Integrating wired connectivity into the era of automation and digital networking involves more than just traditional hardware. A H...
READ MORERail Type Terminal Block Manufacturer
Rail Type Terminal Blocks are professionally used for creating secure and organized electrical connections in a wide range of applications. These terminal blocks are specifically designed for easy installation and integration into rail-mounted electrical panels, distribution boards, and control cabinets, making them ideal for applications that require a compact, reliable, and scalable solution for electrical wiring.
These terminal blocks feature a modular design that allows for secure and stable connections of conductors, without the need for excessive wiring or additional components. The rail mounting design ensures easy installation, compatibility with standard DIN rail systems, and the ability to expand or reconfigure the electrical system as needed.
Rail Type Terminal Blocks are currently a versatile and reliable solution for managing electrical connections. They simplify the wiring process, enhance system reliability, and provide a safe and efficient way to manage multiple circuits in a single terminal block, all while being easily integrated into rail-mounted systems.
The modular design of Rail Type Terminal Blocks allows for easy installation and maintenance. Users can quickly assemble the blocks according to their specific requirements without the need for additional tools or specialized equipment. This feature not only saves time but also reduces the risk of errors during the installation process.
With the ability to accommodate multiple rows of terminals in a single block, these terminal blocks optimize space utilization. High-density configurations are particularly beneficial in environments where space is at a outstanding, such as in control panels or industrial machinery.
The universal compatibility of Rail Type Terminal Blocks ensures that they can be used with a wide variety of cable types and sizes. This adaptability makes them suitable for diverse applications, from low-voltage power distribution to high-voltage connections in heavy industrial settings.
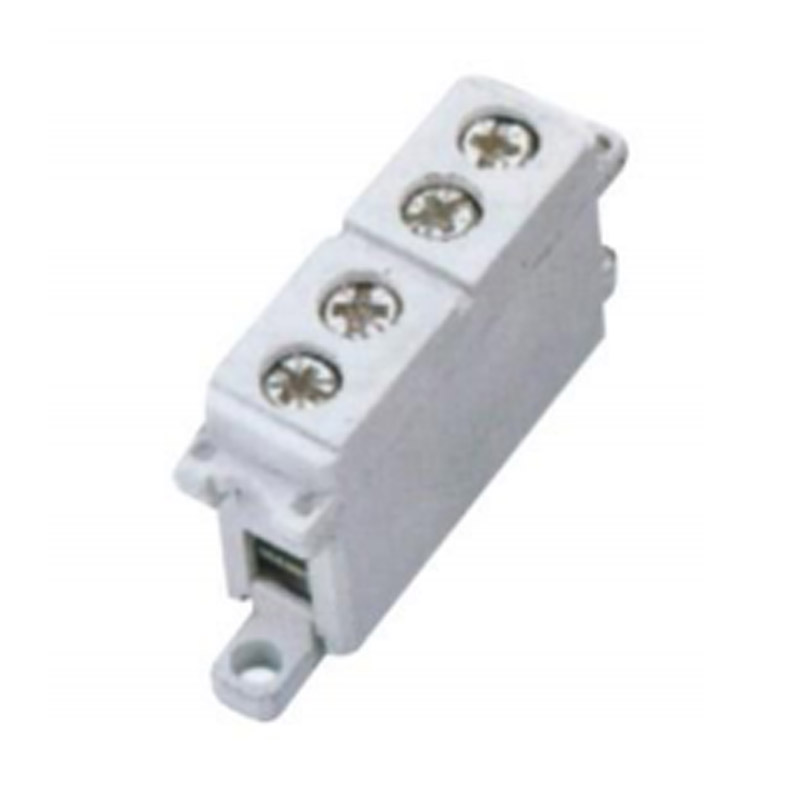
FJ6/JHG-8-1 Rail Terminal Block
FJ6/JHG-8-1
One-inlet one-outlet(1-gear)
Order number:150570+1
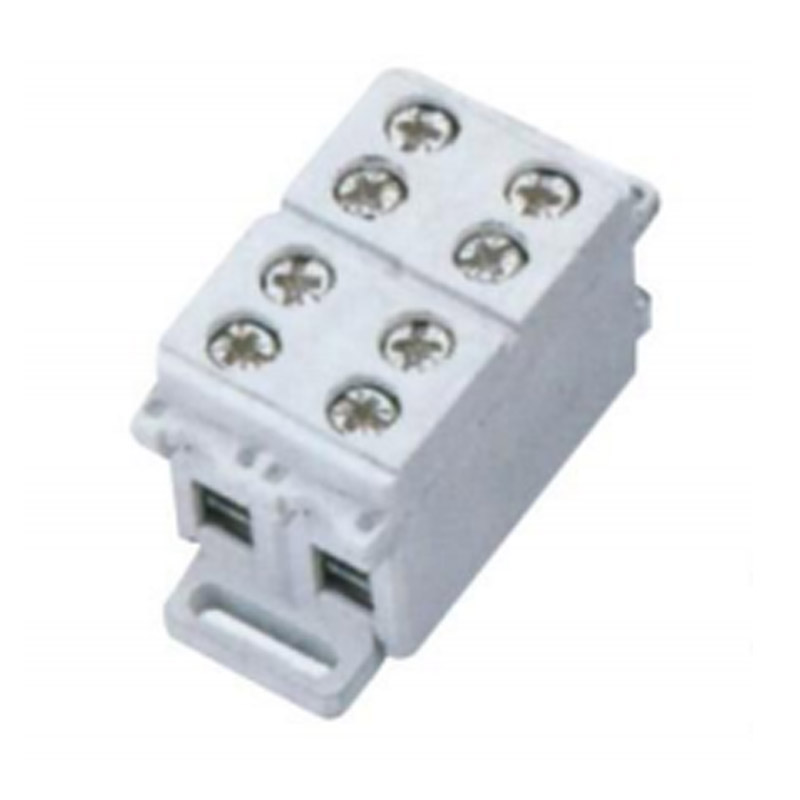
FJ6/JHG-8-2 Rail Terminal Block
FJ6/JHG-8-2
Two-inlet two-outlet(2-gear)
Order number:150570+2
Search
Categories
-
Energy Measuring Terminal Block(314)
- Energy Measuring Joint Terminal Block(16)
- Polycarbonate Energy Measuring Terminal Block(24)
- Standard Wiring Energy Measuring Terminal Block(4)
- Transparent Shell Energy Measuring Terminal Block(6)
- Multifunctional Test Energy Measuring Terminal Block(10)
- Intelligent Safety Energy Measuring Terminal Block(6)
- Single-Phase Multi-Circuit Output Terminal Block(12)
- Self-Elevating Metering Box Terminal Block(7)
- One Household One-Meter Meter Box Dedicated Terminal Block(56)
- Three-Phase Metering Box Dedicated Terminal Block(24)
- Repeatable Grounding Line Terminal Block(20)
- Terminal Block for One-Inlet Multi-Outlet Metering Box(15)
- Closed Terminal Block(11)
- Heavy Current Terminal Block(48)
- Self-Boosting Terminal Block(5)
- Intelligent Self-Locking Terminal Block(3)
- Tool-Free Crimping Type Terminal Block(5)
- Wide Range of Wire Diameters Terminal Block(5)
- Combined Type Energy Measuring Terminal Block(37)
-
Switch Terminal Block(55)
- Pin-Type Incoming Line Switch Terminal Block(4)
- Multi-Way Connection Switch Terminal Block(4)
- Plug-pin Switch Terminal Block(7)
- Combined Type Switch Terminal Block(7)
- High Contact Cross Section Switch Terminal Block(7)
- Wide Range Switch Terminal Block(11)
- One Way in Switch Terminal Block(12)
- Equipped with Circuit Breaker Switch Terminal(3)
-
Heavy-current Terminal Block(631)
- Modular Building Block Terminal Block(156)
- Spherical Non-Destructive Crimp Terminal(120)
- Dual-Mode Connection Electrical Terminal(90)
- Anti-Electricity-Theft Terminal Block(74)
- Convenient Connection Terminal Block(12)
- High-Contact Section Terminal Block(12)
- Wide Range of Wire Diameters Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Heavy-Current Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Upper and Lower Rows of Neutral Terminal(2)
- Independent Neutral Line Terminal(7)
- Nose-Type Neutral Line Terminal(7)
- Rail Type Neutral Line Terminal(9)
- Fixed Neutral Line Terminal(12)
- Double Rail Assembly Electrical Terminal(19)
- Blue Jack-Up Terminal(6)
- Black Base Copper Bar Terminal(5)
- Compact Terminal Block(16)
- Precision Terminal Block(23)
- U-Shaped Harpoon Terminal(2)
- Grounding Metering Box Terminal Block(12)
- High-Performance Terminal Block(19)
- Multifunctional Terminal Block(10)
- Din Rail Terminal Block(76)
- Watt-hour Meter Connector(49)
-
Energy Meter Accessories(116)
-
-
Secure connections are essential for reliable electrical distribution, especially when installing a High-performance Terminal Bloc...
READ MORE -
For engineers and panel builders striving for both efficiency and reliability, wiring errors remain a persistent headache — even w...
READ MORE -
In modern electrical systems, a High-performance Terminal Block plays a critical role in ensuring secure and reliable connections ...
READ MORE -
When building or maintaining electrical systems, one frequently overlooked but critical factor is matching the conductor size to t...
READ MORE -
Effective electrical connections depend on more than simply matching cable sizes. Whether you’re securing a power conductor with a...
READ MORE
How Do You Perform Quality Assurance Testing on Rail Type Terminal Blocks?
Rail type terminal blocks are essential components in electrical and control systems, and their quality directly affects performance and safety. Quality assurance testing ensures that these blocks meet technical standards before being deployed in industrial, commercial, or residential applications. Several methods are commonly used:
Visual and Dimensional Inspection
The step involves checking the overall appearance. Any visible defects, such as cracks in the insulating housing or uneven surfaces, are noted.
Dimensional measurements are taken to confirm that the blocks conform to standardized sizes for DIN rail mounting and wiring compatibility.
Mechanical Testing
Terminal blocks must withstand repeated wire insertions and removals without degradation. Mechanical tests simulate this by applying insertion and withdrawal cycles to verify durability.
Clamping force is also checked to ensure wires are held securely. Both screw and spring clamp versions are tested for consistent grip under varying torque or pressure.
Electrical Performance Tests
Current-carrying capacity is verified by passing rated currents through the terminal blocks and monitoring for heating or voltage drops.
Insulation resistance is measured between conductive parts to ensure proper isolation.
Dielectric withstand tests are performed by applying higher-than-normal voltages to confirm that the block can resist electrical stress.
Environmental and Vibration Testing
Rail type terminal blocks are often used in environments with temperature variations, humidity, or vibration. Tests simulate these conditions to ensure stability of connections.
Thermal cycling, moisture exposure, and vibration tests verify long-term reliability.
Through these combined quality assurance methods, manufacturers and users can be confident that rail type terminal blocks meet both performance and safety expectations.
What Are the Colors of the Disconnect and Test Terminal Blocks? What Do They Represent?
Disconnect and test terminal blocks are specialized components designed for measurement, maintenance, and troubleshooting in electrical systems. Unlike standard terminal blocks, they include a built-in disconnect function, allowing circuits to be separated for testing or monitoring without removing wiring. Their color coding plays an important role in quick identification and proper usage.
Standard Color Variations
Gray: Frequently used as a neutral color for general-purpose connections. Gray disconnect and test blocks are suitable for a wide range of circuits and help maintain a consistent look in panels.
Blue: Typically represents neutral connections in AC systems. Using blue blocks helps technicians easily identify where neutral conductors are terminated.
Green/Yellow: Commonly associated with grounding or protective earth connections. In test terminal blocks, this color ensures grounding points are unmistakably marked for safety.
Red: Often used for live or positive conductors. Red disconnect and test blocks highlight critical circuits that require attention during maintenance.
Orange: Sometimes chosen to represent control circuits or special test points. This adds another layer of organization in complex systems.
Purpose of Color Coding
Identification: Colors reduce the risk of wiring errors, especially when multiple technicians work on the same system.
Safety: Quick recognition of grounding, neutral, and live connections helps prevent accidental mistakes.
Organization: Panels with color-coded terminal blocks are easier to maintain and expand, as technicians can immediately distinguish between different circuit types.
Practical Applications
In power distribution panels, blue and gray blocks are typically grouped together to show neutral circuits.
Red and orange disconnect blocks are often used for circuits requiring frequent monitoring or testing.
Green/yellow blocks provide clear grounding points, ensuring compliance with safety standards.
By following these color conventions, disconnect and test terminal blocks provide both functionality and clarity. Their role extends beyond connectivity, serving as an essential part of system organization and safe operation.


 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى