Integrating wired connectivity into the era of automation and digital networking involves more than just traditional hardware. A H...
READ MOREChina TB TC TD Terminal Supplier
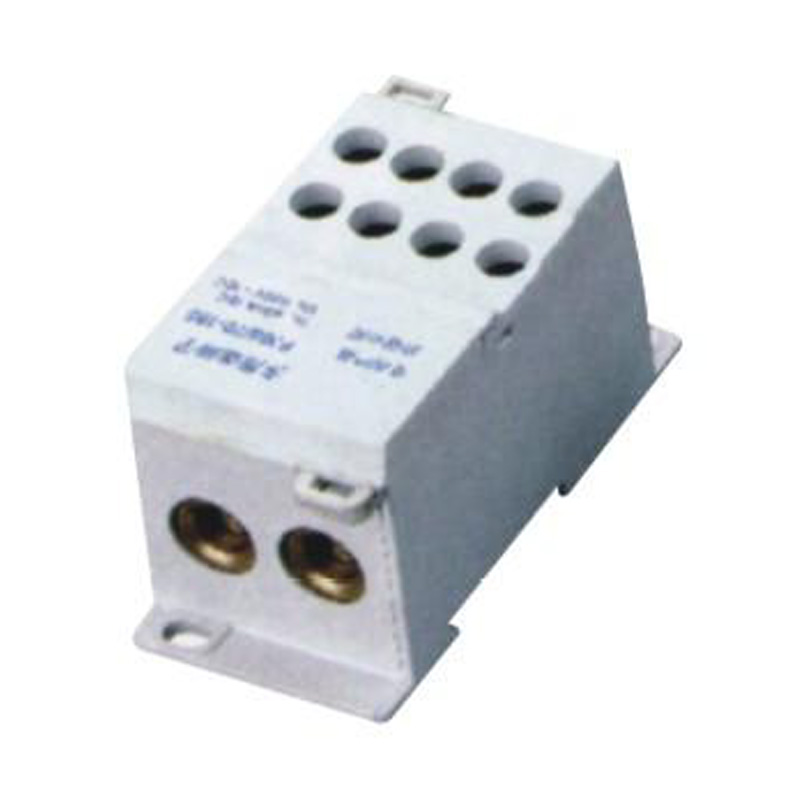
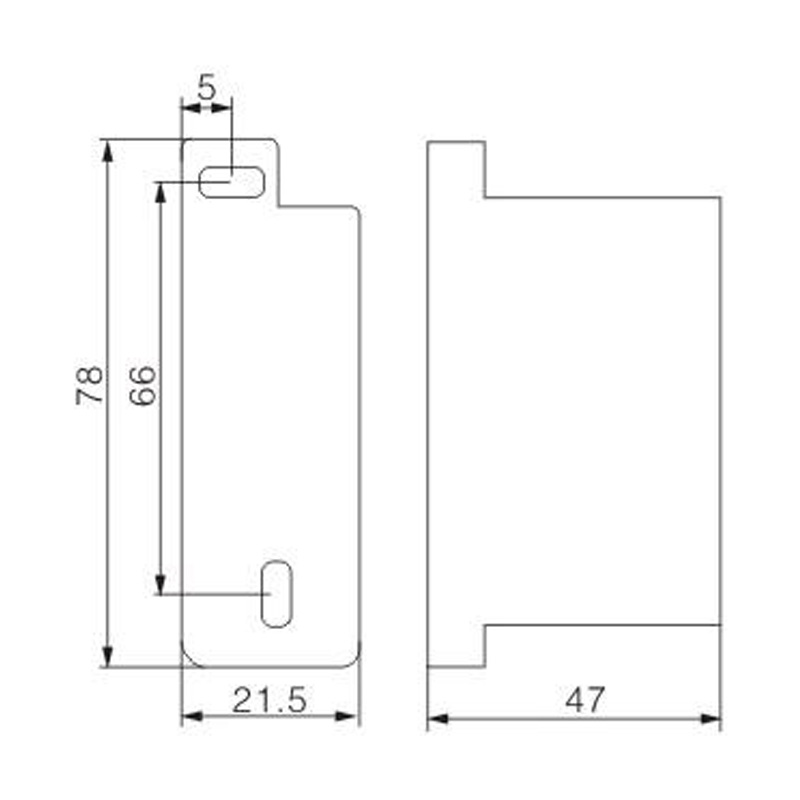
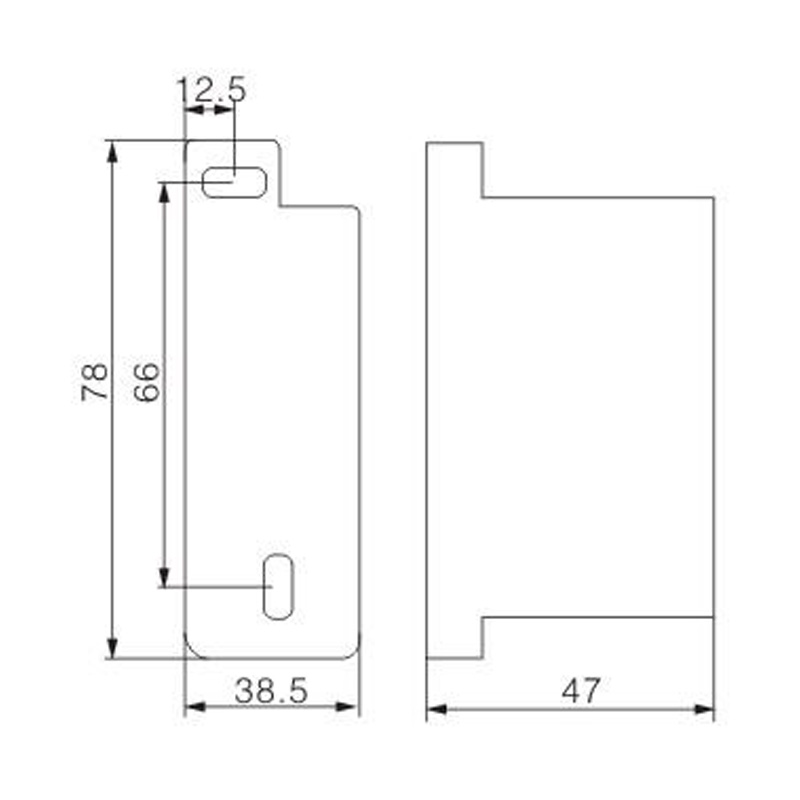
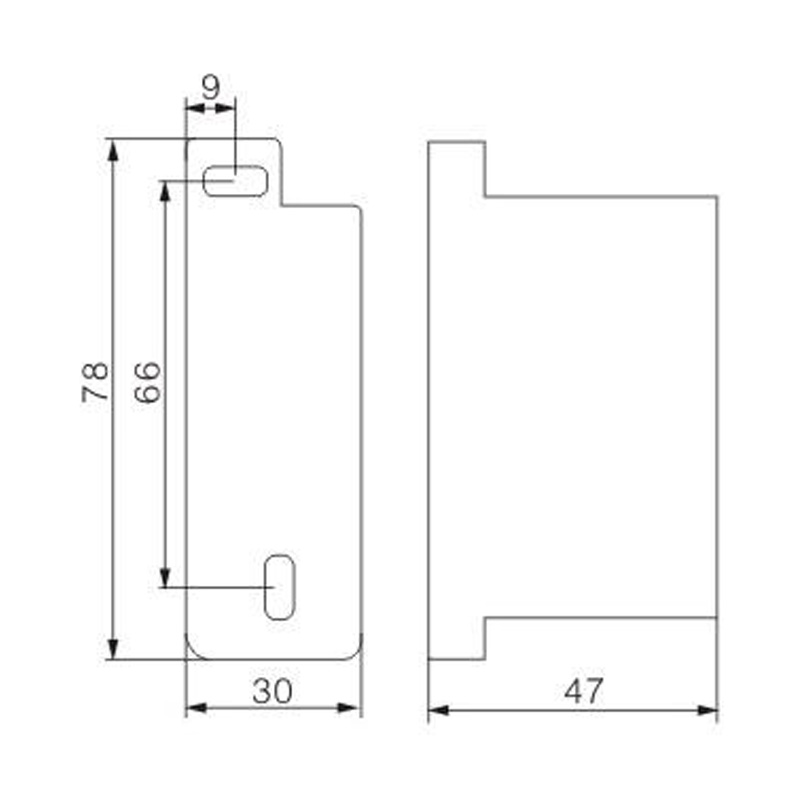
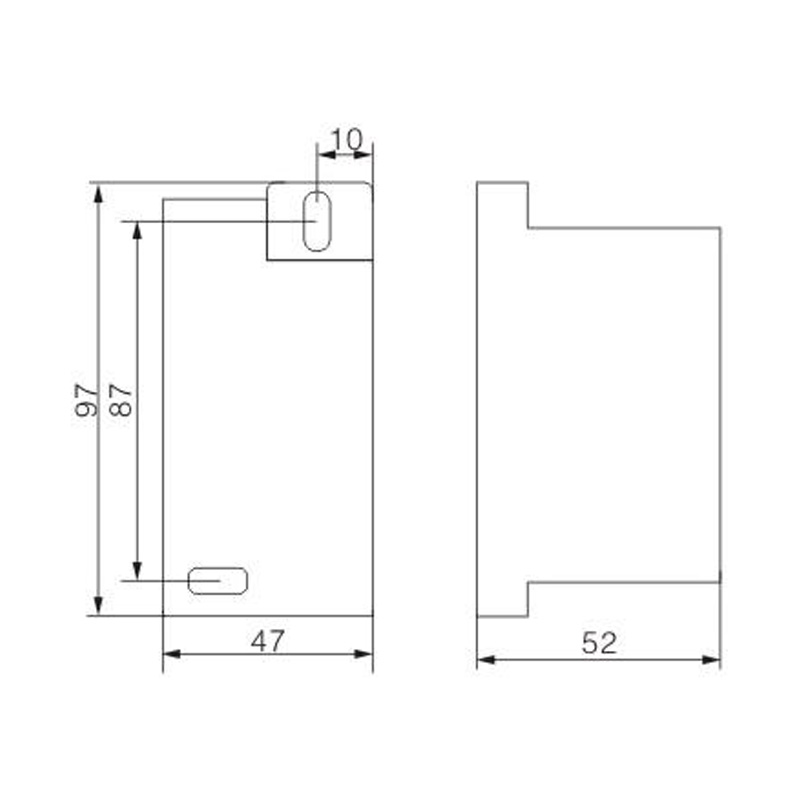
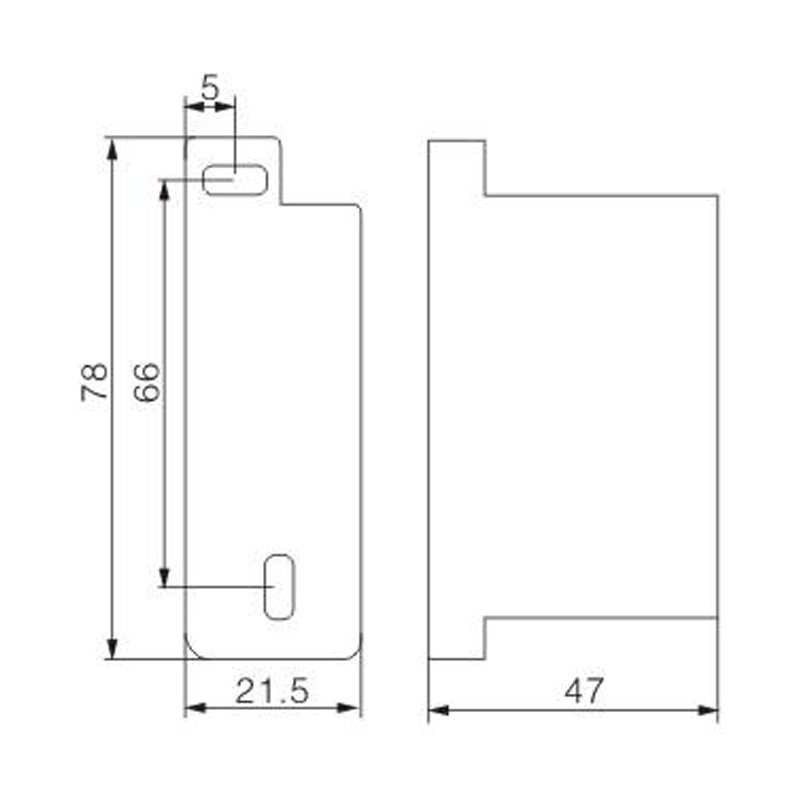
FJ6S-2/50-120/8x25 Elaborate Terminal Block
FJ6S-2/50-120/8x25
Two-inlet,eight-outlet
Inlet wire:50-120mm², outlet wire:6-25mm²
Order number:150686
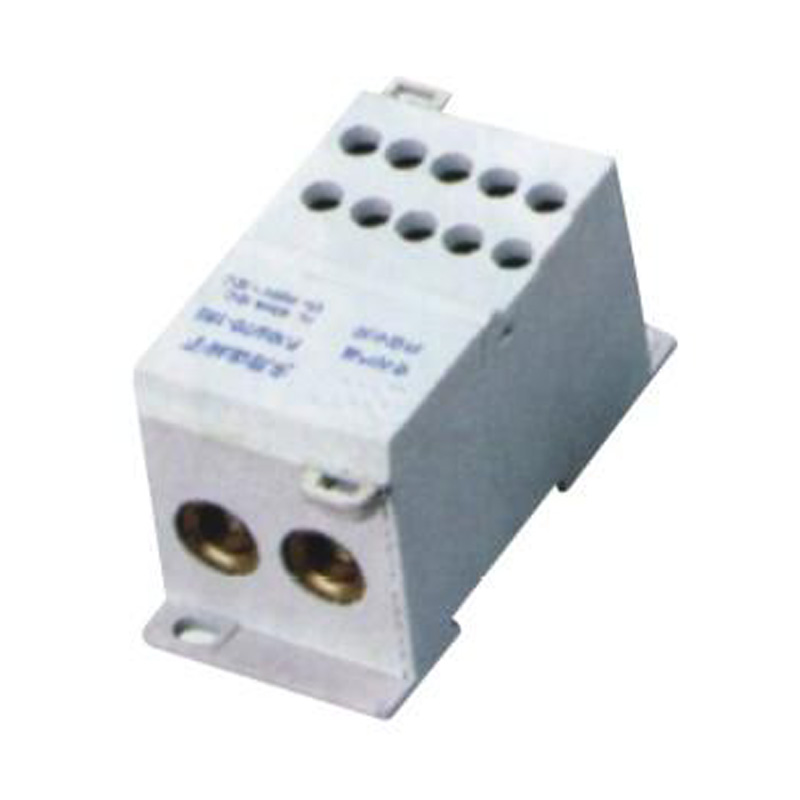
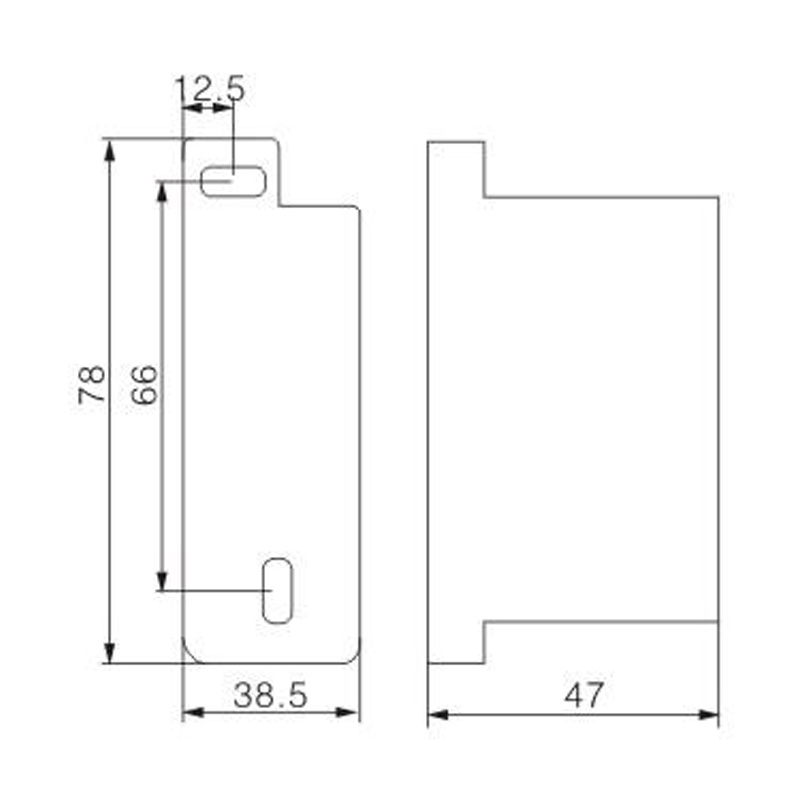
FJ6S-2/50-120/10x16 Elaborate Terminal Block
FJ6S-2/50-120/10x16
Two-inlet,ten-outlet
Inlet wire:50-120mm², outlet wire:6-16mm²
Order number:150687
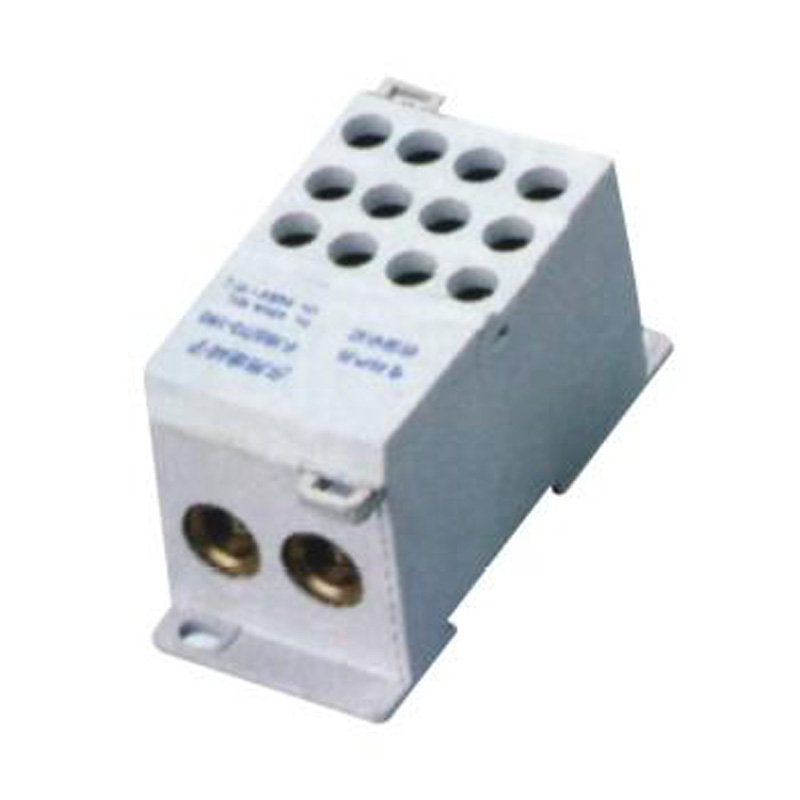
FJ6S-2/50-120/12x 16 Elaborate Terminal Block
FJ6S-2/50-120/12x16
Two-inlet,twelve-outlet
Inlet wire:50-120mm²,outlet wire:6-16mm²
Order number:150688
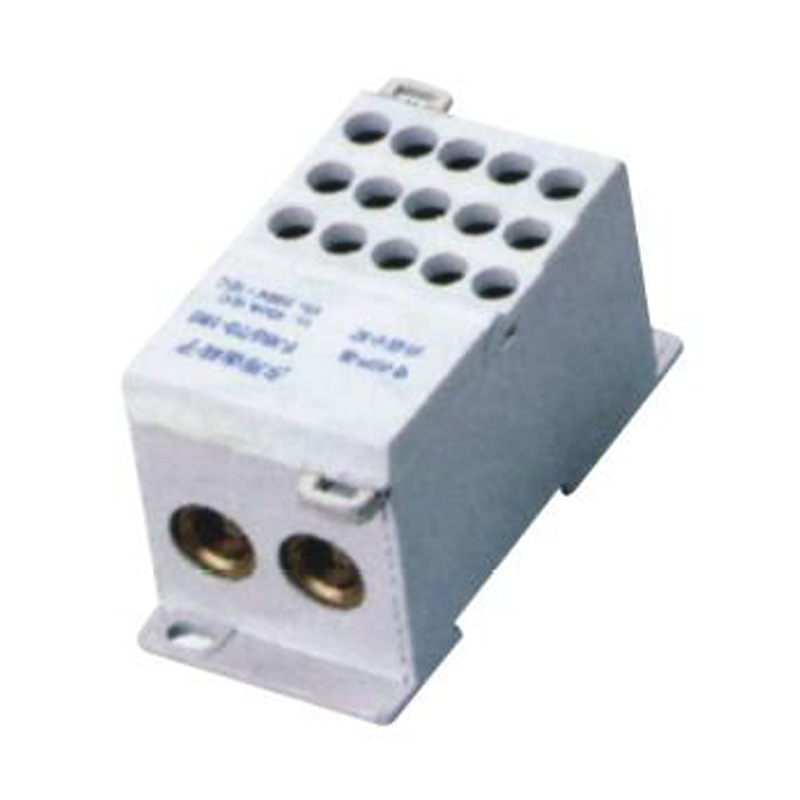
FJ6S-2/50-120/15x16 Elaborate Terminal Block
FJ6S-2/50-120/15x16
Two-inlet,fifteen-outlet
Inlet wire:50-120mm², outlet wire:6-16mm²
Order number:150689
FJ6S-2/50-120/18x10 Elaborate Terminal Block
FJ6S-2/50-120/18x10
Two-inlet,eighteen-outlet
Inlet wire:50-120mm², outlet wire:2.5-10mm²
Order number:150690
FJ6S-2/50-120/21x6 Elaborate Terminal Block
FJ6S-2/50-120/21 x6
Two-inlet,twenty-one-outlet
Inlet wire:50-120mm²,outlet wire:1.5-6mm²
Order number:150691
FJ6S-3/2.5-10/3x10/FJ6S-4/2.5-10/4x10/FJ6S-3/2.5-10/FJ6S-3/2.5-10/9x66x6/
FJ6S-3/2.5-10/3x10
Three-inlet 2.5-10mm²,Three-outlet2.5-10mm²
Order number:150692
FJ6S-4/2.5-10/4x10
Three-inet2.5-10mm²,Four-outlet 2.5-10mm²
Ordernumber:150693
FJ6S-3/2.5-10/6x6
Three-inlet 2.5-10mm²,Six-outlet 1.5-6mm²
Order number:150694
FJ6S-3/2.5-10/9x6
Three-inlet2.5-10mm²,Nine-outlet1.5-6mm²
Order number:150695
FJ6S-3/6-35/3x35
FJ6S-3/6-35/3x35
Three-inlet 6-35mm²,Three-outlet 6-35mm²
Order number:150696
FJ6S-3/6-35/4x25
Three-inet6-35mm²,Four-outlet 6-25mm²
Order number:150697
FJ6S-3/6-35/6x25
Three-inlet 6-35mmv,Six-outlet 6-25mm²
Order number:150698
FJ6S-3/6-35/8x16
Three-inlet6-35mm²,Eight-outlet6-16mm²
Order number:150699
FJ6S-3/6-35/10x16
Three-inlet 6-35mm², Ten-outlet 6-16mm²
Order number:150700
FJ6S-3/6-35/12x6
Three-inlet 6-35mm²,Twelve-outlet 1.5-6mm²
Order number:150701
FJ6S-3/6-35/13x6
Three-inet6-35mm², Thirteen-outlet 1.5-6mm²
Order number:150702
FJ6S-3/6-35/14x6
Three-inlet 6-35mm²,Four-outlet 1.5-6mm²
Order number :150703
FJ6S-3/6-35/15x6
Three-inlet 6-35mm²,Fifteen-outlet 1.5-6mm²
Order number:150704
FJ6S-3/6-25/3x25
FJ6S-3/6-25/3x25
Three-inlet6-25mm²,Three-outlet 6-25mm²
Order number:150705
FJ6S-3/6-25/4x25
Three-inet6-25mm²,Four-outlet 6-25mm²
Order number:150706
FJ6S-3/6-25/6x16
Three-inlet 6-25mm², Six-outlet 6-16mm²
Order number:150707
FJ6S-3/6-25/9x10
Three-inlet 6-25mm²,Nine-outlet 2.5-10mm²
Order number:150708
FJ6S-3/6-25/12x6
Three-inlet6-25mm²,Twelve-outletine-outlet1.5-6mm²
Order number:150709
FJ6S-3/16-50/3x50
FJ6S-3/16-50/3x50
Three-inlet 16-50mm²,Three-outlet 16-50mm²
Order number:150710
FJ6S-3/16-50/4x35
Three-inet16-50mm²,Four-outlet 6-35mm²
Order number:150711
FJ6S-3/16-50/6x25
Three-inlet 16-50mm², Six-outlet 6-25mm²
Order number:150712
FJ6S-3/16-50/8x25
Three-inlet 16-50mm², Eight-outlet 6-25mm²
Order number:150713
FJ6S-3/16-50/10x 16
Three-inlet 16-50mm²,Ten-outlet 6-16mm²
Order number:150714
FJ6S-3/16-50/12x16
Three-inlet16-50mm²,Twelve-outlet 6-16mm²
Order number:150715
FJ6S-3/16-50/15x16
Three-inet16-50mm²,Ffiteen-outlet 6-16mm²
Ordernumber:150716
FJ6S-3/16-50/18x10
Three-inlet 16-50mm², Eifhteen-outlet 2.5-10mm²
Order number:150717
FJ6S-3/16-50/21x6
Three-inlet 16-50mm², Twety-one-outlet 1.5-6mm²
Order number:150718
FJ6S-4/2.5-10/4x10
FJ6S-4/2.5-10/4x10
Four-inlet2.5-10mm²,Four-outlet2.5-10mm²
Ordernumber:150719
FJ6S-4/2.5-10/6x6
Four-inet2.5-10mm²,six-outlet 1.5-6mm²
Order number:150720
FJ6S-4/2.5-10/9x6
Four-inlet 2.5-10mm²,Nine-outlet 1.5-6mm²
Order number:150721
FJ6S-4/6-25/4x25
FJ6S-4/6-25/4x25
Four-inlet 6-25mm²,Four-outlet 6-25mm²
Order number:150722
FJ6S-4/6-25/6x25
Four-inet6-25mm²,Six-outlet 6-25mm²
Order number:150723
FJ6S-4/6-25/8x16
Four-inlet 6-50mm²,Eighr-outlet 6-16mm²
Order number:150724
FJ6S-4/6-25/10x6
Four-inlet6-25mm²,Ten-outlet 1.5-6mm²
Order number:150725
FJ6S-4/6-25/12x6
Four-inlet 6-25mm²,Twelve-outlet 1.5-6mm²
Order number:150726
FJ6S-4/6-25/13x6
Four-inet6-25mm², Thirteen-outlet 1.5-6mm²
Order number:150727
FJ6S-4/6-25/14x6
Four-inlet 6-25mm², Fourteen-outlet 1.5-6mm²
Order number:150728
FJ6S-4/6-25/15x6
Four-inlet 6-25mm²,Fifteen-outlet 1.5-6mm²
Order number:150729
Search
Categories
-
Energy Measuring Terminal Block(314)
- Energy Measuring Joint Terminal Block(16)
- Polycarbonate Energy Measuring Terminal Block(24)
- Standard Wiring Energy Measuring Terminal Block(4)
- Transparent Shell Energy Measuring Terminal Block(6)
- Multifunctional Test Energy Measuring Terminal Block(10)
- Intelligent Safety Energy Measuring Terminal Block(6)
- Single-Phase Multi-Circuit Output Terminal Block(12)
- Self-Elevating Metering Box Terminal Block(7)
- One Household One-Meter Meter Box Dedicated Terminal Block(56)
- Three-Phase Metering Box Dedicated Terminal Block(24)
- Repeatable Grounding Line Terminal Block(20)
- Terminal Block for One-Inlet Multi-Outlet Metering Box(15)
- Closed Terminal Block(11)
- Heavy Current Terminal Block(48)
- Self-Boosting Terminal Block(5)
- Intelligent Self-Locking Terminal Block(3)
- Tool-Free Crimping Type Terminal Block(5)
- Wide Range of Wire Diameters Terminal Block(5)
- Combined Type Energy Measuring Terminal Block(37)
-
Switch Terminal Block(55)
- Pin-Type Incoming Line Switch Terminal Block(4)
- Multi-Way Connection Switch Terminal Block(4)
- Plug-pin Switch Terminal Block(7)
- Combined Type Switch Terminal Block(7)
- High Contact Cross Section Switch Terminal Block(7)
- Wide Range Switch Terminal Block(11)
- One Way in Switch Terminal Block(12)
- Equipped with Circuit Breaker Switch Terminal(3)
-
Heavy-current Terminal Block(631)
- Modular Building Block Terminal Block(156)
- Spherical Non-Destructive Crimp Terminal(120)
- Dual-Mode Connection Electrical Terminal(90)
- Anti-Electricity-Theft Terminal Block(74)
- Convenient Connection Terminal Block(12)
- High-Contact Section Terminal Block(12)
- Wide Range of Wire Diameters Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Heavy-Current Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Upper and Lower Rows of Neutral Terminal(2)
- Independent Neutral Line Terminal(7)
- Nose-Type Neutral Line Terminal(7)
- Rail Type Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Fixed Neutral Line Terminal(12)
- Double Rail Assembly Electrical Terminal(19)
- Blue Jack-Up Terminal(6)
- Black Base Copper Bar Terminal(5)
- Compact Terminal Block(16)
- Precision Terminal Block(23)
- U-Shaped Harpoon Terminal(2)
- Grounding Metering Box Terminal Block(12)
- High-Performance Terminal Block(19)
- Multifunctional Terminal Block(10)
- Din Rail Terminal Block(76)
- Watt-hour Meter Connector(49)
-
Energy Meter Accessories(116)
-
-
Secure connections are essential for reliable electrical distribution, especially when installing a High-performance Terminal Bloc...
READ MORE -
For engineers and panel builders striving for both efficiency and reliability, wiring errors remain a persistent headache — even w...
READ MORE -
In modern electrical systems, a High-performance Terminal Block plays a critical role in ensuring secure and reliable connections ...
READ MORE -
When building or maintaining electrical systems, one frequently overlooked but critical factor is matching the conductor size to t...
READ MORE -
Effective electrical connections depend on more than simply matching cable sizes. Whether you’re securing a power conductor with a...
READ MORE
How to Use Connector Terminals?
1. Core Principles: Safety!
Before you touch any wires, always follow these rules:
Power Off: Always disconnect power at the source before making or modifying any connections. Verify with a multimeter or voltage tester that the circuit is dead.
Right Tool for the Job: Using the proper tools (wire strippers, crimpers, screwdrivers) is not just a recommendation—it's essential for a safe connection.
Match the Specifications: Ensure the terminal is rated for the voltage and current (amps) of your circuit. Using an under-rated terminal is a fire hazard.
Secure Connections: Loose connections cause arcing, heat buildup, and failure. Tug on the wire after connecting to ensure it's secure.
2. Common Types of Connector Terminals & How to Use Them
Here's a breakdown of the frequently encountered terminals.
A. Screw Terminals
These are very common in household outlets, light switches, industrial control panels, and many consumer electronics.
How They Work: A screw clamps down on a wire (either bare or with a ferrule) to make a connection.
How to Use:
Strip the Wire: Strip about 3/4" (10-12mm) of insulation from the wire.
Prepare the Wire (Recommended): For stranded wire, always use a ferrule or twist the strands neatly clockwise and tin them with a small amount of solder to prevent fraying. (Note: Some experts advise against soldering for screw terminals under vibration, as it can make the wire brittle. A ferrule is often the solution.)
- Loosen the Screw: Turn the screw counterclockwise until there is enough space to insert the wire.
- Insert the Wire: Place the bare wire under the screw terminal plate or into the insertion hole.
- Tighten the Screw: Tighten the screw firmly clockwise. Do not overtighten, as this can strip the screw threads or cut the wire.
- Tug Test: Gently pull on the wire to ensure it is held fast.
B. Crimp Terminals (Spade, Ring, Butt Splices)
These are ubiquitous in automotive, appliance, and low-voltage DC wiring. They require a special tool called a crimper.
Types:
Spade (Fork) Terminal: Easy to connect and disconnect. Good for spaces where a ring terminal won't fit.
Ring Terminal: Provides the secure, permanent connection. The screw is completely captured, preventing it from slipping out.
Butt Splice: Used to connect two wires end-to-end.
Pin Terminal: Used in plastic housing connectors (e.g., Molex, JST).
How to Use (The Crimping Process):
Strip the Wire: Strip a length of insulation that matches the metal barrel of the terminal.
Select the Correct Size: Terminals and crimpers are sized by wire gauge (e.g., 22-16 AWG) and stud size (e.g., #8, 1/4"). Match them correctly.
Insert and Crimp:
Place the metal barrel of the terminal into the correctly sized slot on your crimping tool.
Insert the bare wire into the barrel until it is flush with the end.
Squeeze the crimper handles with firm, even pressure until it releases or fully closes.
The crimp should be tight and uniform, not smashed or crooked.
What Are the Differences Between TB, TC, and TD Terminals?
When choosing between different types of terminals, how do TB, TC, and TD varieties compare? Could a simple table clarify their main distinctions?
| Terminal Type | Main Function | Typical Use Case | Key Feature |
| TB (Terminal Block) | Provides a base for multiple wire connections | Control panels, distribution boards | Modular structure for neat arrangement |
| TC (Terminal Connector) | Connects two or more conductors directly | Wiring in appliances or small circuits | Simple and compact design |
| TD (Terminal Distribution) | Distributes one input to several outputs | Power distribution systems | Efficient splitting of circuits |
Is the FJ6 Terminal Suitable for 240V?
When considering voltage ratings, how can one determine whether a specific terminal, such as the FJ6, is suitable for 240V systems? Does it depend on the manufacturer's specification, the material, and the design?
Is it important to verify the rated voltage and current capacity of the FJ6 terminal before installation? If the FJ6 is generally rated for household and light industrial applications, could it be expected to handle 240V under normal conditions? Yet, should one also ask whether environmental factors, such as humidity, dust, or heat, might affect its performance?
Would it be reasonable to compare the FJ6 terminal to other commonly used terminals to see how it performs under similar voltage levels? If the insulation material is of sufficient quality and the clamping mechanism is firm, might it support safe operation at 240V? Conversely, if the wire gauge is incompatible or the terminal is improperly tightened, could that overheating or reduced reliability?
Should electricians or technicians consult the product datasheet before using the FJ6 terminal in 240V circuits? Could compliance with local electrical standards serve as a guide in confirming suitability? Ultimately, is it fair to say that the FJ6 terminal can be considered suitable for 240V if used within its rated specifications and installed according to proper practices?


 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى