Integrating wired connectivity into the era of automation and digital networking involves more than just traditional hardware. A H...
READ MOREHeavy Current Terminal Block Manufacturer
According to the Ministry of Electric Power Grid Renovation Plan, in order to improve the electricity conditions of residents, our company has developed a Heavy Current Terminal Block according to market needs. Since its product was put into the market, it has been welcomed by the majority of electricity metering workers. It is convenient to operate, and ensures the firmness and reliability of wiring, achieving the purpose of safe electricity use, and promoting the standardization and standardization of metering devices. This series of products has been certified by the state and all technical indicators comply with the requirements of GB14048 national standards and IEC international standards. It has now been promoted and used by the power department.
The product has a small size, large current carrying capacity, high pressure resistance, reasonable structure, beautiful appearance, flame retardant, high temperature resistance, non-absorbing, moisture resistance, good insulation performance, impact resistance, anti-aging and other high-quality characteristics. The cover plate is made of transparent material and is easy to disassemble and assemble, achieving the purpose of transparent, intuitive and safe use of electricity.
This is suitable for the supporting use of various epitope metering. After installation, it not only solves the problem of directly entering the bare copper ship in the home line, causing many accident hazards such as small current, unsafe, unreliable, and inconvenient. And reduce the cost of the metering box. According to the number of poles of the product, it is divided into single pole (1P), single phase (2P), three-phase three-wire (3P), three-phase four-wire (4P), and according to the outgoing line, it is divided into one, two, three, four, and twenty-four.
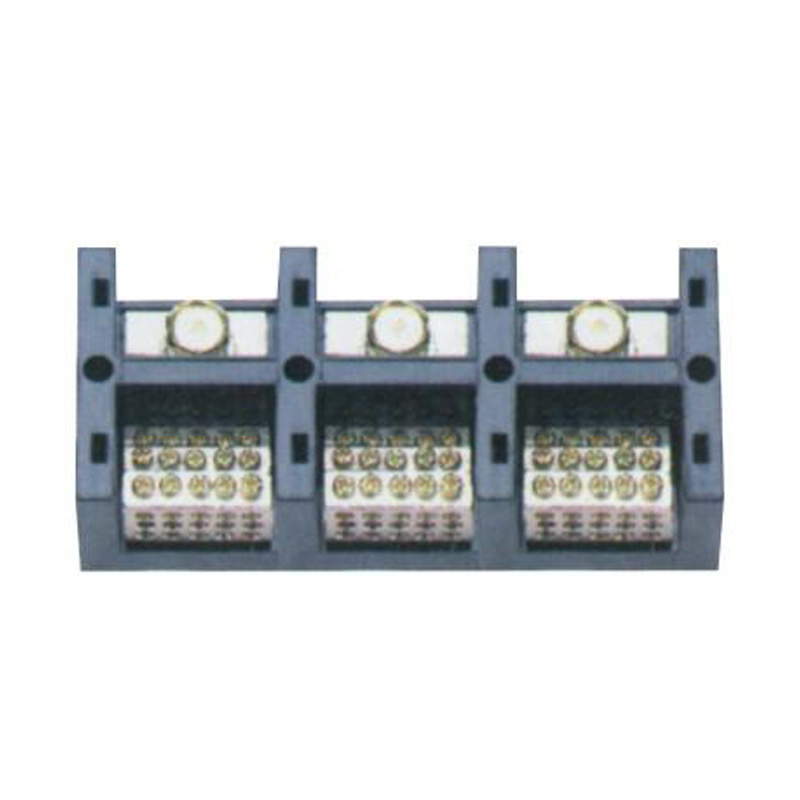
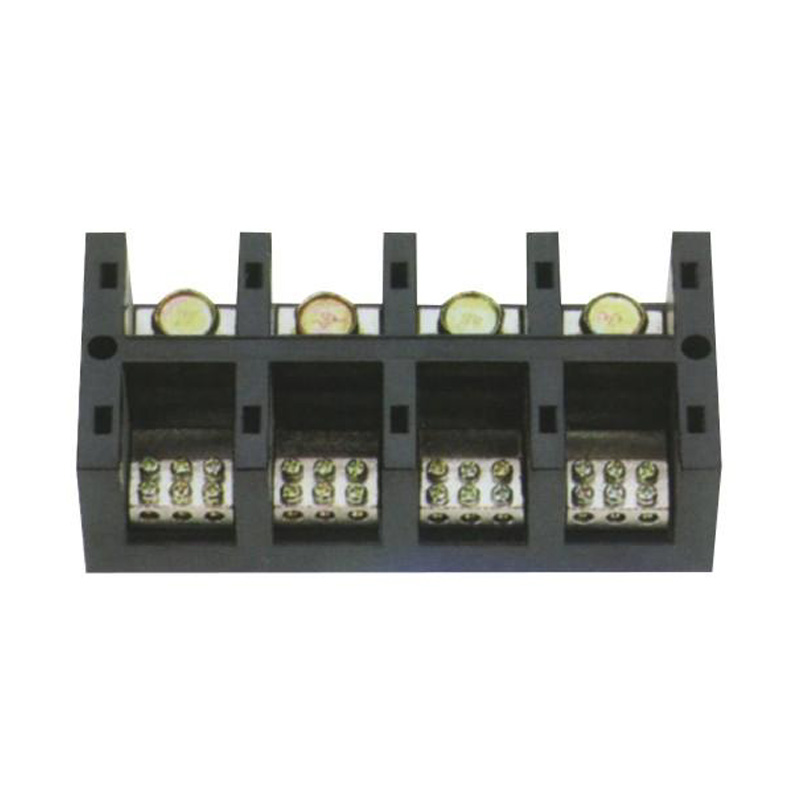
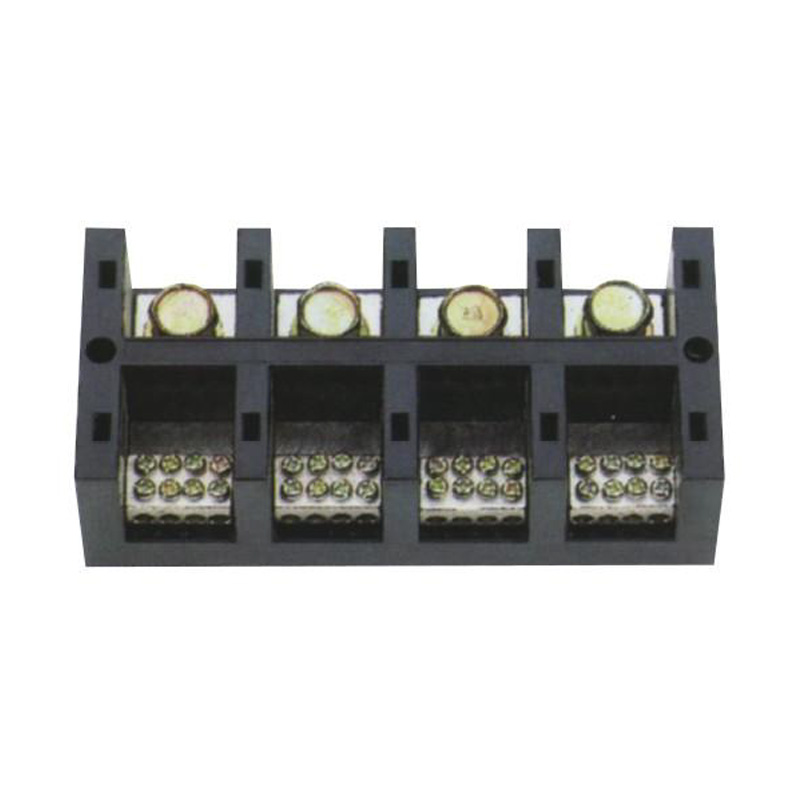
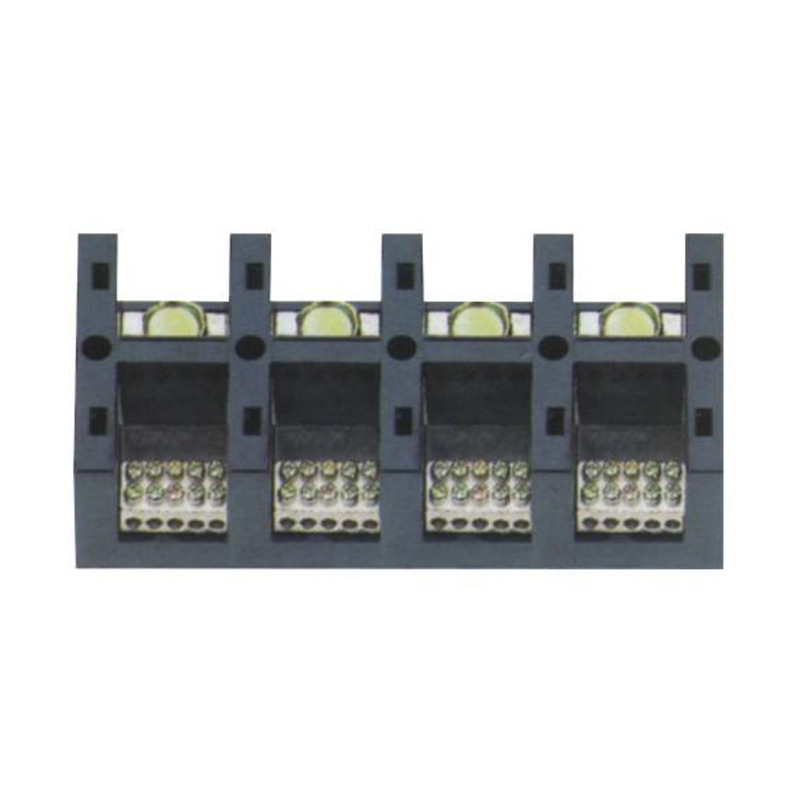
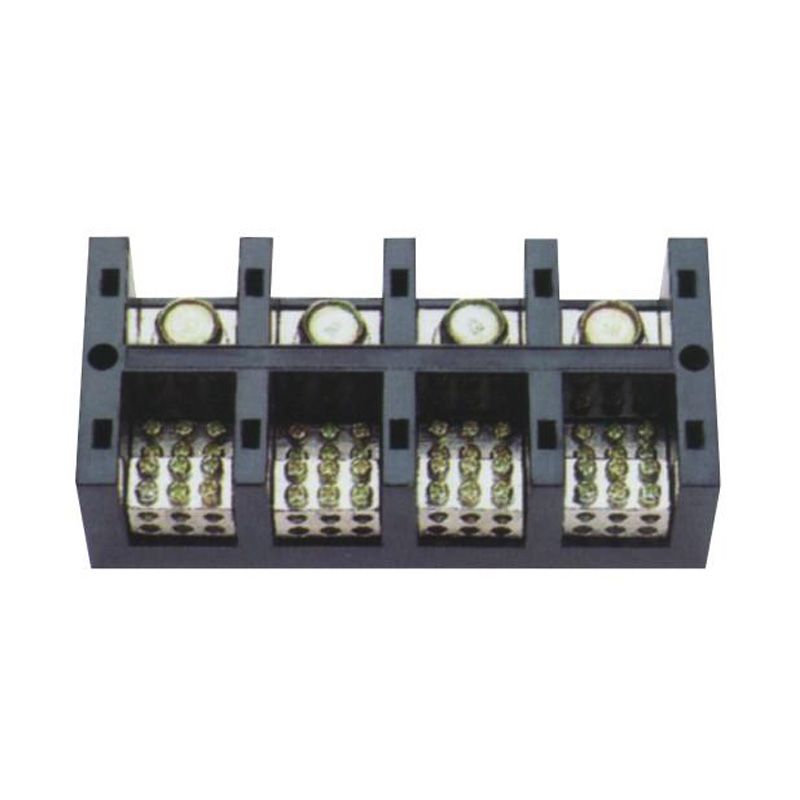
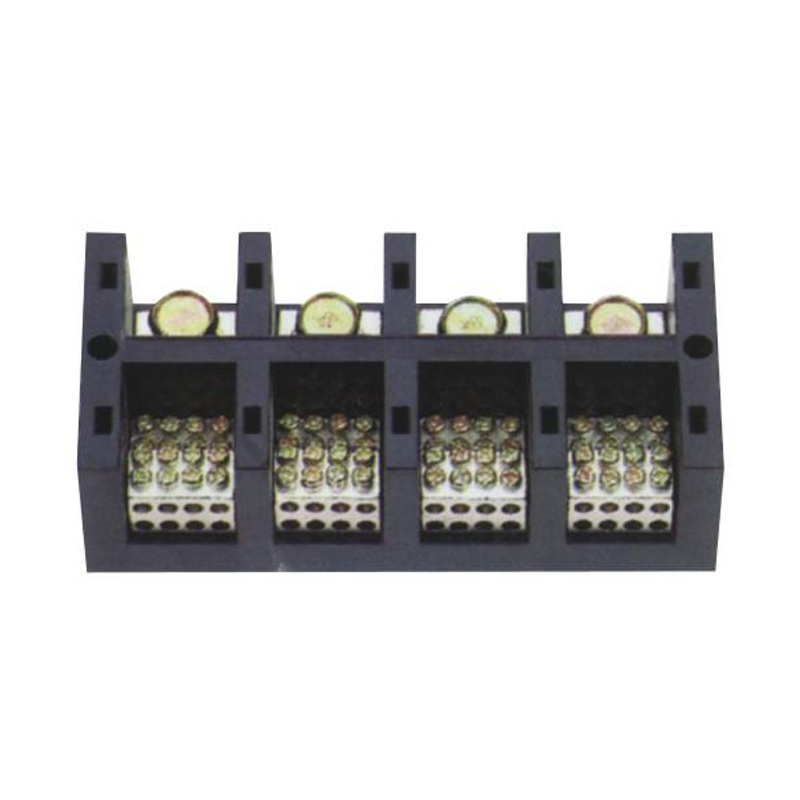
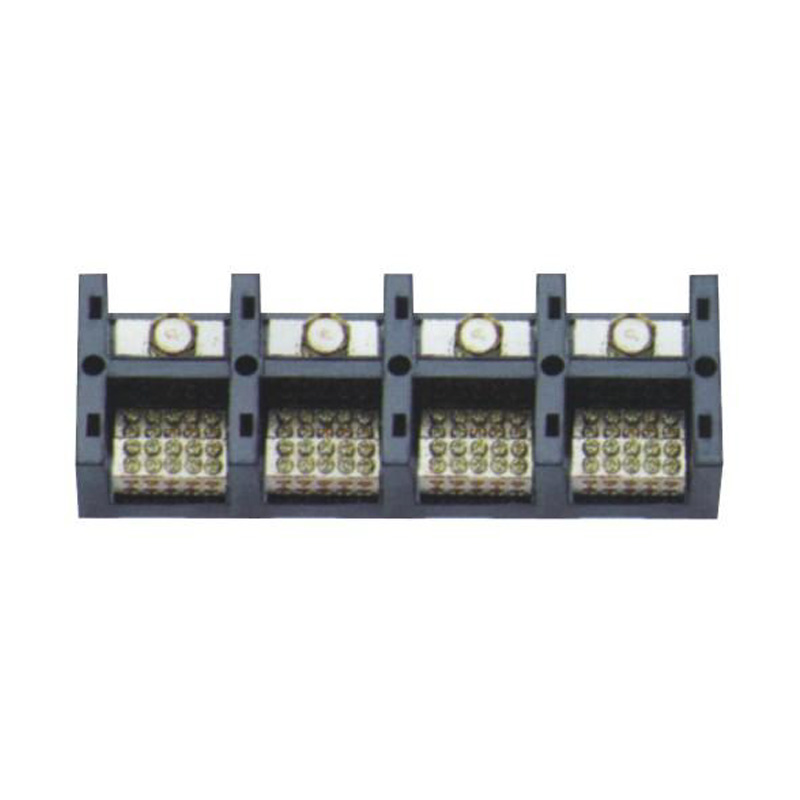
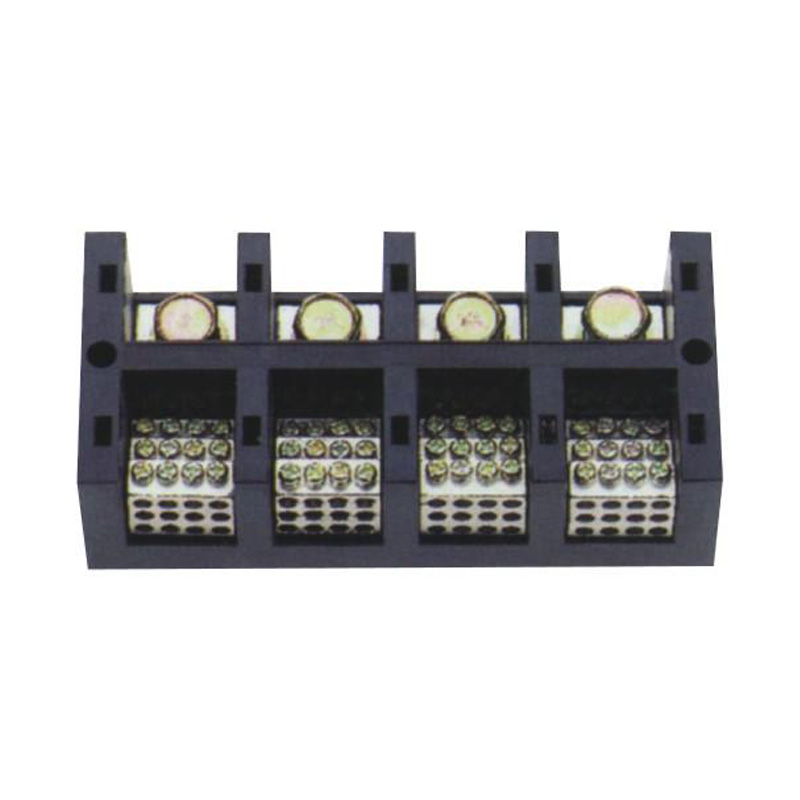
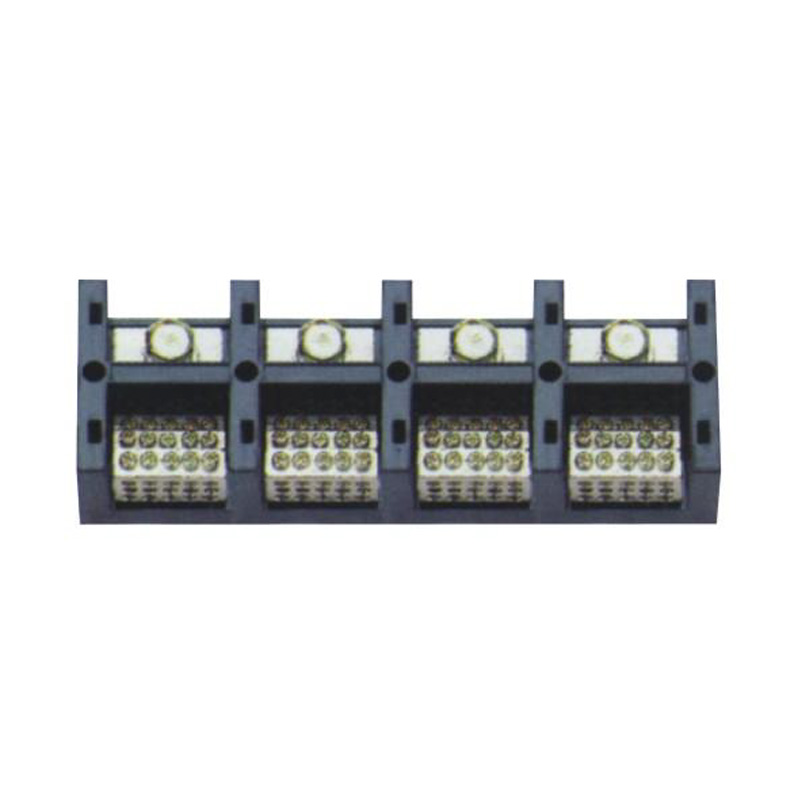
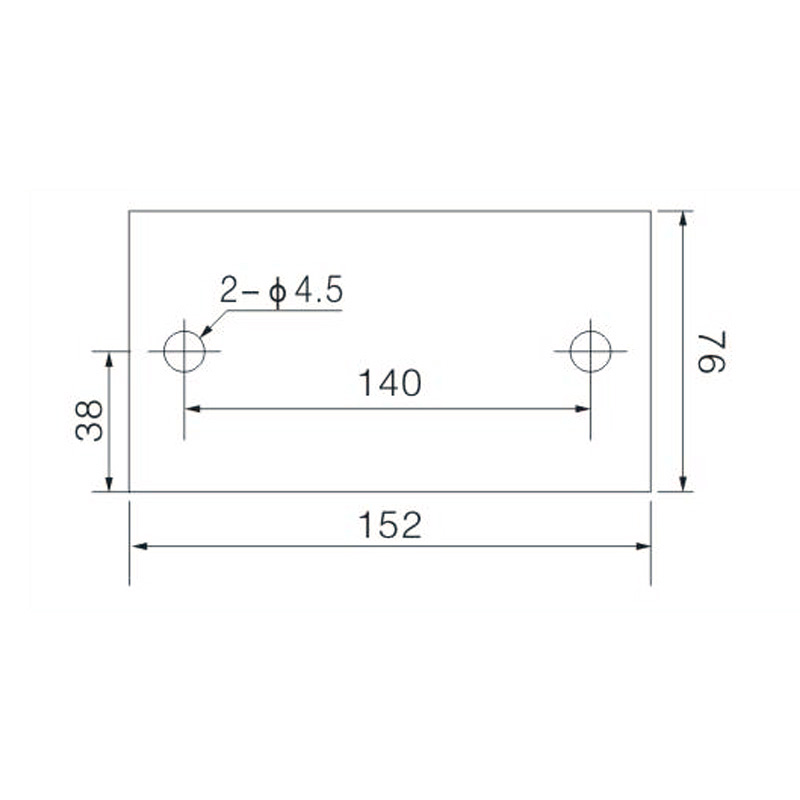
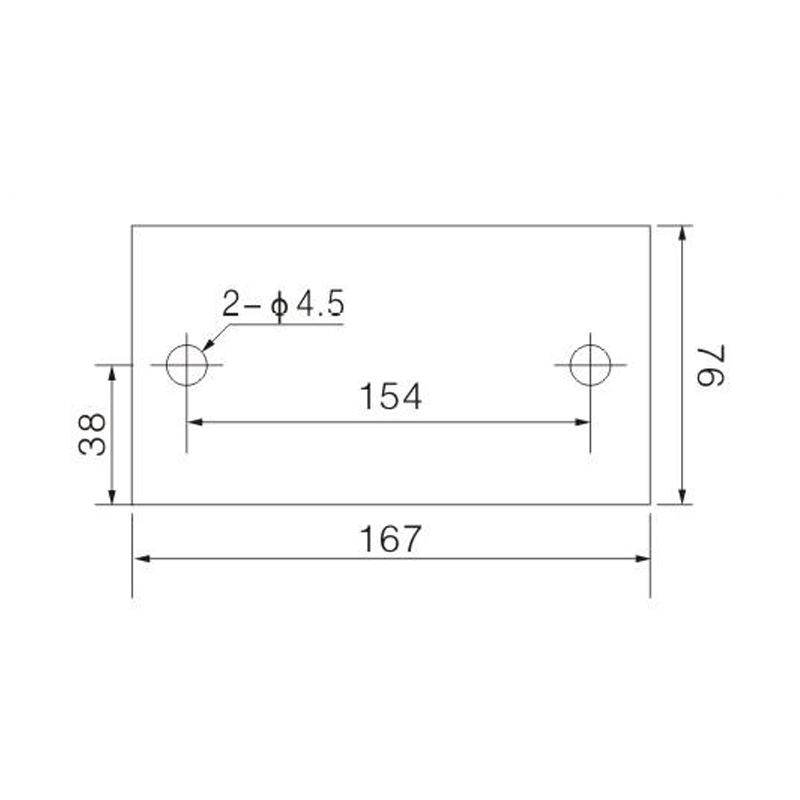
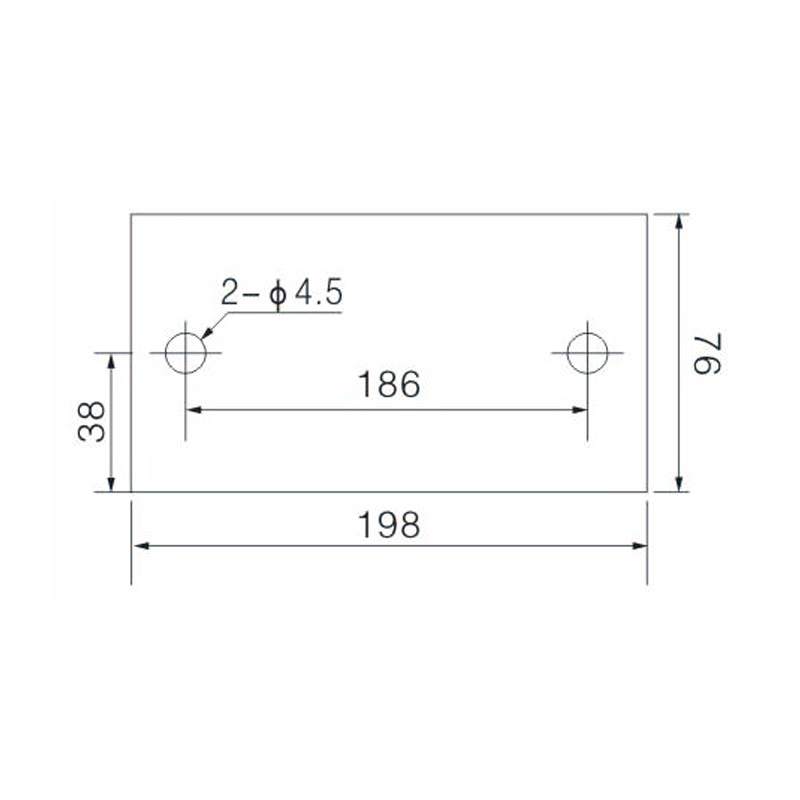
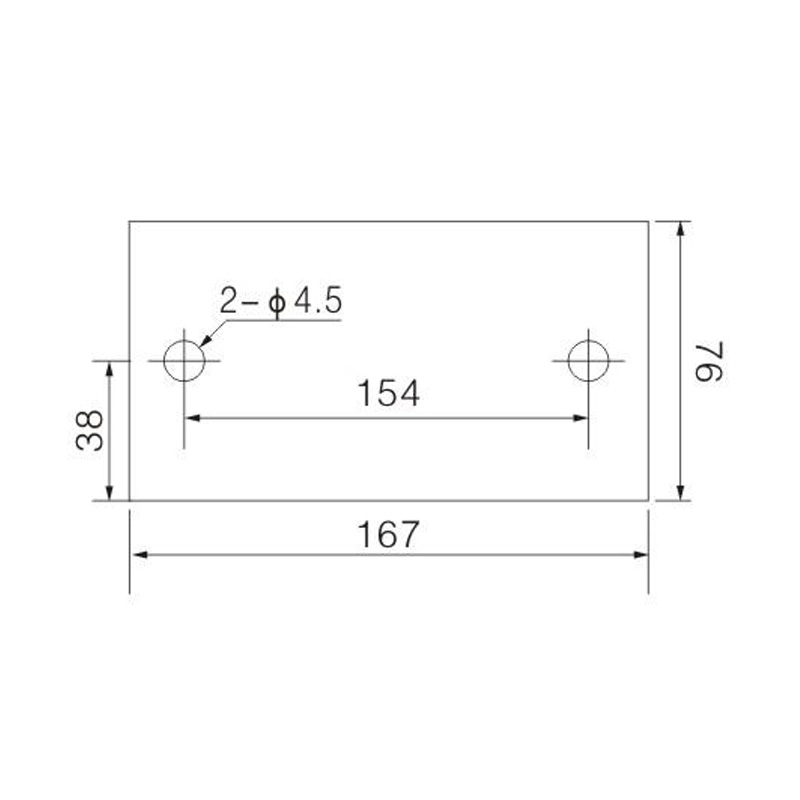
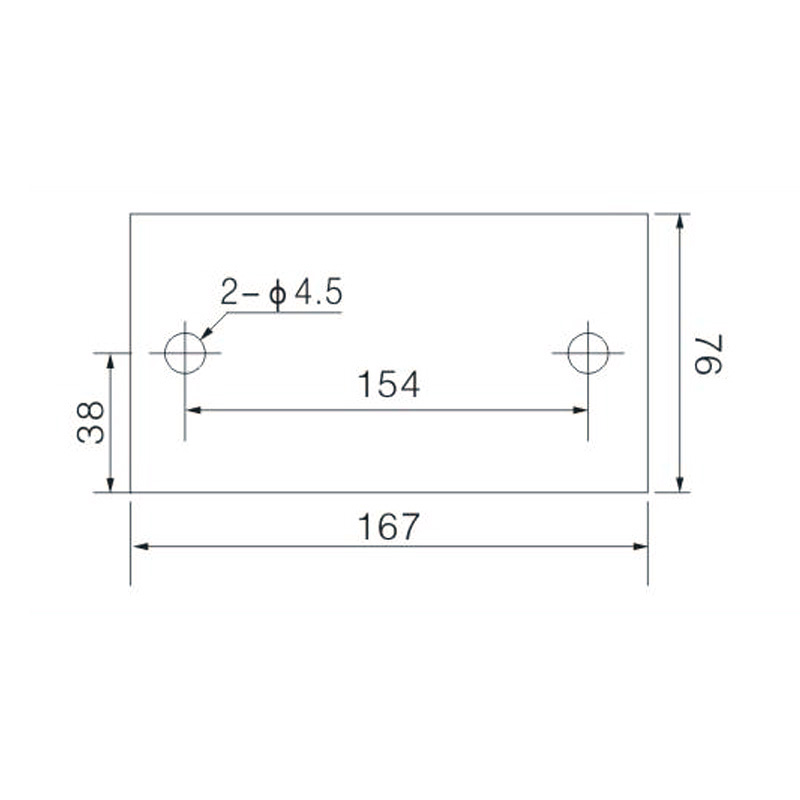
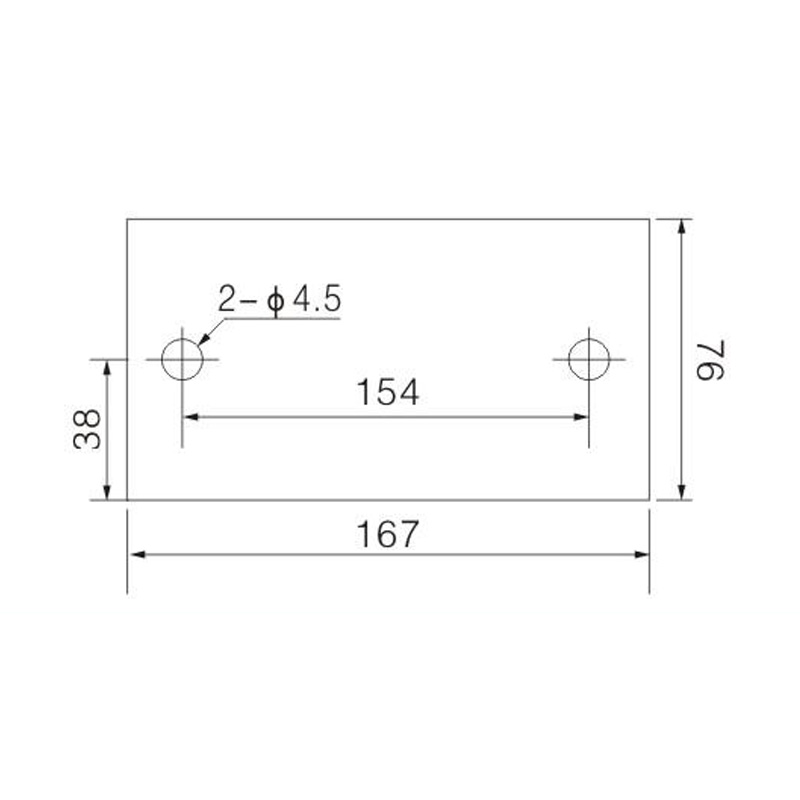
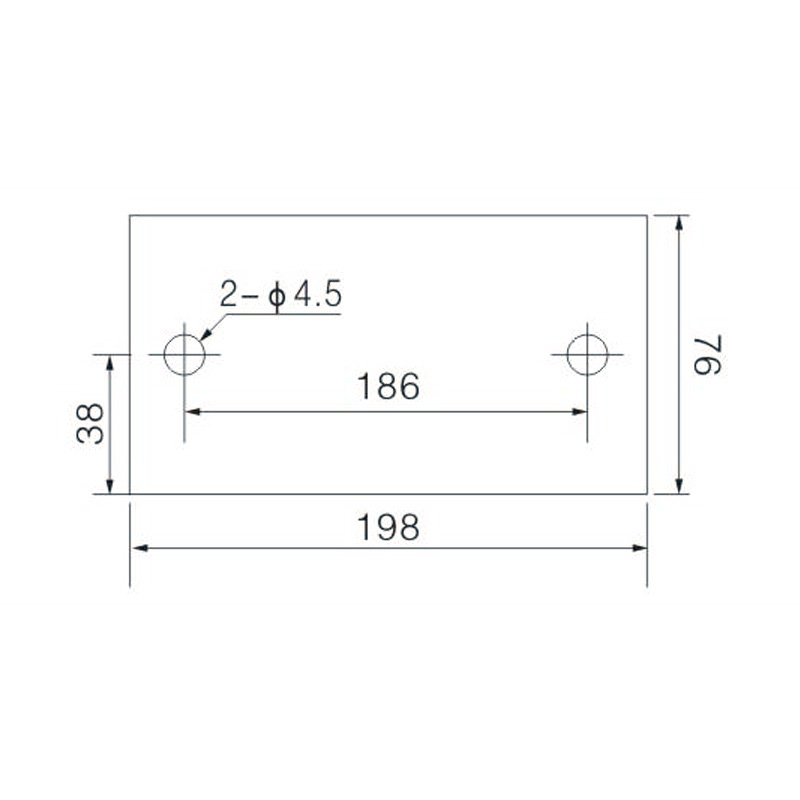
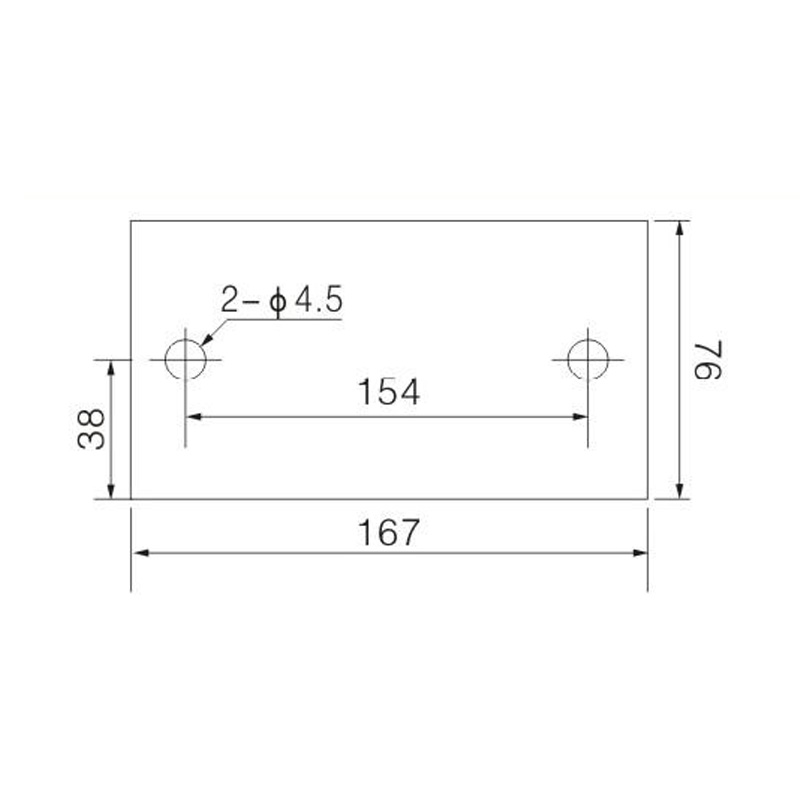
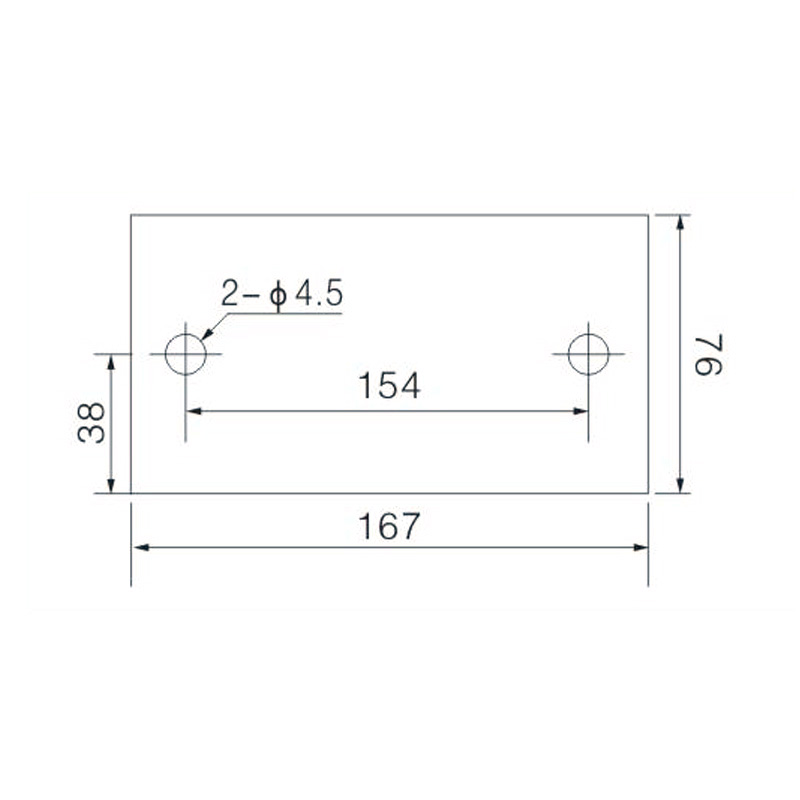
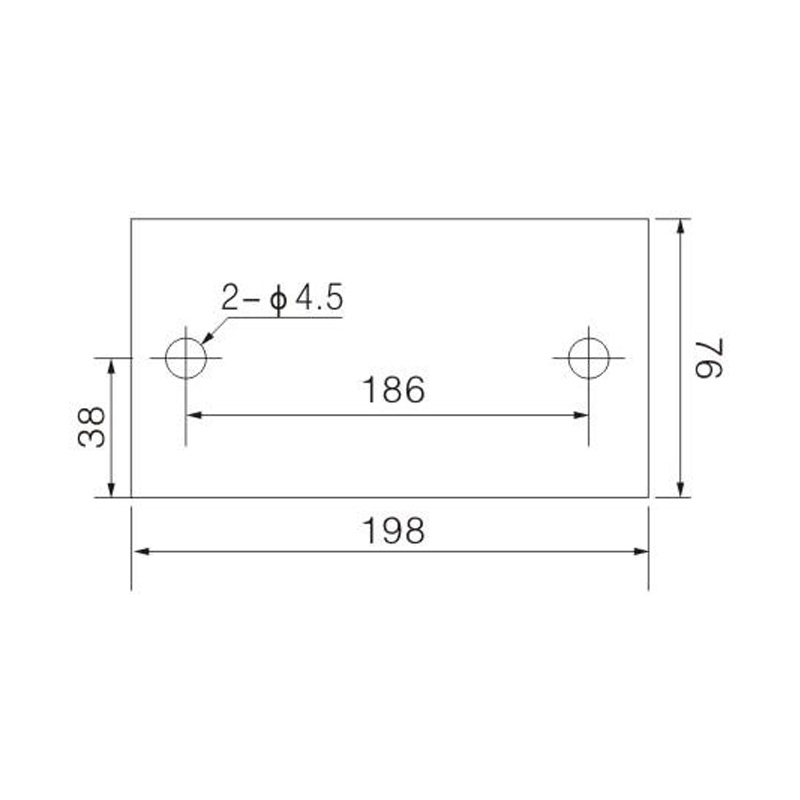
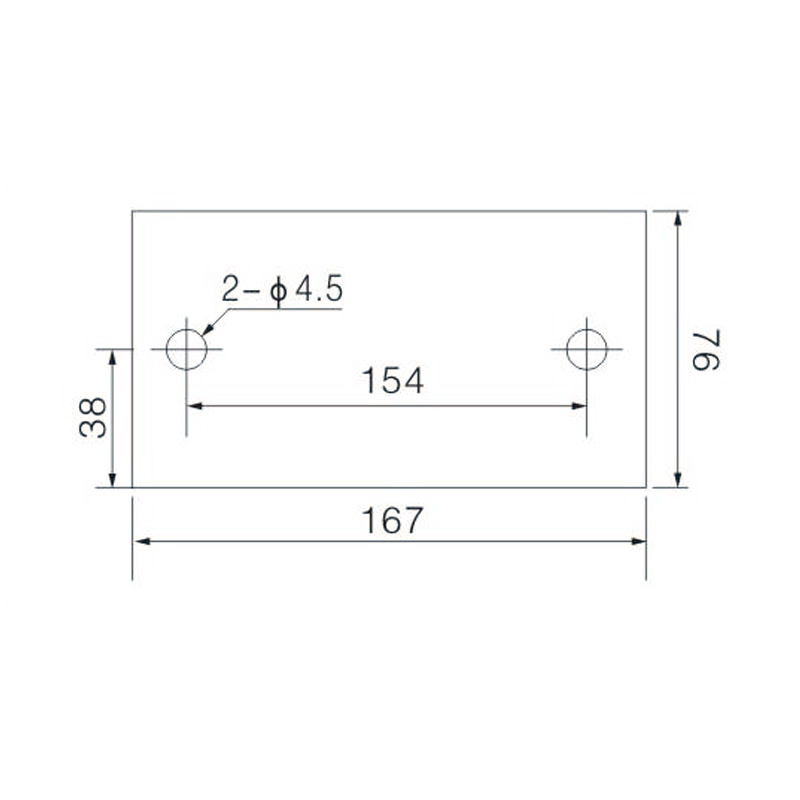
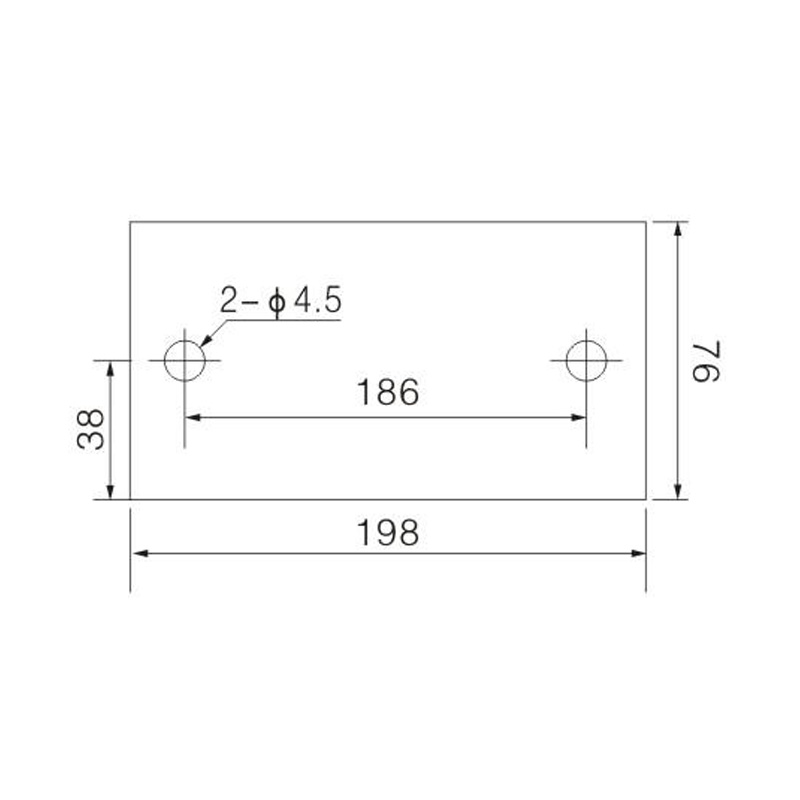
FJ6/JHT-3003/15 Heavy Current Terminal Block
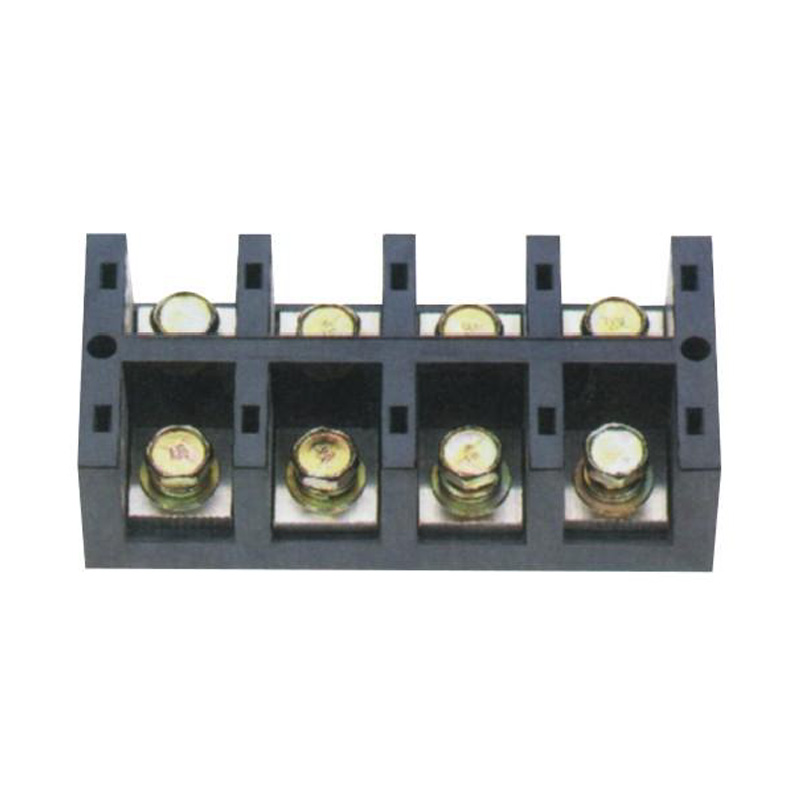
FJ6/JHT-2504 Heavy Current Terminal Block
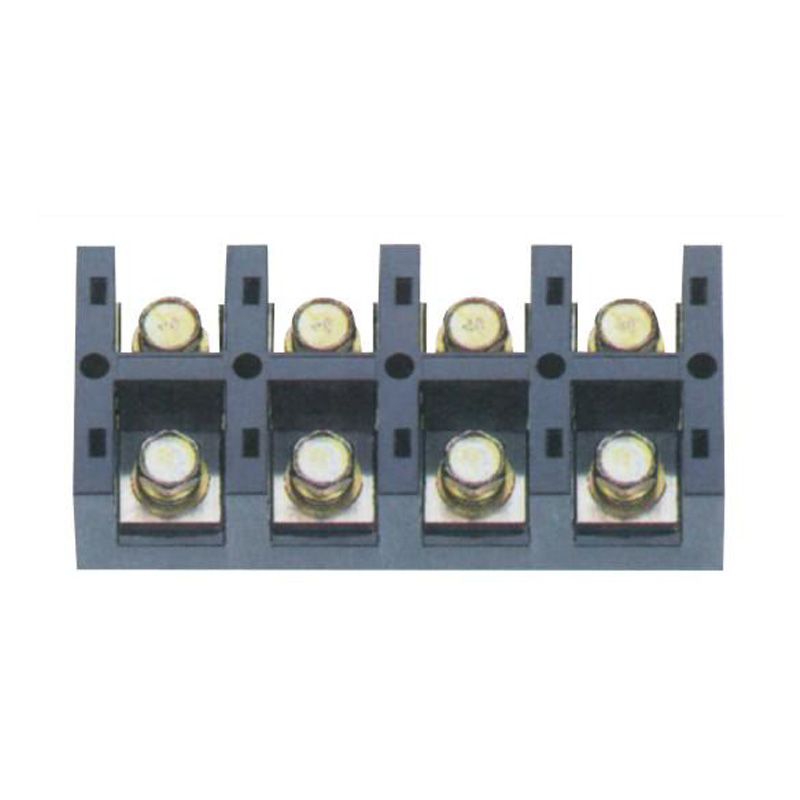
FJ6/JHT-3004 Heavy Current Terminal Block
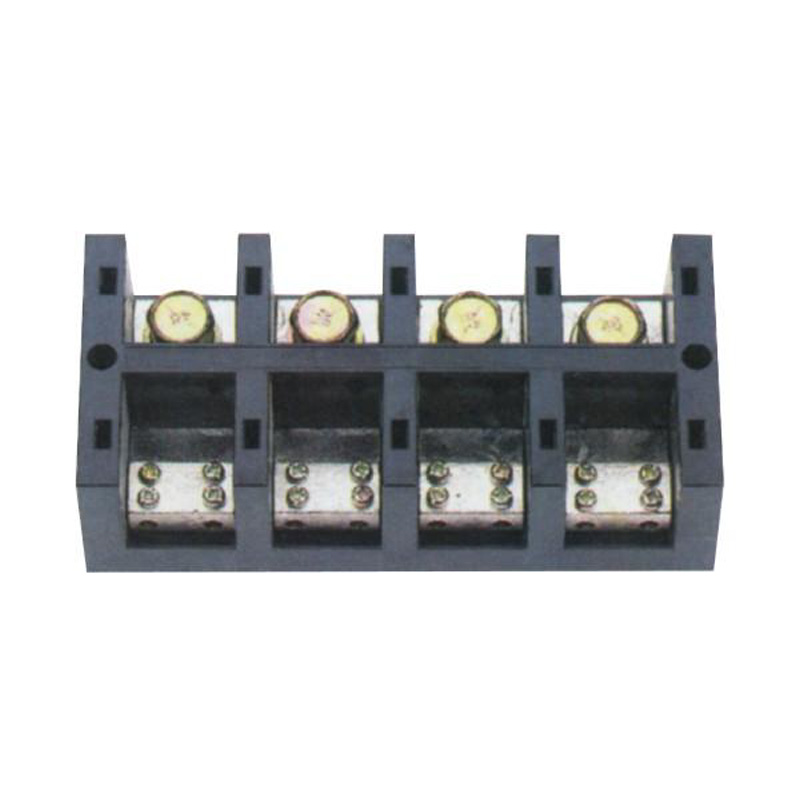
FJ6/JHT-2504/2 Heavy Current Terminal Block
FJ6/JHT-2504/3 Heavy Current Terminal Block
FJ6/JHT-2504/4 Heavy Current Terminal Block
FJ6/JHT-3004/5 Heavy Current Terminal Block
FJ6/JHT-2504/6 Heavy Current Terminal Block
FJ6/JHT-2504/8 Heavy Current Terminal Block
FJ6/JHT-3004/10 Heavy Current Terminal Block
FJ6/JHT-2504/12 Heavy Current Terminal Block
FJ6/JHT-3004/15 Heavy Current Terminal Block
Search
Categories
-
Energy Measuring Terminal Block(314)
- Energy Measuring Joint Terminal Block(16)
- Polycarbonate Energy Measuring Terminal Block(24)
- Standard Wiring Energy Measuring Terminal Block(4)
- Transparent Shell Energy Measuring Terminal Block(6)
- Multifunctional Test Energy Measuring Terminal Block(10)
- Intelligent Safety Energy Measuring Terminal Block(6)
- Single-Phase Multi-Circuit Output Terminal Block(12)
- Self-Elevating Metering Box Terminal Block(7)
- One Household One-Meter Meter Box Dedicated Terminal Block(56)
- Three-Phase Metering Box Dedicated Terminal Block(24)
- Repeatable Grounding Line Terminal Block(20)
- Terminal Block for One-Inlet Multi-Outlet Metering Box(15)
- Closed Terminal Block(11)
- Heavy Current Terminal Block(48)
- Self-Boosting Terminal Block(5)
- Intelligent Self-Locking Terminal Block(3)
- Tool-Free Crimping Type Terminal Block(5)
- Wide Range of Wire Diameters Terminal Block(5)
- Combined Type Energy Measuring Terminal Block(37)
-
Switch Terminal Block(55)
- Pin-Type Incoming Line Switch Terminal Block(4)
- Multi-Way Connection Switch Terminal Block(4)
- Plug-pin Switch Terminal Block(7)
- Combined Type Switch Terminal Block(7)
- High Contact Cross Section Switch Terminal Block(7)
- Wide Range Switch Terminal Block(11)
- One Way in Switch Terminal Block(12)
- Equipped with Circuit Breaker Switch Terminal(3)
-
Heavy-current Terminal Block(631)
- Modular Building Block Terminal Block(156)
- Spherical Non-Destructive Crimp Terminal(120)
- Dual-Mode Connection Electrical Terminal(90)
- Anti-Electricity-Theft Terminal Block(74)
- Convenient Connection Terminal Block(12)
- High-Contact Section Terminal Block(12)
- Wide Range of Wire Diameters Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Heavy-Current Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Upper and Lower Rows of Neutral Terminal(2)
- Independent Neutral Line Terminal(7)
- Nose-Type Neutral Line Terminal(7)
- Rail Type Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Fixed Neutral Line Terminal(12)
- Double Rail Assembly Electrical Terminal(19)
- Blue Jack-Up Terminal(6)
- Black Base Copper Bar Terminal(5)
- Compact Terminal Block(16)
- Precision Terminal Block(23)
- U-Shaped Harpoon Terminal(2)
- Grounding Metering Box Terminal Block(12)
- High-Performance Terminal Block(19)
- Multifunctional Terminal Block(10)
- Din Rail Terminal Block(76)
- Watt-hour Meter Connector(49)
-
Energy Meter Accessories(116)
-
-
Secure connections are essential for reliable electrical distribution, especially when installing a High-performance Terminal Bloc...
READ MORE -
For engineers and panel builders striving for both efficiency and reliability, wiring errors remain a persistent headache — even w...
READ MORE -
In modern electrical systems, a High-performance Terminal Block plays a critical role in ensuring secure and reliable connections ...
READ MORE -
When building or maintaining electrical systems, one frequently overlooked but critical factor is matching the conductor size to t...
READ MORE -
Effective electrical connections depend on more than simply matching cable sizes. Whether you’re securing a power conductor with a...
READ MORE
What Needs Does The Heavy Current Terminal Block Meet?
Managing Significant Power Loads
The primary purpose of a heavy-current terminal block is to safely conduct and distribute large amounts of electrical current, often ranging from hundreds to thousands of amperes. Standard terminals would overheat and fail under such loads. These blocks are engineered with larger contact surfaces, robust conductive materials like high-grade copper alloys, and designs that minimize electrical resistance. This focus on efficient power handling prevents energy loss and dangerous heat buildup, ensuring the system operates as intended.
Enhancing Operational Safety
High current levels inherently present greater risks, including the potential for arcing, overheating, and catastrophic failure. Heavy-current terminal blocks are designed to mitigate these risks. They feature secure clamping mechanisms that maintain a firm grip on conductors, even under the stress of vibration or thermal expansion. Many designs include protective features like fully insulated housings and arc barriers to contain any potential faults. This built-in safety protects both the equipment and personnel.
Facilitating Maintenance and Reliability
Industrial and power distribution systems are expected to operate for long periods with minimal downtime. Heavy-current terminal blocks support this need for reliability and ease of maintenance. Their design allows for secure, organized, and accessible connections. This organization simplifies initial wiring, troubleshooting, and any necessary modifications. The robust construction ensures the connection remains stable over time, resisting corrosion and loosening, which contributes to the overall longevity and dependability of the entire electrical system.
What Is The Function Of The High Current PCB Terminal Block?
A High Current PCB Terminal Block serves a specific and critical function: it acts as the secure and reliable bridge between the high-power external wiring and the printed circuit board (PCB) itself. Unlike standard PCB terminals designed for signal-level currents, these components are built to handle substantial power directly on the board.
Their primary role is to provide a safe and mechanically strong point of entry for wires carrying high current from an external source, such as a power supply or a motor. They eliminate the need for soldering large-gauge wires directly to the PCB, which can create mechanical stress and unreliable joints. Instead, the terminal block is soldered directly to the board's pads, creating a solid electrical and mechanical connection. The external wire is then clamped securely into the block using a screw or spring clamp mechanism.
This setup offers significant advantages. It simplifies assembly and field wiring, as connections can be made and unmade without applying heat to the PCB. It also improves serviceability; a faulty wire can be easily replaced without needing to re-solder the board. By managing the high current at the point of entry, these blocks also help protect the more delicate traces and components on the PCB from heat and stress, enhancing the overall durability of the assembly.
What Are The Differences Between The Dual-Row Terminal Block?
Dual-row terminal blocks offer a distinct alternative to traditional single-row designs, with differences primarily centered on density, wiring, and circuit organization.
Circuit Density and Space Saving
Main Body: The apparent difference is the physical layout. Dual-row blocks feature two parallel rows of connections, effectively doubling the number of terminals within a nearly equivalent footprint on a DIN rail or panel. This vertical stacking is a primary advantage for circuit density in control cabinets where real estate is limited. It allows designers to fit more connections into a smaller space, more compact and efficient enclosure designs.
Wiring and Maintenance Access
Main Body: The wiring approach differs significantly between the two styles. While single-row blocks offer unimpeded access from one direction, dual-row blocks require careful planning for wire routing. The top row can be easily accessed, but wiring the bottom row may be more challenging, especially in tight spaces or with thicker cables. This can sometimes make maintenance or troubleshooting more complex compared to the single-row layout where all terminals are immediately visible and accessible.
Internal Layout and Potential for Bridging
Main Body: Internally, the arrangement of two rows creates a natural separation. This layout can be advantageous for organizing different types of circuits. For instance, one row could be dedicated to power inputs while the other is used for output signals. However, implementing common power rails across multiple blocks (using jumper bars) becomes more complex than with a single-row design. Some dual-row blocks are designed with internal connections between rows, but often, custom bridging is required to link circuits between the upper and lower levels.


 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى