Interchangeability:
Watt-hour Meter Connectors are designed to be compatible with a wide range of watt-hour meters and other electrical equipment. This standardization allows for easy integration into existing systems and facilitates maintenance and upgrades without the need for complete system overhauls.
4. Safety Features:
Safety is a important concern in electrical systems, and watt-hour meter connectors are no exception. They often incorporate features such as insulation resistance, dielectric strength, and protection against reverse polarity, which help prevent electrical accidents and damage to connected equipment.
5. Ease of Installation:
Watt-hour Meter Connectors are designed for easy installation, reducing the time and effort required to integrate them into electrical systems. This can translate into cost savings for both installers and end-users.
6. Corrosion Resistance:
The connectors are often treated or made from materials that resist corrosion, ensuring that they maintain their integrity over time, even in environments prone to moisture and other corrosive elements.
7. Environmental Stability:
They are designed to operate reliably across a wide range of temperatures and conditions, ensuring consistent performance in diverse climates and environments.
8. Data Integrity:
In the context of smart grids and advanced metering infrastructure, watt-hour meter connectors are critical for maintaining the integrity of the data being transmitted. They ensure that the energy consumption data is accurately captured and transmitted without errors.
9. Conformance to Standards:
These connectors adhere to international standards for electrical safety and performance, ensuring that they meet the requirements of various regulatory bodies and can be used globally.
10. Cost-Effectiveness:
Despite their advanced features, watt-hour meter connectors are designed to be cost-effective, offering a balance between performance and price that makes them accessible to a wide range of customers.
11. Sustainability:
The production of watt-hour meter connectors often takes into account environmental impact, with an emphasis on using sustainable materials and practices that minimize ecological footprint.
Watt-hour Meter Connectors are a critical link in the chain of energy measurement and management. Their precision, durability, and versatility make them an indispensable tool for utilities, energy managers, and consumers alike. As the world moves towards smarter and more efficient energy use, the role of watt-hour meter connectors will only become more significant.
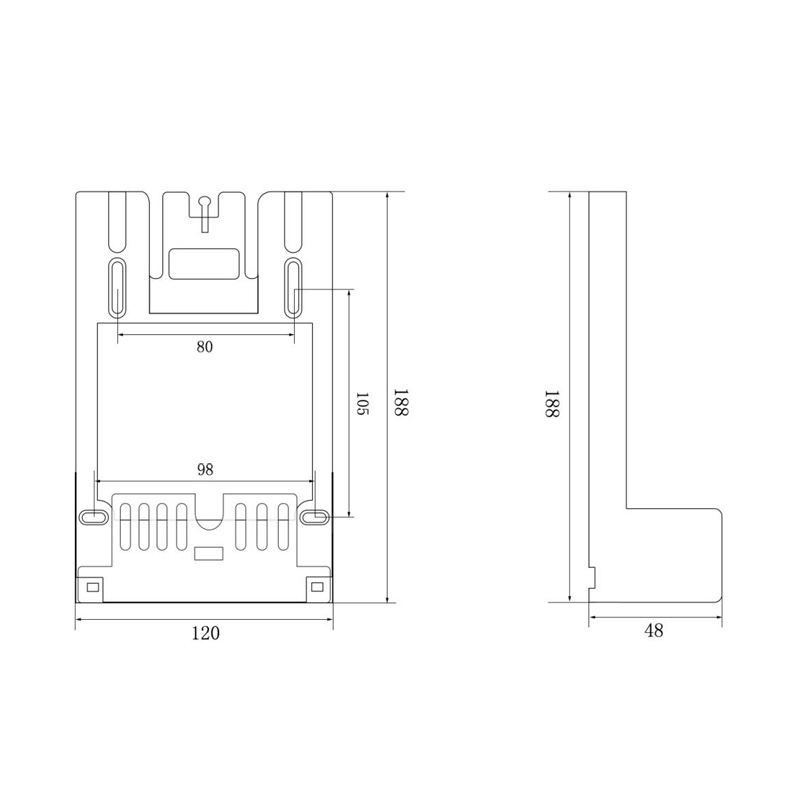
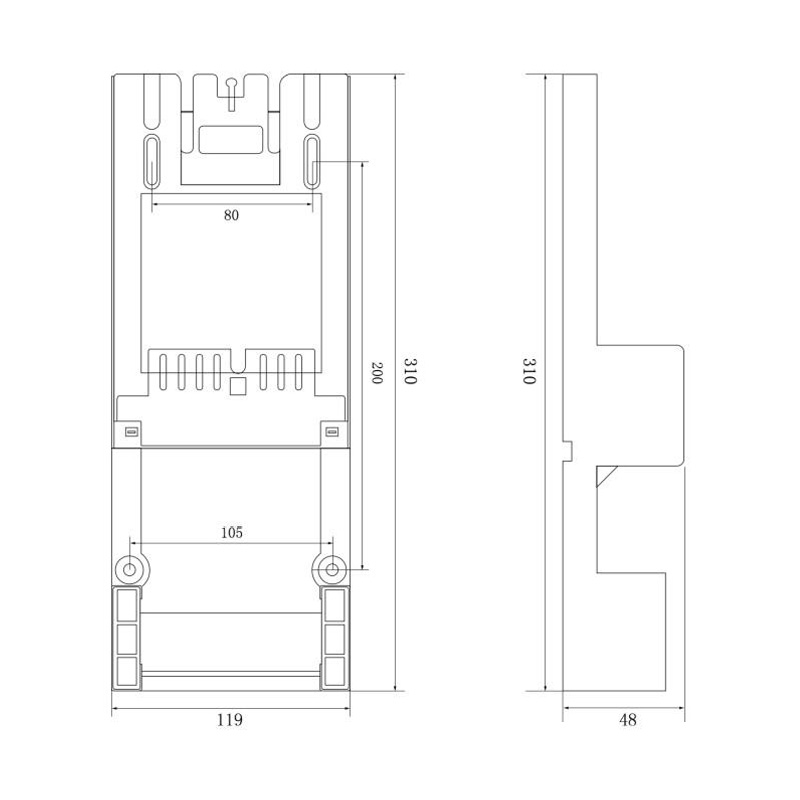
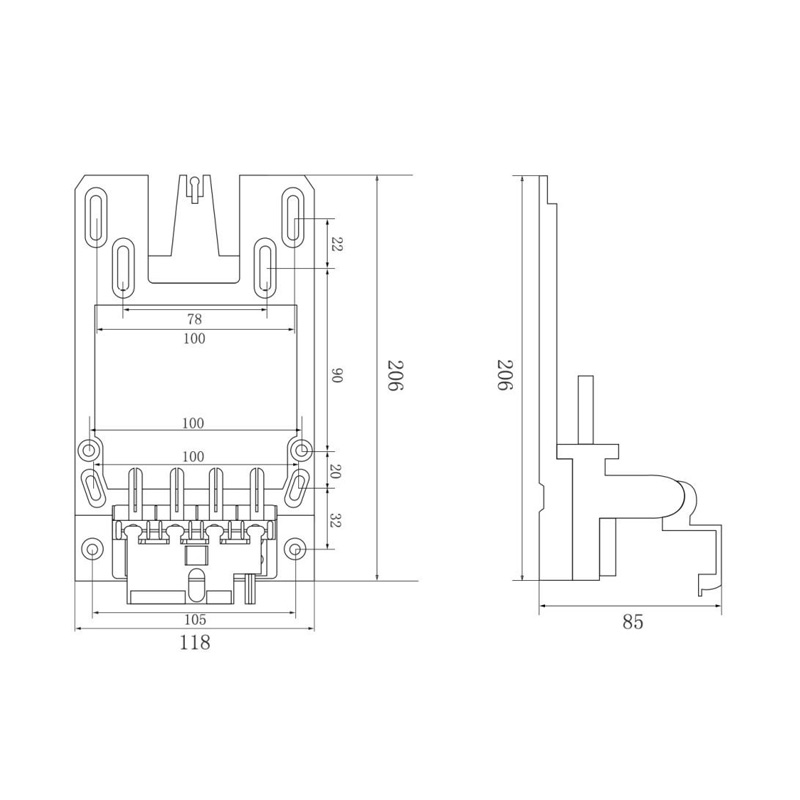
HD-GY01 Watt-Hour Meter Connector
Model:HD-GY01
Single-phase interference watt-hour meter connector
Order number:152399
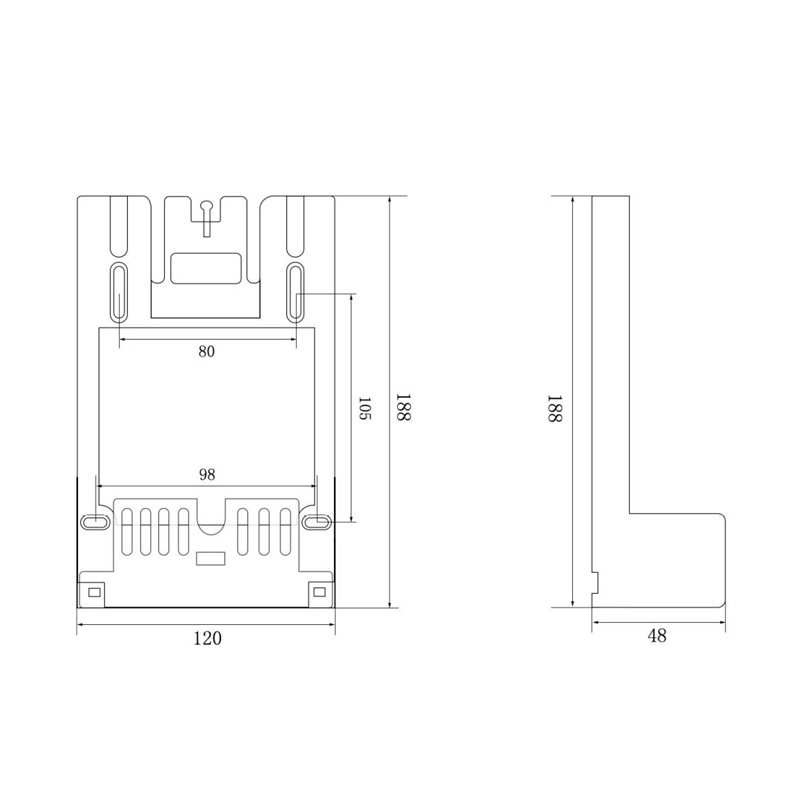
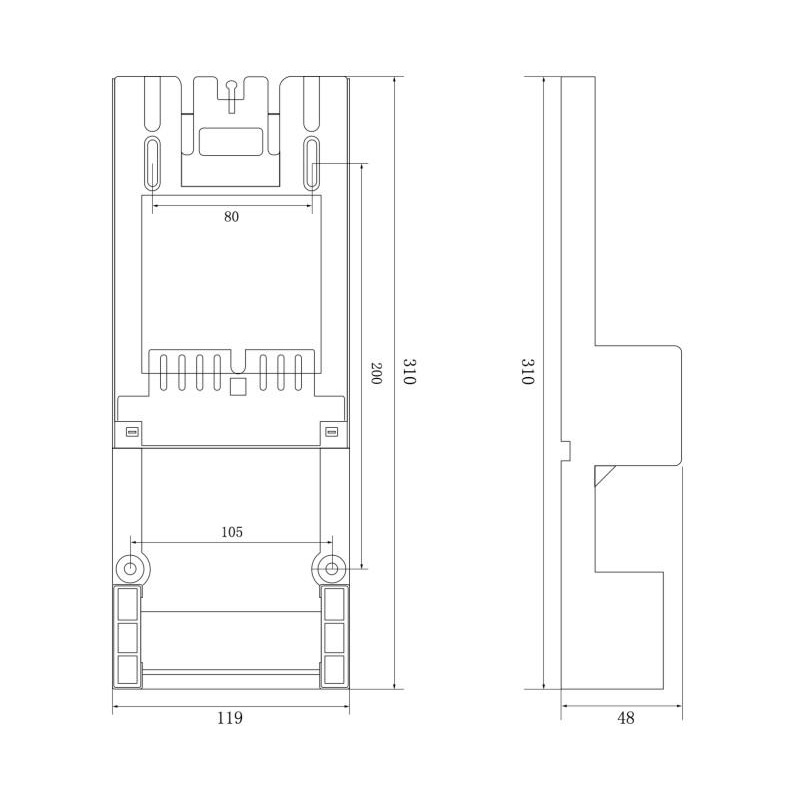
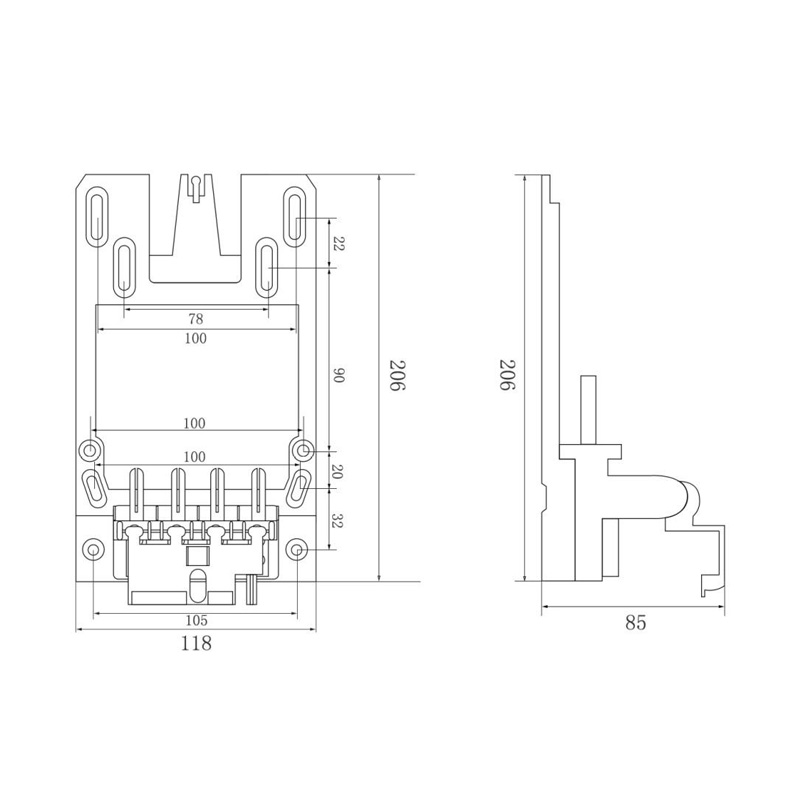
HD-JX01 Watt-Hour Meter Connector
Model:HD-JX01
Single-phase gap watt-hour meter connector
Order number:152400
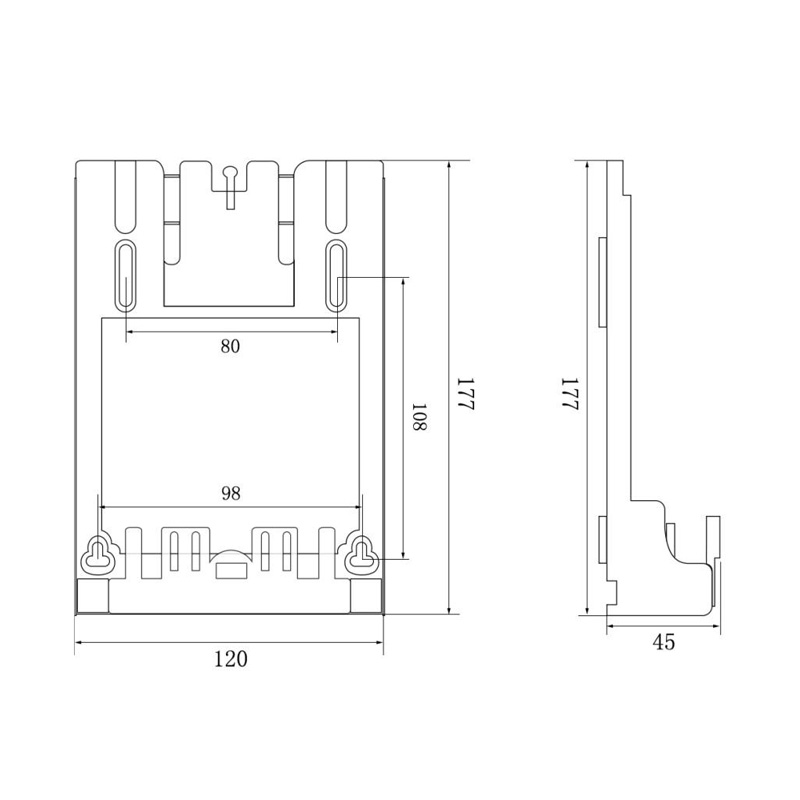
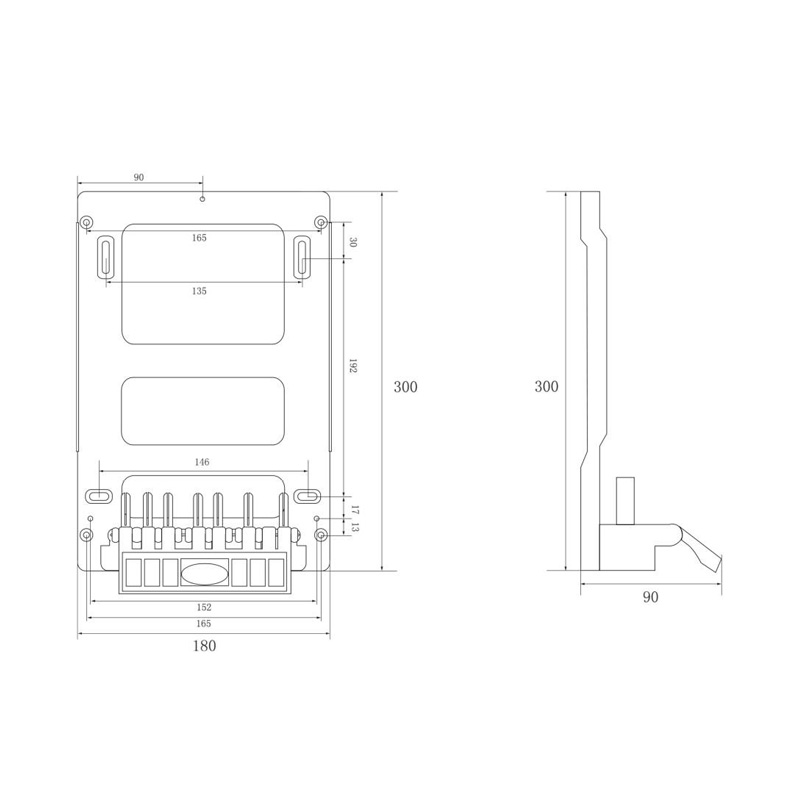
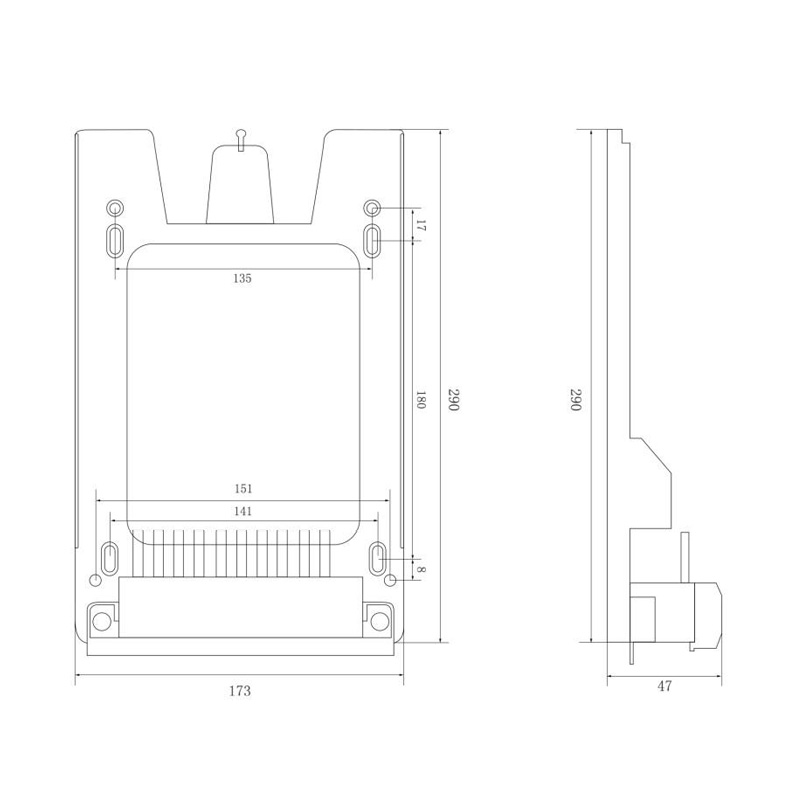
HD-JX01D Watt-Hour Meter Connector
Model:HD-JX01D
Single hole single phase gap watt-hour meter connector
Order number:152401
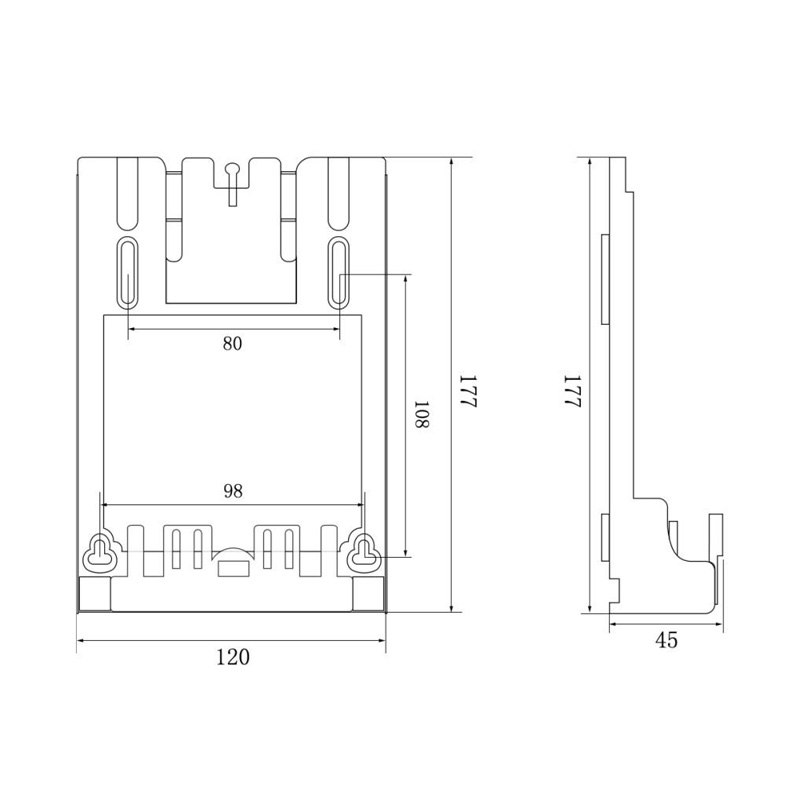
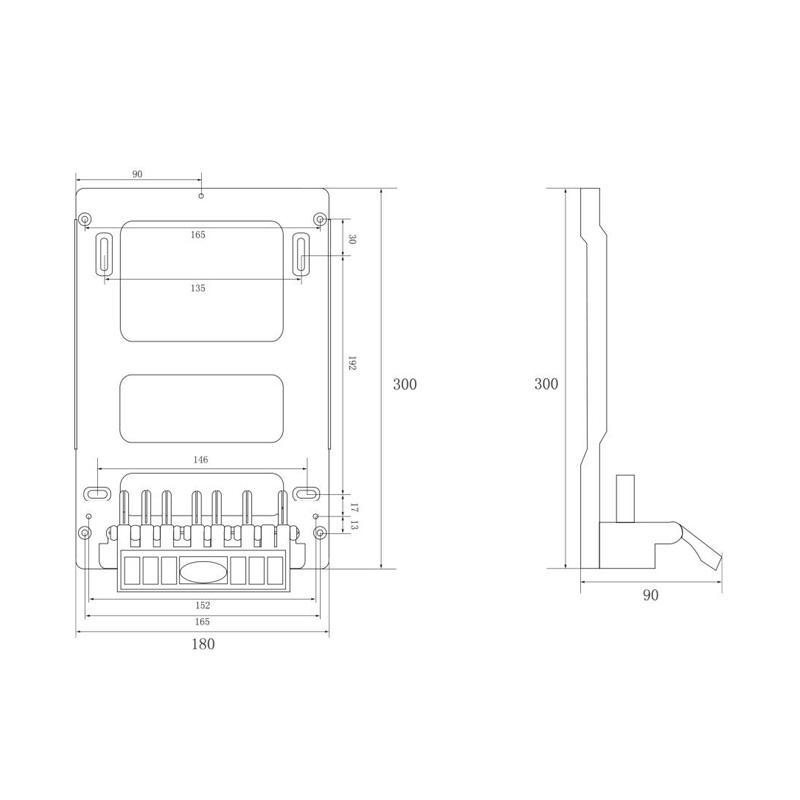
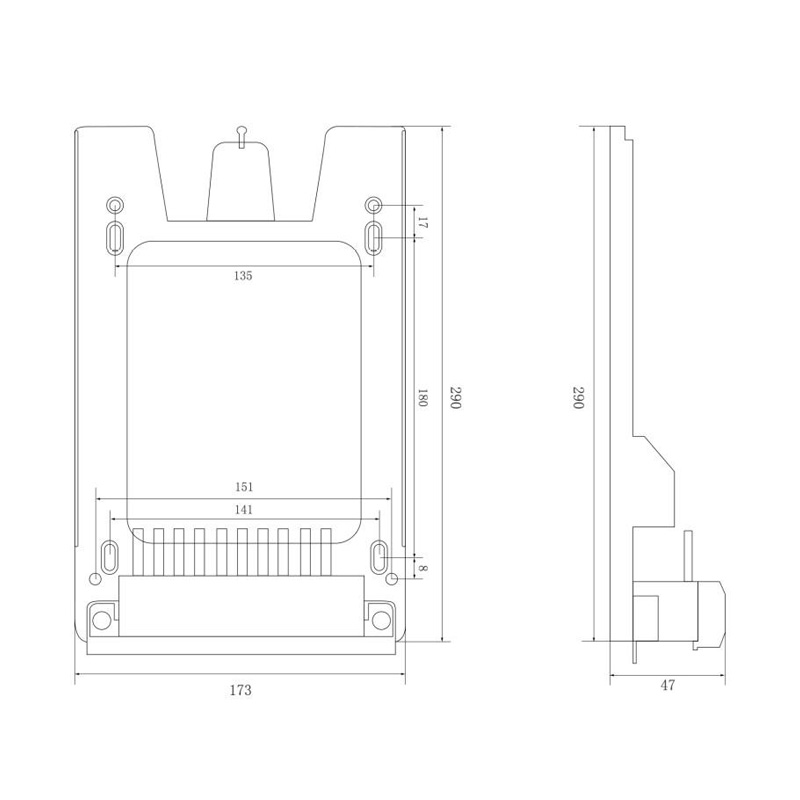
HD-GY01D Watt-Hour Meter Connector
Model:HD-GY01D
Single hole single phase interference watt-hour meter connector
Order number:152402
HD-JX01Y Watt-Hour Meter Connector
Model:HD-JX01Y
Single-phase gap watt-hour meter plug (integrated)
Order number:152403
HD-GY01Y Watt-Hour Meter Connector
Model:HD-GY01Y
Single-phase interference watt-hour meter plug (integrated)
Order number:152404
HD-SC03/60A Watt-Hour Meter Connector
Model:HD-SC03/60A
Three-phase manual watt-hour meter connector
Order number:152405
HD-SC03/80A/100A Watt-Hour Meter Connector
Model:HD-SC03/80A/100A
Three-phase manual watt-hour meter connector
Order number:152406
HD-JY07/60A Watt-Hour Meter Connector
Model:HD-JY07/60A
Single-phase manual watt-hour meter connector
Order number:152408
HD-JY07/100A Watt-Hour Meter Connector
Model:HD-JY07/100A
Single-phase manual watt-hour meter connector
Order number:152409
HD-HGQ03J Watt-Hour Meter Connector
Model:HD-HGQ03J
Three mutual inductance gap type split watt-hour meter connector (without junction box)
Order number:152410
HD-HGQ03Y Watt-Hour Meter Connector
Model:HD-HGQ03Y
Three mutual inductance interference type split watt-hour meter connector (without junction box)
Order number:152411
Search
Categories
-
Energy Measuring Terminal Block(314)
- Energy Measuring Joint Terminal Block(16)
- Polycarbonate Energy Measuring Terminal Block(24)
- Standard Wiring Energy Measuring Terminal Block(4)
- Transparent Shell Energy Measuring Terminal Block(6)
- Multifunctional Test Energy Measuring Terminal Block(10)
- Intelligent Safety Energy Measuring Terminal Block(6)
- Single-Phase Multi-Circuit Output Terminal Block(12)
- Self-Elevating Metering Box Terminal Block(7)
- One Household One-Meter Meter Box Dedicated Terminal Block(56)
- Three-Phase Metering Box Dedicated Terminal Block(24)
- Repeatable Grounding Line Terminal Block(20)
- Terminal Block for One-Inlet Multi-Outlet Metering Box(15)
- Closed Terminal Block(11)
- Heavy Current Terminal Block(48)
- Self-Boosting Terminal Block(5)
- Intelligent Self-Locking Terminal Block(3)
- Tool-Free Crimping Type Terminal Block(5)
- Wide Range of Wire Diameters Terminal Block(5)
- Combined Type Energy Measuring Terminal Block(37)
-
Switch Terminal Block(55)
- Pin-Type Incoming Line Switch Terminal Block(4)
- Multi-Way Connection Switch Terminal Block(4)
- Plug-pin Switch Terminal Block(7)
- Combined Type Switch Terminal Block(7)
- High Contact Cross Section Switch Terminal Block(7)
- Wide Range Switch Terminal Block(11)
- One Way in Switch Terminal Block(12)
- Equipped with Circuit Breaker Switch Terminal(3)
-
Heavy-current Terminal Block(631)
- Modular Building Block Terminal Block(156)
- Spherical Non-Destructive Crimp Terminal(120)
- Dual-Mode Connection Electrical Terminal(90)
- Anti-Electricity-Theft Terminal Block(74)
- Convenient Connection Terminal Block(12)
- High-Contact Section Terminal Block(12)
- Wide Range of Wire Diameters Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Heavy-Current Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Upper and Lower Rows of Neutral Terminal(2)
- Independent Neutral Line Terminal(7)
- Nose-Type Neutral Line Terminal(7)
- Rail Type Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Fixed Neutral Line Terminal(12)
- Double Rail Assembly Electrical Terminal(19)
- Blue Jack-Up Terminal(6)
- Black Base Copper Bar Terminal(5)
- Compact Terminal Block(16)
- Precision Terminal Block(23)
- U-Shaped Harpoon Terminal(2)
- Grounding Metering Box Terminal Block(12)
- High-Performance Terminal Block(19)
- Multifunctional Terminal Block(10)
- Din Rail Terminal Block(76)
- Watt-hour Meter Connector(49)
-
Energy Meter Accessories(116)
-
-
Secure connections are essential for reliable electrical distribution, especially when installing a High-performance Terminal Bloc...
READ MORE -
For engineers and panel builders striving for both efficiency and reliability, wiring errors remain a persistent headache — even w...
READ MORE -
In modern electrical systems, a High-performance Terminal Block plays a critical role in ensuring secure and reliable connections ...
READ MORE -
When building or maintaining electrical systems, one frequently overlooked but critical factor is matching the conductor size to t...
READ MORE -
Effective electrical connections depend on more than simply matching cable sizes. Whether you’re securing a power conductor with a...
READ MORE
What Are the Watt-Hour Meter Connectors and Accessories?
These components bridge the gap between the stationary electrical wiring within a property and the meter, which may need to be installed, removed, or replaced throughout its service life. Without robust and well-designed connectors, the entire metering system would be prone to failures, safety hazards, and inaccurate readings. The category encompasses a variety of parts, each serving a distinct purpose in the overall assembly.
The following table outlines the common types of watt-hour meter connectors and accessories, along with their primary functions and typical composition:
|
Component Name |
Primary Function |
Common Materials & Description |
|
Meter Mounting Sockets |
The base unit installed into the wall or panel that receives the meter itself. It contains the female terminals that make contact with the meter's blades. |
High-temperature thermoplastics or thermosets. Housing contains brass or copper alloy terminals, often tin or silver-plated to reduce oxidation and ensure good conductivity. |
|
Terminal Blocks/Connectors |
The specific internal components within the socket that clamp onto the meter's blades. They are the direct point of electrical contact. |
Phosphor bronze or beryllium copper for spring tension and electrical conductivity. Design is critical for maintaining constant pressure and contact resistance. |
|
Test Switches & Test Blocks |
Devices installed between the meter socket and the utility's current transformers (CTs). They allow utility personnel to safely bypass the meter for testing and calibration without disconnecting live circuits. |
Durable insulating housing with specially designed contacts and shorting mechanisms to prevent open circuits, which are hazardous. |
|
Sealing Rings |
Small, often transparent rings used with a unique wire or clip. They are applied to the meter and socket after installation to provide tamper evidence. |
Plastic or lead. They are designed to be broken if the meter is removed, providing a clear visual indication of unauthorized access. |
|
CT/VT Connectors |
Used in high-capacity installations where Current Transformers (CTs) or Voltage Transformers (VTs) are needed to scale down the current/voltage for the meter to handle. |
Precision-machined terminals and heavy-duty insulating bodies to manage the secondary, low-current signals from the transformers to the meter accurately. |
|
Data & Communication Plugs |
For smart meters, these connectors facilitate the plug-in connection for communication modules (e.g., RF, PLC, or cellular modems) that transmit consumption data. |
Industrial-grade plastic with gold-plated pins for reliable data transmission, allowing for easy module upgrades or replacements. |
What is the Service Life of the Smart Meter Accessories Terminal Connector under Normal Conditions?
The service life of a smart meter accessories terminal connector is a critical consideration for utilities and manufacturers, as it directly impacts the reliability and longevity of the entire metering system. From a manufacturing perspective, this lifespan is not a matter of chance but the result of deliberate engineering choices aimed at matching or exceeding the operational life of the smart meter itself. Under normal conditions, this period is typically designed to be 20 to 25 years or more. This extensive durability is achieved through three fundamental pillars: material selection, mechanical design, and validation testing.
1. Material Selection and Composition
The longevity of the terminal connector is fundamentally rooted in the materials from which it is constructed. The conductive elements are typically crafted from high-performance copper alloys, such as phosphor bronze or beryllium copper. These specific alloys are chosen not only for their electrical conductivity but also for their mechanical properties, including inherent springiness and resistance to fatigue. To combat corrosion and oxidation—which can increase electrical resistance and generate heat over time—these metal components are plated with protective layers like tin or silver. This plating ensures a stable, low-resistance contact surface for the duration of the connector's life. The insulating housing is equally important, made from high-grade, glass-reinforced thermoplastics or thermosets designed to withstand prolonged exposure to heat, UV radiation, and environmental pollutants without degrading, cracking, or becoming brittle.
2. Rigorous Validation and Accelerated Life Testing
Before a terminal connector design is approved for production, it undergoes a battery of rigorous tests designed to simulate decades of service in a condensed timeframe. This accelerated life testing provides empirical data to support the claimed service life. Key tests include:
Thermal Cycling: The connector is subjected to repeated cycles of high and low temperatures to simulate years of daily and seasonal temperature fluctuations, checking for material expansion, contraction, and resulting stress.
Long-Term Heat Aging: Components are held at elevated temperatures significantly above their normal operating range for extended periods to accelerate the aging process of both the metal and plastic parts, verifying they will not degrade prematurely.


 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى