Integrating wired connectivity into the era of automation and digital networking involves more than just traditional hardware. A H...
READ MORERepeatable Grounding Line Terminal Block Manufacturer
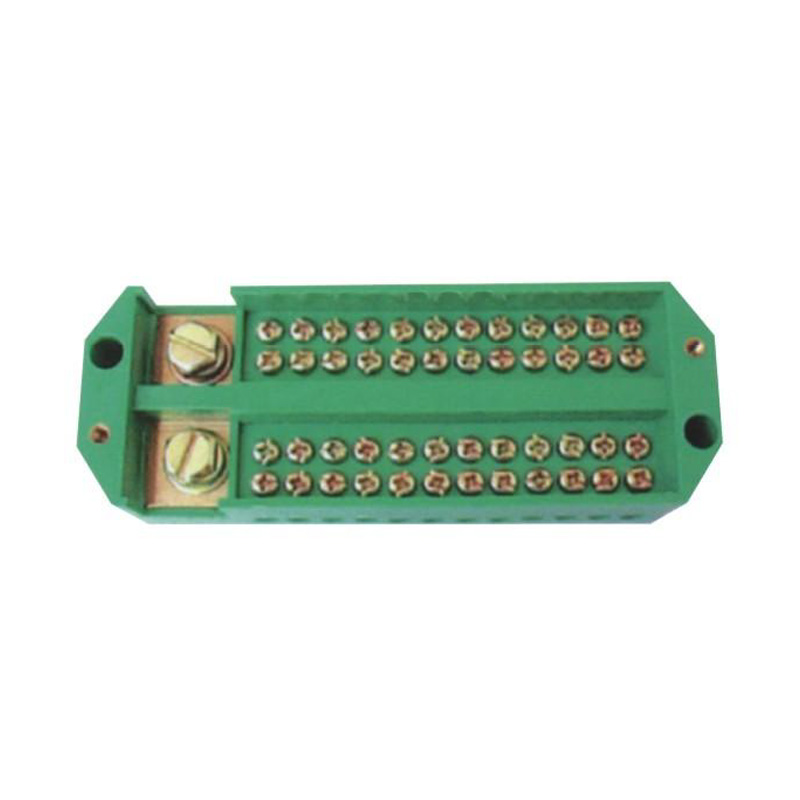
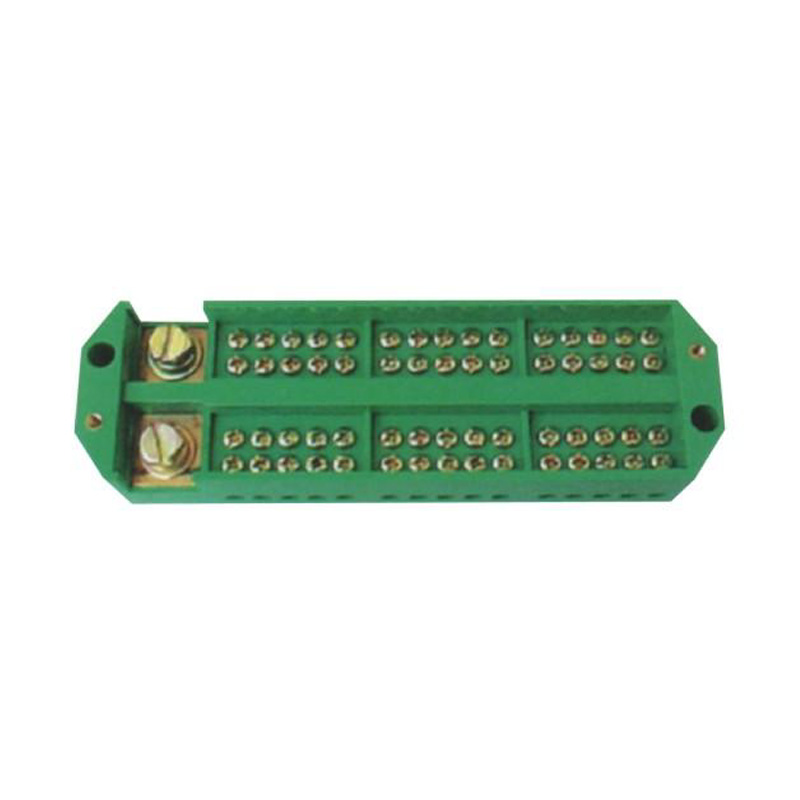
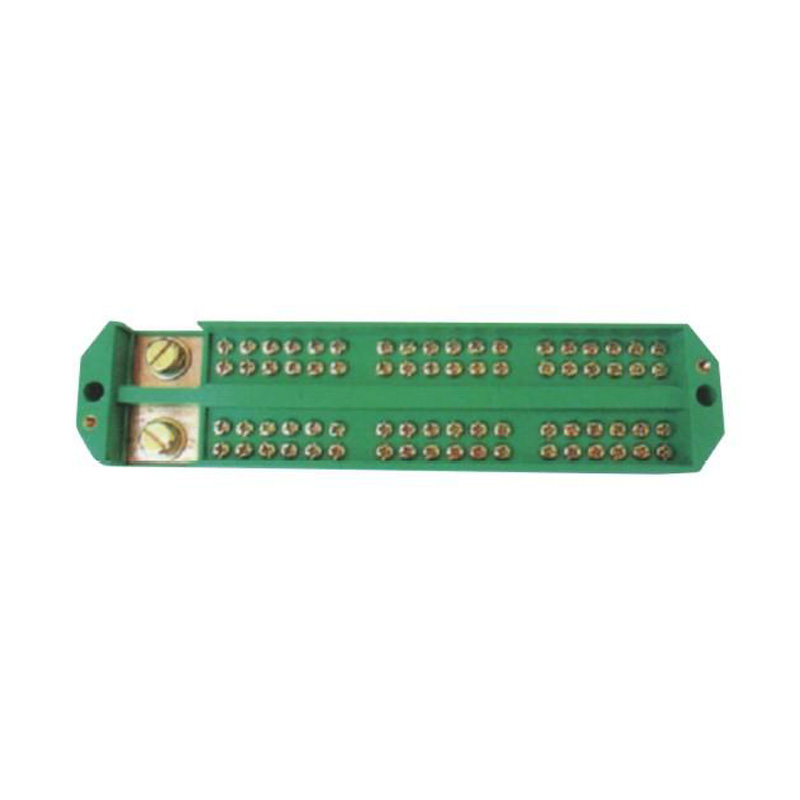
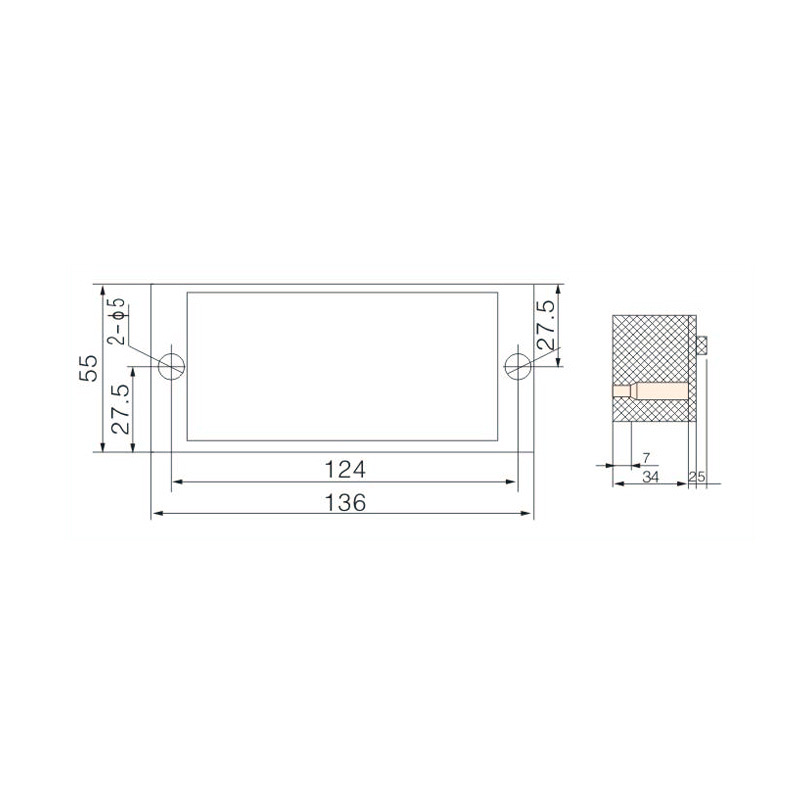
Repeatable Grounding Line Terminal Blocks are professionally used for grounding connections in electrical systems, control panels, and distribution boards, and are specifically designed to provide reliable and consistent grounding points. These terminal blocks are ideal for wiring in electrical installations where multiple grounding points are required to ensure electrical safety and system stability. The insulation voltage is 690V, and the rated voltage is 380V. These grounding terminal blocks feature a secure and stable connection design, without the need for excessive wiring or additional conductors. They are currently a novel product offering a convenient and highly reliable solution for repeatable grounding connections in various electrical applications.
The Repeatable Grounding Line Terminal Block allows for multiple connections and disconnections without compromising the integrity of the electrical connections. This feature is crucial in environments where frequent testing and maintenance are required, ensuring that the connections remain secure and reliable over time.
Constructed from high-quality materials, the Repeatable Grounding Line Terminal Block is designed to withstand harsh conditions and resist corrosion. This durability ensures that the box maintains its structural integrity even in challenging environments, such as outdoor installations or industrial settings.
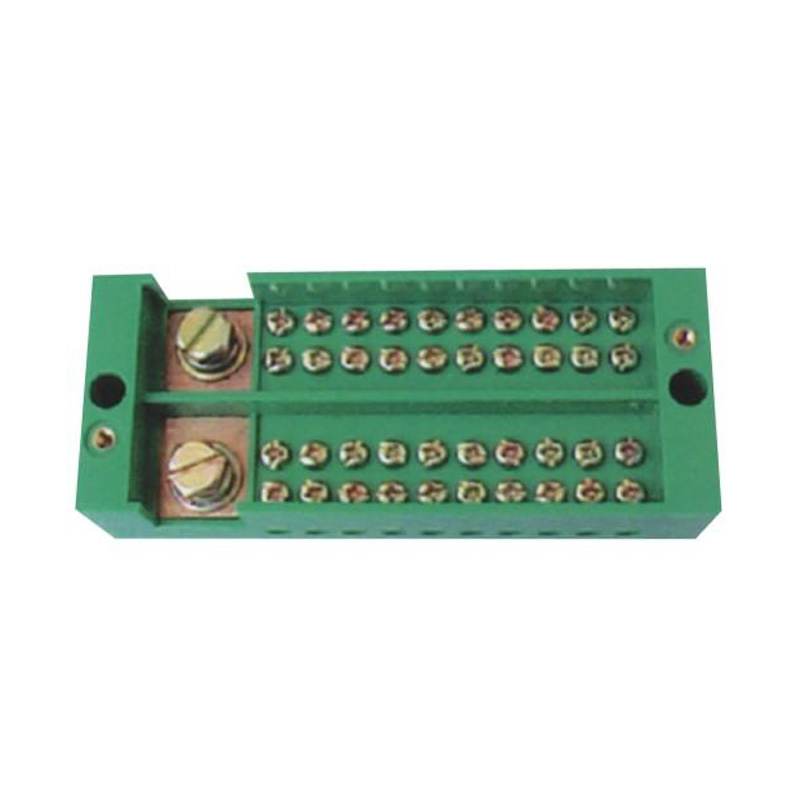
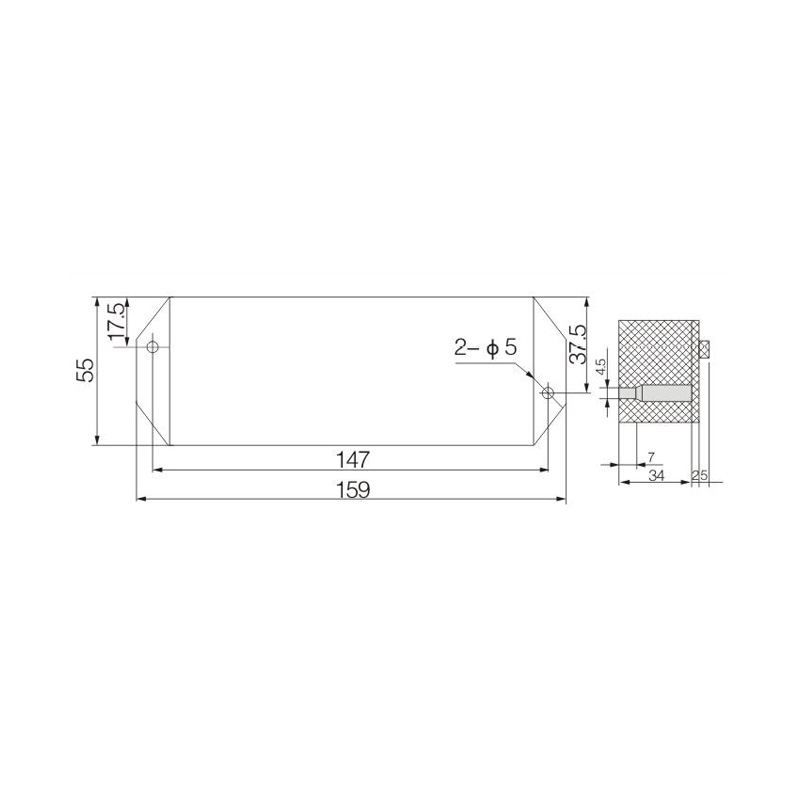
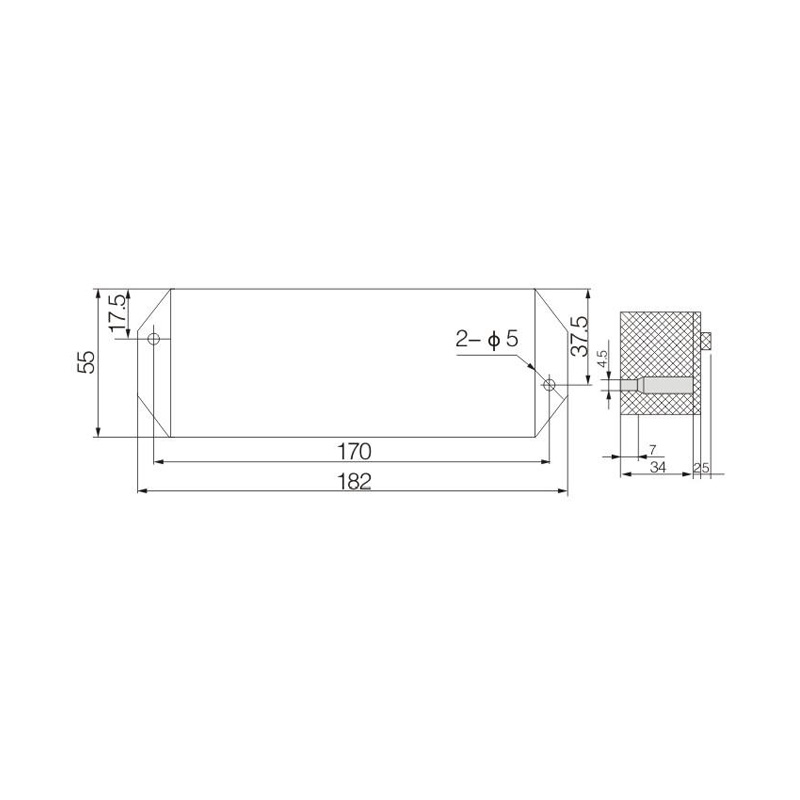
FJ6/JHD-3/B Twenty-Circuit Neutral Line Box
Model:FJ6/JHD-3/b
Product name: Twenty-circuit neutral line box
Order number: OrderNo.150178
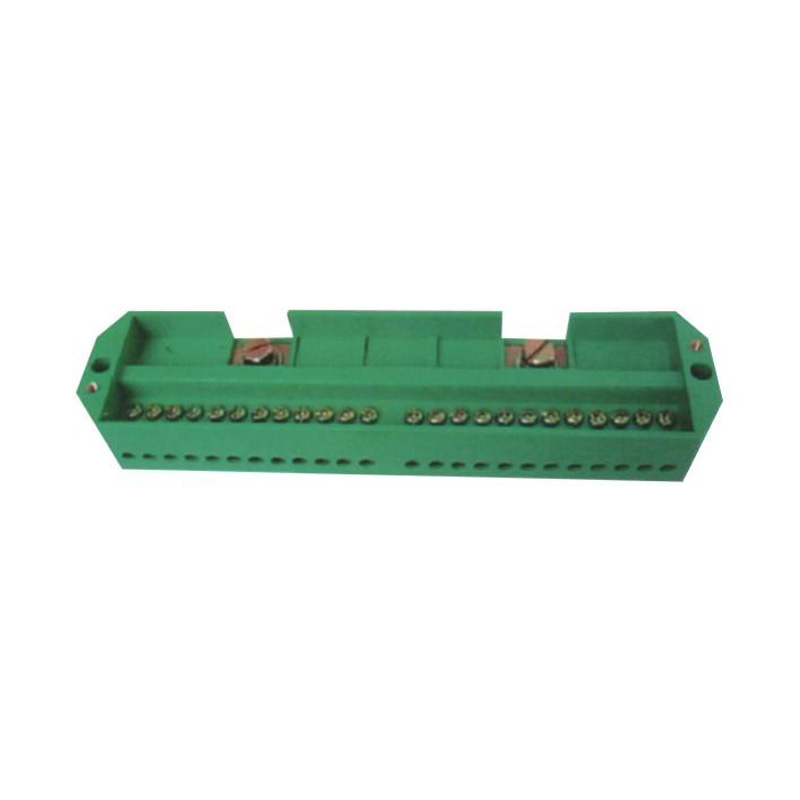
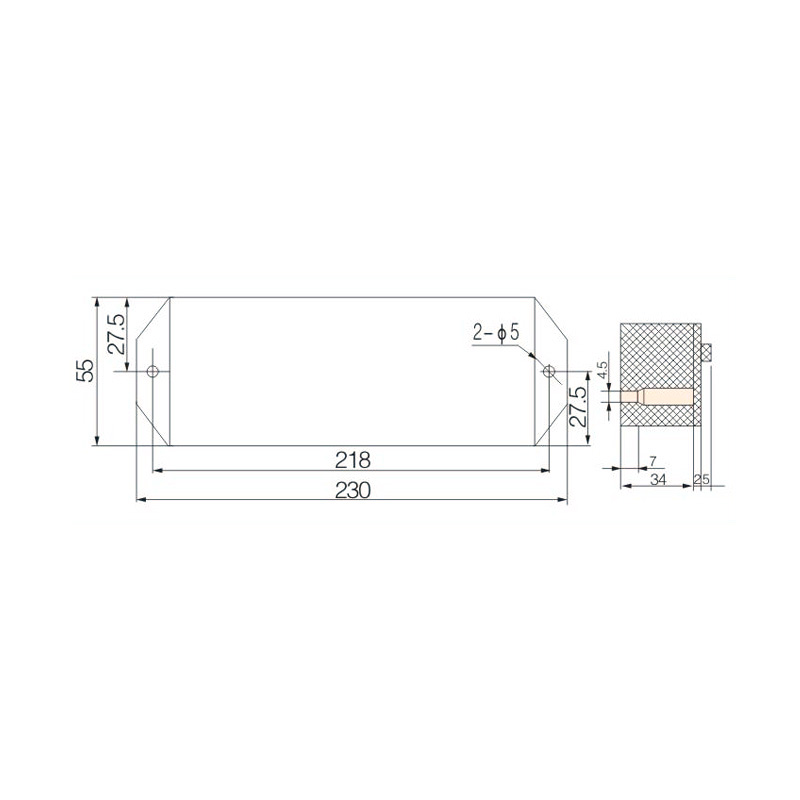
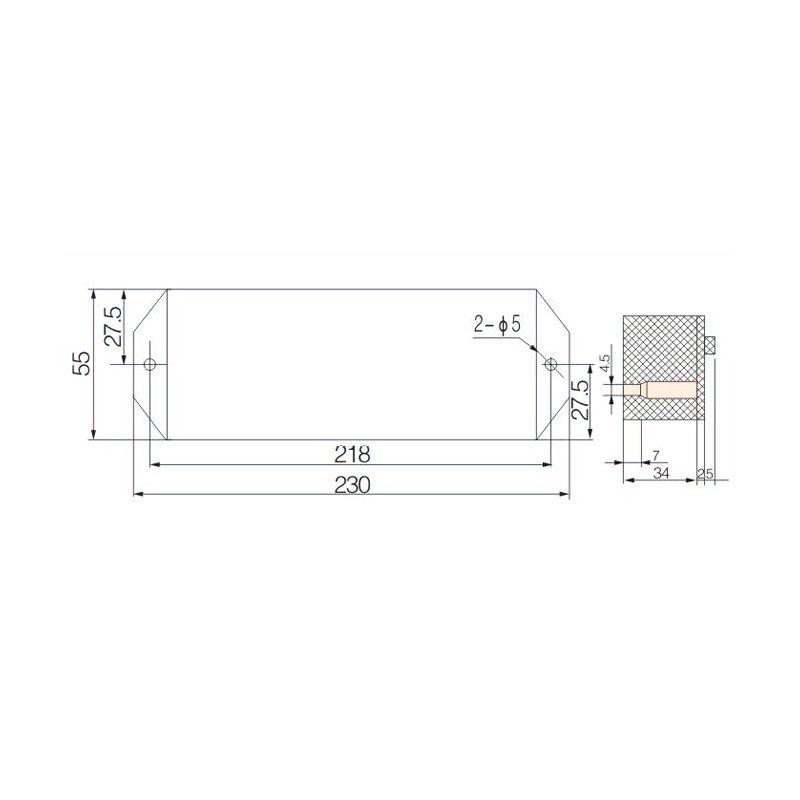
FJ6/JHD-3/C Twenty-Four-Circuit Neutral Line Box
Model:FJ6/JHD-3/c
Product name: Twenty-four-circuit neutral line box
Order number: OrderNo.150179
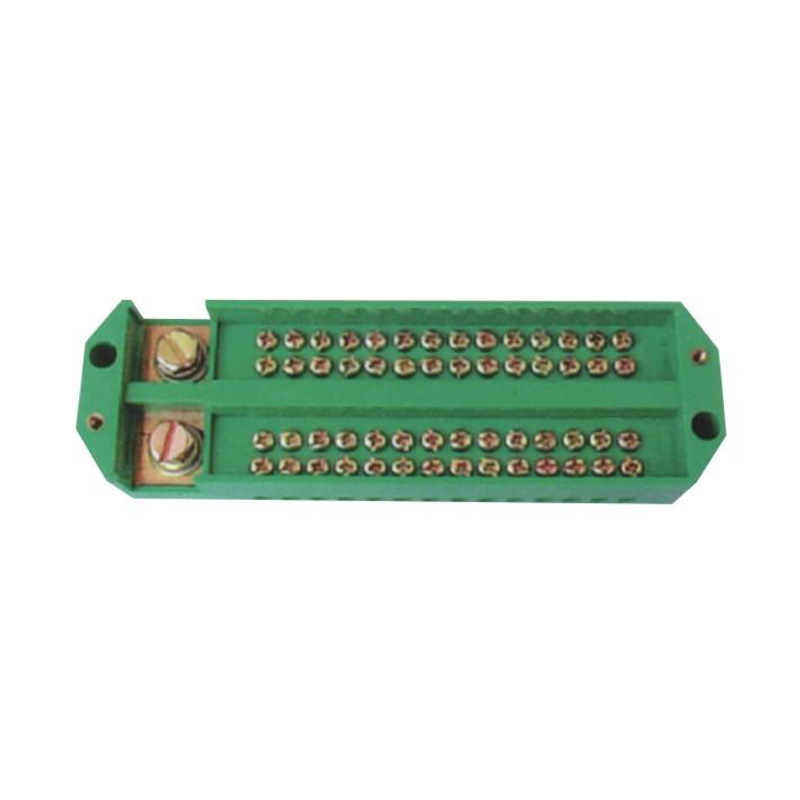
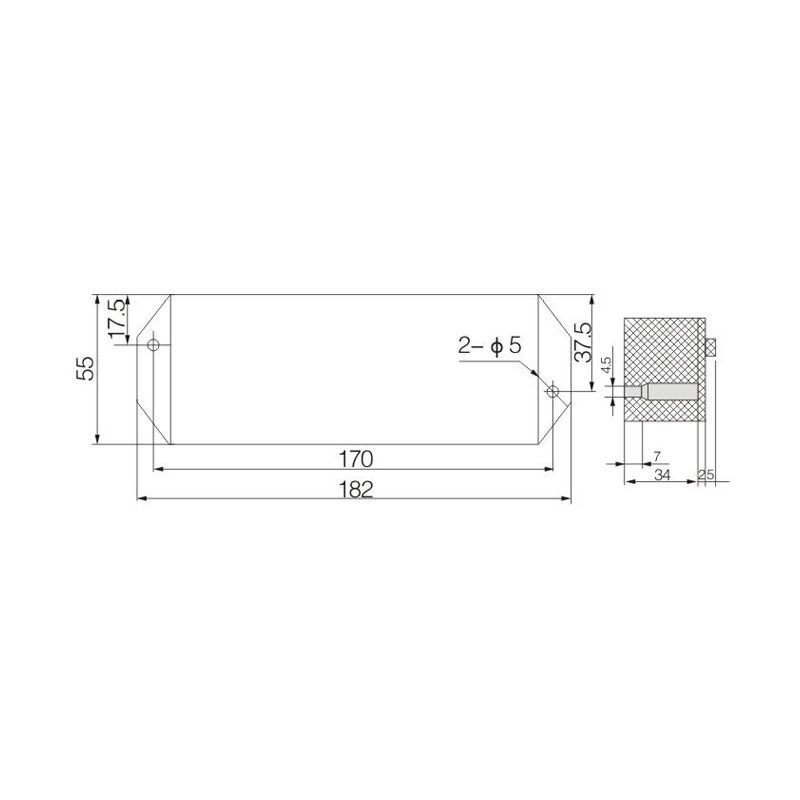
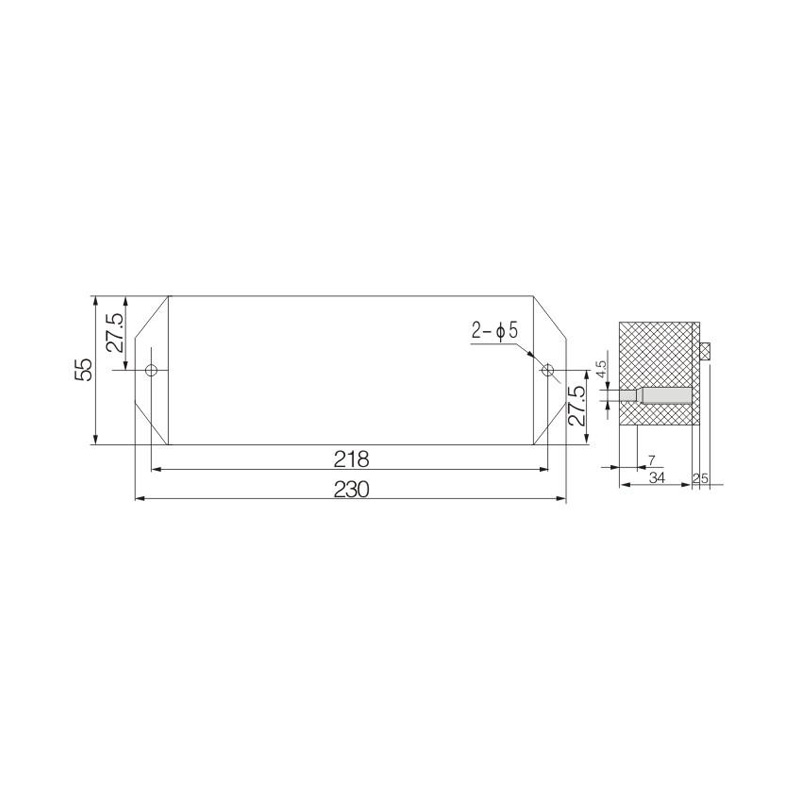
FJ6/JHD-3/E Two-Inlet Twenty-Four-Outlet Neutral Line Box
Model:FJ6/JHD-3/E
Product name: Two-inlet twenty-four-outlet neutral line box
Order number: OrderNo.150180
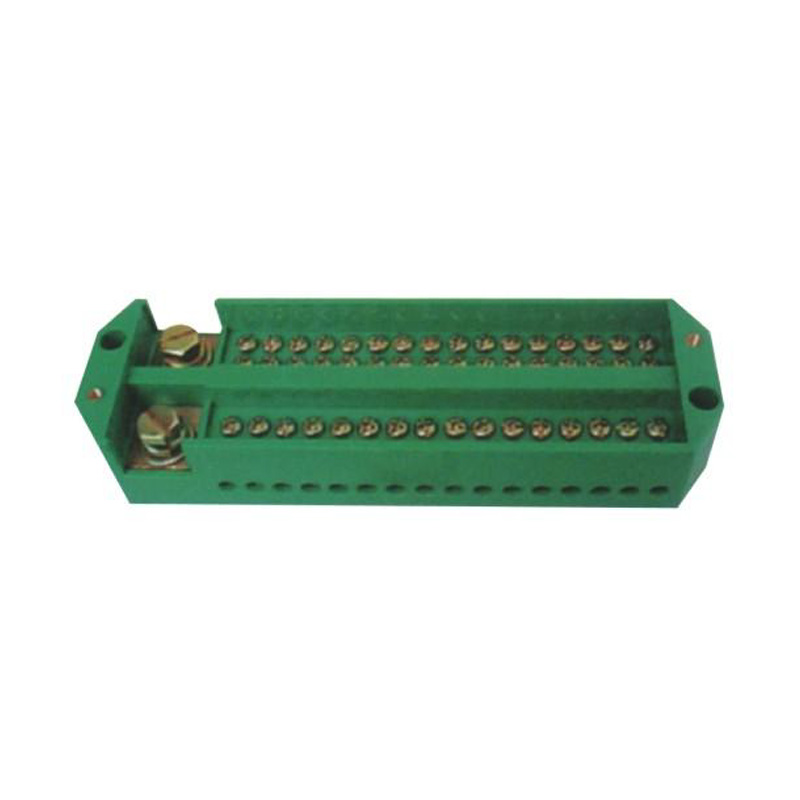
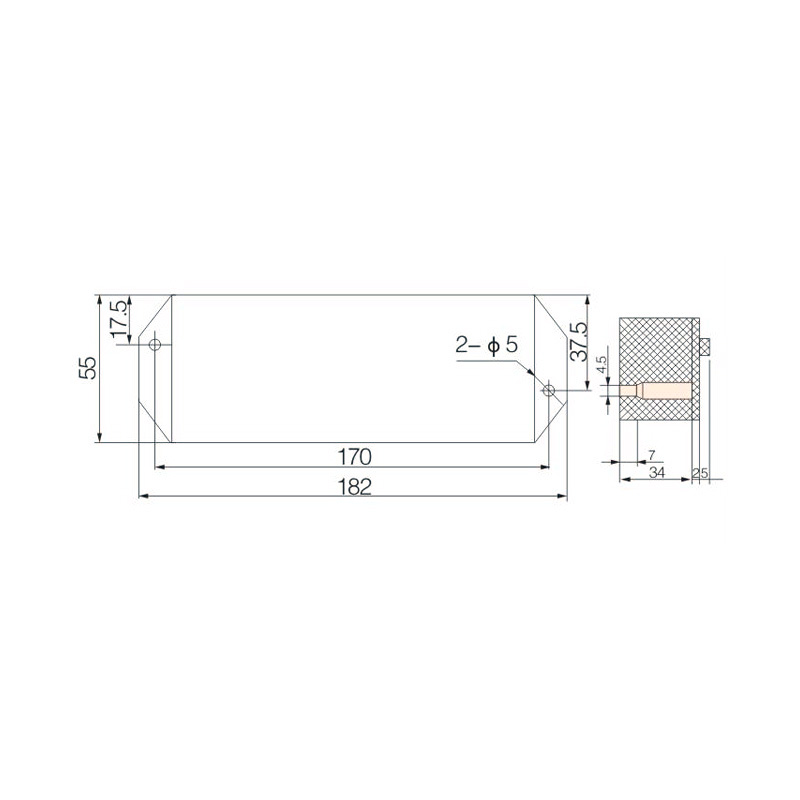
FJ6/JHD-3/C Twenty-Eight-Circuit Neutral Line Box
Model:FJ6/JHD-3/c
Product name: Twenty-eight-circuit neutral line box
Order number: OrderNo.150181
FJ6/JHD-3/C Thirty-Circuit Neutral Line Box
Model:FJ6/JHD-3/c
Product name: Thirty-circuit neutral line box
Order number: OrderNo.150182
FJ6/JHD-3/C Thirty-Two-Circuit Neutral Line Box
Model:FJ6/JHD-3/c
Product name: Thirty-two-circuit neutral line box
Order number: OrderNo.150183
FJ6/JHD-3/E Thirty-Six-Circuit Neutral Line Box
Model:FJ6/JHD-3/E
Product name: Thirty-six-circuit neutral line box
Order number: OrderNo.150184
FJ6/JHD-3/E Forty-Circuit Neutral Line Box
Model:FJ6/JHD-3/E
Product name: Forty-circuit neutral line box
Order number: OrderNo.150185
Search
Categories
-
Energy Measuring Terminal Block(314)
- Energy Measuring Joint Terminal Block(16)
- Polycarbonate Energy Measuring Terminal Block(24)
- Standard Wiring Energy Measuring Terminal Block(4)
- Transparent Shell Energy Measuring Terminal Block(6)
- Multifunctional Test Energy Measuring Terminal Block(10)
- Intelligent Safety Energy Measuring Terminal Block(6)
- Single-Phase Multi-Circuit Output Terminal Block(12)
- Self-Elevating Metering Box Terminal Block(7)
- One Household One-Meter Meter Box Dedicated Terminal Block(56)
- Three-Phase Metering Box Dedicated Terminal Block(24)
- Repeatable Grounding Line Terminal Block(20)
- Terminal Block for One-Inlet Multi-Outlet Metering Box(15)
- Closed Terminal Block(11)
- Heavy Current Terminal Block(48)
- Self-Boosting Terminal Block(5)
- Intelligent Self-Locking Terminal Block(3)
- Tool-Free Crimping Type Terminal Block(5)
- Wide Range of Wire Diameters Terminal Block(5)
- Combined Type Energy Measuring Terminal Block(37)
-
Switch Terminal Block(55)
- Pin-Type Incoming Line Switch Terminal Block(4)
- Multi-Way Connection Switch Terminal Block(4)
- Plug-pin Switch Terminal Block(7)
- Combined Type Switch Terminal Block(7)
- High Contact Cross Section Switch Terminal Block(7)
- Wide Range Switch Terminal Block(11)
- One Way in Switch Terminal Block(12)
- Equipped with Circuit Breaker Switch Terminal(3)
-
Heavy-current Terminal Block(631)
- Modular Building Block Terminal Block(156)
- Spherical Non-Destructive Crimp Terminal(120)
- Dual-Mode Connection Electrical Terminal(90)
- Anti-Electricity-Theft Terminal Block(74)
- Convenient Connection Terminal Block(12)
- High-Contact Section Terminal Block(12)
- Wide Range of Wire Diameters Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Heavy-Current Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Upper and Lower Rows of Neutral Terminal(2)
- Independent Neutral Line Terminal(7)
- Nose-Type Neutral Line Terminal(7)
- Rail Type Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Fixed Neutral Line Terminal(12)
- Double Rail Assembly Electrical Terminal(19)
- Blue Jack-Up Terminal(6)
- Black Base Copper Bar Terminal(5)
- Compact Terminal Block(16)
- Precision Terminal Block(23)
- U-Shaped Harpoon Terminal(2)
- Grounding Metering Box Terminal Block(12)
- High-Performance Terminal Block(19)
- Multifunctional Terminal Block(10)
- Din Rail Terminal Block(76)
- Watt-hour Meter Connector(49)
-
Energy Meter Accessories(116)
-
-
Secure connections are essential for reliable electrical distribution, especially when installing a High-performance Terminal Bloc...
READ MORE -
For engineers and panel builders striving for both efficiency and reliability, wiring errors remain a persistent headache — even w...
READ MORE -
In modern electrical systems, a High-performance Terminal Block plays a critical role in ensuring secure and reliable connections ...
READ MORE -
When building or maintaining electrical systems, one frequently overlooked but critical factor is matching the conductor size to t...
READ MORE -
Effective electrical connections depend on more than simply matching cable sizes. Whether you’re securing a power conductor with a...
READ MORE
What Are The Inspection Routines For a Repeatable Grounding Line Terminal Block?
A consistent and repeatable inspection routine for grounding line terminal blocks is essential for maintaining system safety and preventing unexpected downtime. The goal is to identify potential issues before they failure. A thorough routine can be broken down into a few key areas.
Perform a visual inspection. Look for any obvious signs of damage, such as cracking, melting, or discoloration on the terminal block's housing. These can indicate past overheating or physical stress. Check for signs of corrosion on the metal components, which can increase resistance and create a poor connection.
Verify the tightness of the connection. Using a calibrated torque screwdriver, check that all terminal screws are tightened to the manufacturer's specified value. Loose connections are a primary cause of heat buildup. As you do this, inspect the wire itself. Ensure it is properly seated under the clamp and that there are no stray strands that could cause a short. Finally, if possible, use a thermal scanner to take a temperature reading of the block during operation. Compare it to adjacent blocks and ambient temperature; a noticeably warmer block suggests a high-resistance connection that needs immediate attention.
What Are The Installation Options For a Circuit Breaker Block Junction Box?
When installing a junction box that houses circuit breaker terminal blocks, there are several mounting and layout options to consider. The choice depends on factors like available space, wiring complexity, and maintenance needs.
The common approach is DIN Rail Mounting. The circuit breaker blocks snap onto a standard DIN rail, which is secured to the backplate of the junction box. This method offers flexibility, allowing for easy rearrangement, addition, or removal of blocks without the need for tools in many cases. It keeps the installation organized and modular.
For smaller setups or fixed applications, Direct Panel Mounting is an option. Here, the individual breaker blocks are screwed directly onto the backplate of the enclosure. This provides a very secure and permanent installation but lacks the flexibility of a DIN rail system. Adding or changing circuits later is more difficult.
The layout within the box is also important. A Top-Entry vs. Bottom-Entry design choice must be made. Top-entry boxes, with conduits entering from the top, help protect against dust and dripping liquids. Bottom-entry is often chosen for cleaner cable management when wires are coming from below. Finally, selecting an enclosure with a transparent or opaque door is a decision. A transparent door allows for quick visual status checks without opening the box, enhancing safety.
What do you know about Grounding Terminal Blocks?
Part 1: Enclosure Material
The material of a grounding terminal block's housing plays a critical role in its performance and longevity. The two common materials are thermoplastics and thermosets. Engineering thermoplastics, like nylon or polyamide, are widely used. They offer a good balance of mechanical strength, impact resistance, and cost-effectiveness. They are suitable for a broad range of general-purpose applications with standard temperature requirements.
For more demanding environments, thermoset materials such as phenolic resins are often chosen. These materials provide performance in high-temperature settings. They are more rigid and exhibit resistance to creep and deformation under continuous heat and mechanical stress, ensuring the clamping force on the critical ground connection remains stable over time. The material selection directly influences the block's ability to maintain a safe and reliable connection.
Part 2: Color Coding
Color coding is a simple but vital safety feature for grounding terminal blocks. Internationally, the color green, or green with a yellow stripe, is exclusively used to identify grounding and bonding components. This immediate visual identification ensures that installers and maintenance technicians can quickly and accurately distinguish safety ground connections from live power connections.
This practice prevents accidental misuse of the terminal for a current-carrying wire. The consistent use of green terminals across different equipment and panels creates a universal language of safety, reducing the risk of errors during installation, modification, or troubleshooting. This color standard is a fundamental requirement in electrical safety regulations.


 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى